* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download First generation CT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
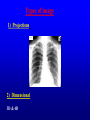
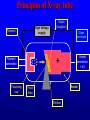
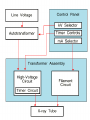
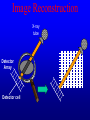
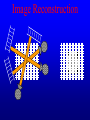
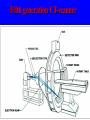
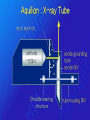
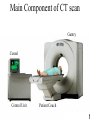
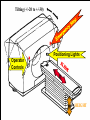
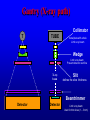
Computer Tomography By Moustafa M. Mohamed Introduction to Medical Imaging Uses of medical imaging NON Invasive Obtain information about internal body organs or the skeleton to determine a patient’s physical state. Imaging Modalities: * X-ray (plan , Dental, Panorama, Mammo, Angio, …) * C.T * Ultrasound * MRI * Gamma Camera * PET SPECT Types of image 1) Projections 2) Dimensional 3D & 4D 3) Slices • • • • Trans axial - plane normal to a vector from head to toe. Coronal - plane normal to a vector from front to back Sagittal - plane normal to a vector from left to right. Oblique - a slice that is not (at least approximately) one of the above. Principles of X-ray tube High Voltage supply Filament Glass envelope + Filament connection Focussing cup Target (tungsten) Anode connection + kV Anode Focal Area Window • CAT Scan ---- Computerized Axial Tomography • CT Scan ---- Computed Tomography • Produce thin cross-sectional images • Non-traumatic radiographic technique Based on Reconstruction of a tomographic plane of the body (a slice) from a large number of collected xray absorption measurements taken during a scan around the body’s periphery. Image Reconstruction X-ray tube Detector Array Detector cell Image Reconstruction CT Generations • 4 Generations • Based on Tube / Detector setting First generation CT-scanner “Translate – Rotate” Translation Rotation • Single Detector Cell • First Translation then Rotation. Second generation CT-scanner “Translate – Rotate” • Array of Detector Cell ( e.g. 20) • First Translation then Rotation. • Scan Time could be reduced to 1/10 Third generation CT-scanner “Rotate – Rotate” • Array of Detector Cell ( e.g. 896) • NO Translation movement. • Scan Time Reduced. Fourth generation CT-scanner Tube rotates, Detector is stationary (full ring of detectors) Fifth generation CT-scanner Main Component of CT scan Gantry Consol Control Unit Patient Couch TUBE CT Scan General Block Diagram Pre-Proc DAS DETECTOR Reconstructor Tilting (+/-20 to +/-30) Positioning Lights Operator Controls HEIGHT Gantry (X-ray path) Collimator T TUBE metal plate with a hole Limit x-ray beam Wedge Limit x-ray beam Prevent detector overflow X-ray beam Slit defines the slice thickness Beamtrimmer Detector Detector Limit x-ray beam Used for thin slices (1 – 3 mm) Data Transfer from DAS to Console In non-continuous rotating system the data is transferred from the DAS to the Console via parallel cable. D.A.S. CONSOLE Data Transfer from DAS to Console In continuous rotating system the DAS data is: • converted from parallel to serial, • transferred (via slipring or optical) • converted back from serial to parallel. D.A.S. Parallel to Serial Serial to Parallel CONSOLE