* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CT Imaging
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
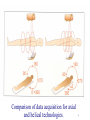
CT Scanner Presented by: Dr M A Oghabian Medical Physics Department, Tehran University of Medical Sciences Computed Tomography CT uses a rotating x-ray tube, with the beam in the form of a thin slice (about 1 - 10 mm) The “image” is a simple array of x-ray intensity (Projections), and many hundreds of these are used to make the CT image, which is a “slice” through the patient 2 3 First generation CT Scanner (Rotate/Translate Pencil beam) 180 translational movement 180 Rotary movement 160 parallel rays across a 24 cm FOV Each 2 slices=4.5 min. Processing time=1.5min. 4 Second generation CT scanners Rotate/Translate Narrow fan beam~10 degree Narrow fan beam~10 degree Linear array of 30 detectors 6 linear movement 6 rotary movement Scan time~ 18 Sec. 5 Third generation CT Scanners (Rotate/Rotate , Wide fan beam) Wide fan beam More than 800 detectors No translational motion Scan time ~ 0.5 Sec. 6 4th Generation CT Scanners Rotate/Stationary Fan beam geometry More than 4800 detectors 7 Electron Beam Computed Tomography (EBCT) - x-ray source is not x-ray tube but a focused, steered, microwaveaccelerated EB incident on a tungsten target. - It has no moving parts . - Target covers one-half of the imaging circle; detector array covers the other half. - Images in less than 50ms. 8 EBCT(CONT’D) There are 4 targets and 4 detector arrays resulting in 4 contiguous images simultaneously. The detector array may consists of two separate rings Each solid -state detector consists of a luminescent crystal and cadmium tungstate coupled with silicon photodiodes. Heat dissipation is no problem in EBCT. Developed for fast imaging. Used for cardiac imaging 9 A look inside a rotate/rotate CT Detector Array and Collimator X-Ray Tube 10 Comparison of data acquisition for axial and helical technologies. 12 Reciprocating rotation (A) versus fast continuous rotation using slip-ring technology (B) 13 A Look Inside a Slip Ring CT X-Ray Tube Detector Array Note: how most of the electronics is placed on the rotating gantry Slip Ring 14 (A) Pitch =1 (B) Pitch = 2 15 16 Comparison of the accuracy of 3D reconstruction for conventional (A) and spiral/helical (B) CT scanning. 17 More New CT Features: Multislice Scanning 18 Multislice CT, where up to 64 variable thickness slices can be collected simultaneously CT fluoroscopy, where the patient is stationary, but the tube continues to rotate 3-dimensional CT and CT endoscopy 19 Clinical Benefits Of Multi-Slice Multi-phase Organ Studies Liver – Pancreas Arterial, Renal Nephrogram Arterial Phase Scanning Hypervascular Tumors CT Angiography Multi-Plane Reconstructions, Contrast Enhancement New CT Applications CT fluoroscopy CT Colonography Cardiac: morphology, function Advanced Lung Analysis 21 22 23 24 Detector Configurations X-ray Tube Focal Spot X-ray Beam Collimator a 4 x 1.25 mm Detector Configuration 16-row Mosaic Detector Flex Connector A Flex Connector B Diode FET Switching Array Detector Configurations X-ray Tube Focal Spot X-ray Beam Collimator 4 x 2.5 mm Detector Configuration 16-row Mosaic Detector Flex Connector A Flex Connector B Diode FET Switching Array Detector Configurations X-ray Tube Focal Spot X-ray Beam Collimator 4 x 3.75 mm Detector Configuration 16-row Mosaic Detector Flex Connector A Flex Connector B Diode FET Switching Array Detector Configurations X-ray Tube Focal Spot X-ray Beam Collimator 4 x 5.0 mm Detector Configuration 16-row Mosaic Detector Flex Connector A Flex Connector B Diode FET Switching Array Multi slice CT collimation 5mm 2,5mm 1mm 0,5mm 29 Speed: Single vs. 4 Slice Single Slice Chest Coverage Thickness Time (s) mA Abdomen/Pelvis Coverage Thickness Time (s) mA Scan Time (s) Tube Load (mAs) 4 slice 235 mm 5 mm 31 240 235 mm 5 mm 8 240 255 mm 5 mm 34 300 255 mm 5 mm 9 300 65 17,720 17 4,725 MULTISLICE SPIRAL CT Introduced at the 1998. They are based multiple detector. rows ranging between 8, 16, 24, 32 and 64 depending on the manufacturer. The overall goal is to improve the volume coverage speed performance. Complete x-ray tube/detector array rotation in less than 1s. Partial scan images can be obtained in approximately 100ms. 31 MULTISLICE IMAGING(CONT’D) ADVANTAGES Improved spatial resolution this advantage improved MPR,3D images. Reduction of radiation exposure. Motion artifacts are greatly reduced. Patient breathhold is much less demanding. Imaging larger z-axis volume in less time is possible with MI. Less contrast medium required. Because of imaging speed, coronary artery is comparable with EBCT. Improved accuracy in needle placement CT fluoroscopy. 32 CT Fluoroscopy Real Time Guidance Great Image Quality Low Risk Faster Procedures 33 REAL-TIME CT FLUOLOROSCOPY CT fluoroscopy acquire dynamic images in real time. Fast continuous imaging, fast image reconstruction & continuous image display. Patient movement is low during Tube rotation. Fast image Reconstruction algorithm is required. 34 CT ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) CTA allows maximum visualization of the pulmonary artery and its segmental braches. CTA requires low kVp and MA, for example 90Kvp/100mA. CTA employs MIP and MPR to maximum advantage. 35 3D Stereo Imaging 36 Enhanced 3D 37 CT Endoscopy 38 CT VIRTUAL REALITY IAMAGING The use of virtual reality is the creation the inner views of tubular structures. Offers both endoluminal and extra luminal information. It reduces complication (eg. infection and perforation). Four requirements: data acquisition image processing 3D rendering image display and analysis. 39