* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Plants chapter 18
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
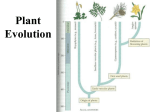
Kingdom Plants chapter 18 Multicellular – formed of many specialized cells Autotrophic – make food by photosynthesis Eukaryote – formed of one or many eukaryotic cells Gametophyte – haploid sexual generation Sporophyte – diploid asexual generation Thallus – a haploid plant body without true roots, stem and leaves 1. Plants are multicellular, autotrophic, eukaryotes. 2. Plants originated from ancestral green algae and the closest relatives today are stoneworts like Chara. 3. Earlier Algae was a part of kingdom Plants but was shifted to kingdom protists. 4. Now main plant groups include Nonvascular plants having liverworts and mosses; Seedless vascular plants include Ferns and fern like plants; Seeded plants include Gymnosperms, including pines and cycads and Angiosperms, flowering plants. 5. Nonvascular Plants: Habitat – Live in moist and shady places. Some can live in dry places and have growth only in rainy days. Dominant generation is Gametophyte and has root like unicellular or multicellular Rhizoids for absorption of water and minerals and anchor the gametophyte. Sporophyte is dependent on The Gametophyte. Male sex organs called Antheridia – produce sperms and female sex organs called Archegonia – have eggs inside. Sex organs produce gametes by Mitosis. Fertilization needs external water of rain or dew for sperms to swim and reach inside ready archegonia. Fertilization leads to development of embryo and Sporophyte by mitotic divisions. The Sporophyte has foot seta and capsule and lacks vascular tissues xylem and phloem and also roots, stem or leaves. Sporophyte produce spores by Meiosis. The spores germinate to produce gametophyte. This is called alternation of generations – Gametophyte gametes Sporophyte spores again gametophyte and cycle goes on. 1 6. In Nonvascular plants, dominant, larger and longer living generation is Gametophyte (liverwort or moss plant). Sporophyte is multicellular but remains attached to gametophyte. It lacks xylem and phloem. 7. Adaptations for land life – achieved by nonvascular plants. All aerial parts are covered by a waxy Cuticle to prevent water loss. Sex organs are covered by a sterile jacket of cells to conserve moisture. A multi-celled Sporophyte is formed to produce Spores by Meiosis. The dispersal by spores proved a good adaptation to live on land. Liverworts 1 Thallus is flat, thin and branched like liver, upper green for photosynthesis and lower for storage 2 Polygonal areas with pores observed on dorsal surface 3 Rhizoids unicellular unbranched Mosses Thallus vertical with stem and leaf like green parts for photosynthesis Absent Multicellular and branched Kingdom Plants – the life cylcels 1. In Non-Vascular Plants, liverworts and mosses, main plant is Gametophyte, haploid sexual generation. Zygote divides with Mitosis to form a multicellular Sporophyte, diploid asexual generation but the Sporophyte remains attached to gametophyte and is dependent on it. Sporophyte lacks xylem and phloem, the vascular tissues. 2 2. In Seedless Vascular plants like ferns the main plant body is a Sporophyte and has xylem and phloem. It is also differentiated into true roots, stem and leaves. Sporophyte produces spores by Meiosis. Spores germinate to form a heart shaped, flat, green, tiny gametophyte called Prothallus. Prothallus bears female sex organs Archegonia, just behind apical notch, in maximum thick part. Prothallus also bears male sex organs Antheridia near posterior end. Therefore ferns exhibit an alternation of 2 independent generations. In Gymnosperms like Pines the dominant plant body is Sporophyte and has root, stem and leaves. It has vascular tissues Xylems and phloem. In addition it developed Pollens and Seeds to become more successful on land. The plants bear 2 types of cones – male cones and female cones. Male Cone microsporophyll microsporangium microspores (Pollen) pollination sperms Female cone megasporophyll megasporangium = ovule female gametophyte egg 3 There are no flowers therefore no ovary is present. The seeds remain naked. In Angiosperms just like gymnosperms dominant generation is Sporophyte, root-stem-leaves are present. Xylem and phloem are present. But seeds develop in fruits. Flowers and fruits are present. OVULE SEED; OVARY FRUIT Flowers lure insects and other animals to pollinate flowers. Pollination by insects/animals is more target-oriented and more efficient. Fruits invite them to disperse seeds. Flower has modified leaves. Sepals - The outermost green ones protect the young flower. Petals – inner to sepals, are colored or white. The petals attract insects/animals and may have nectar. Stamens- male part– have stalk like part = Filament and upper swollen part = Anther, having pollens. Pistil-female part – is formed of 3 parts. Ovary is the lowermost swollen part having ovules. Style is the stalk like middle part and upper Stigma. The stigma is sticky and receives pollen during pollination. The 2 major groups of flowering plants are monocots and dicots (eudicots). Characteristic Monocots (Corn) Dicots = eudicots (Pea) 1. # of cotyledons 1 2 2. veins in leaves parallel Net like 3. # of floral parts (petals, stamens etc.) 3 or multiple of 3 4 or 5 or its multip 4