* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO152 DiscussTerm Test 2 Term Test 2: inheritance
Survey
Document related concepts
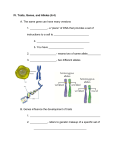
Transcript
BIO152 DiscussTerm Test 2 Tutorial 9 November 24 Term Test 2: inheritance • • • • Statistics Diagnosis Next step Questions + answers 1 How did you do? 730 students wrote the test Cummulative % Mark number % A 39 (10 A+) 5 B 66 9 ≥ B =14% C 159 22 ≥ C =36% D 184 25 ≥ D = 61% diagnosis • Check your mark—STORM (course webpage: Marks) • Pick up the test questions (wooden boxes outside 1087) • Print the correct answers (NEWS on course web page) • Print the list questions you got wrong 2 How did you study? Did you… • Do the Freeman tutorials ch 12 & 13 (CD or online)? • Work through the end of chapter problems? • Work through the problems discussed in tutorials & lectures? • Draw out the chromosomes in all stages of meiosis? • Draw out the chromosomes if nondisjunction occurred? • Look at the answer AFTER you did the problems? Were you… • At the lectures & tutorials • Awake 3 Possible problems DURING the test Did you read the question? Some questions were very similar to the study questions: many of you gave the answer to the study question, not the answer to the test question. Possible problems DURING the test Time? Time management is really hard, but important 28 questions 7 about the figure—easy if you drew out meiosis 8-9 concepts 12-13 problems-fast if you did lots before except for the 3 hard ones. 4 What is the number of chromosomes in each of the figures? C. I 2; II 4; III 4; IV 4 • I • II • III • IV What is the amount of DNA in each figure? b. I 1n; II 4n; III 4n; IV 2n • I • II • III • IV 5 In which of the figures do the chromosomes have both sister and nonsister chromatids? e. II and III • I • II • III • IV What is the 2n number of chromosomes for this organism? b. 4 • I • II • III • IV 6 What is the stage of division for Figure I? d. telophase II – meiosis • I • II • III • IV What is the stage of division for Figure III? a. metaphase I – meiosis • I • II • III • IV 7 Arrange the figures in the correct ORDER so that the stages are listed from first to occur to last to occur. c. • I telophase II • III metaphase I III II IV I • II anaphase I • IV anaphase II 8. Which of the following statements is true? [at the beginning of Prophase I] 52% a. Alleles on sister chromatids must be the same. b. Alleles on non sister chromatids must be the same. c. Alleles on homologs must be the same d. Alleles on sister chromatids may be the same. e. a, b and c 8 11. In a cross between peas heterozygous for two traits , the probability of the offspring exhibiting both recessive traits is 1/16. If the parents were heterozygous for THREE traits, what is the probability that each offspring exhibited all three dominant traits? [hint for one trait 3:1 or 3/4] 3 traits = ¾ x ¾ x ¾ = 27/64 [24%] Exhibited all 3 recessive traits? ¼ x ¼ x ¼ = 1/64 [61%] 13. A man and woman are both of normal pigmentation, but both have one parent who is albino (without melanin pigmentation). Albinism is an autosomal recessive trait. Their first child is a girl with albinism. What is the probability that their second child is a boy and has albinism? [just like the one in class for a girl] = ¼ [albino] x ½ [boy] = 1/8 b. 41% 9 16. A recessive allele on the X chromosome is responsible for redgreen color blindness in humans. A woman with normal vision whose father is color-blind marries a color-blind male. What is the probability that this couple's first son will be color-blind? why is b. 50% correct this time? Boys get X from mom Girls get X from dad Mom is heterozygous (1/2 chance to give X with colour blindness to sons) First son is not the same as the first child being a son This one is hard [45%] 17. Hemophilia is caused by several genetic factors; one, a sex-linked recessive gene, is the subject of this problem. Assume that (1) a man with hemophilia marries a (2) normal woman whose father had hemophilia. What is the probability that they will have a daughter with hemophilia? Dad and mom give an X to daughters ½ (mom is heterozygous) x ½ (girl) = 1/4 10 This is the other hard question this form of sex determination gives predictable, but “reversed” results. Do a Punnett square Female = ZW female gametes Z or W Male = Z- Z ZZ [male gametes] Z Z Z- ZZ male offspring W W Z- WZ female offspring, but W Z- die A lethal recessive allele that causes death of the embryo occurs on the Z chromosome in pigeons so W Z- die e. 2:1 male to female [25%] 11 20. If a diploid cell undergoes meiosis and produces two gametes that are normal, and one with n – 1 chromosomes, and one with n + 1 chromosomes, what type of error occurred? Nondisjunction but WHEN? See tutorial Ch 12; draw it out; see figure 12.14 for the OTHER type of nondisjunction 21. Suppose 64% of a remote mountain village can taste phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) …what percentage of the population must be homozygous dominant for this trait? p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 tasters = p2 + 2pq = 64% q2= 1-.64 = .36 q=.6 p=1-0.6= 0.4 Homozygous dominant = 0.42 = 0.16 Heterozygous? = 2pq = 2(0.4 x 0.6) or 0.64 - 0.16 12 25. In tomatoes, tall is dominant to short, and smooth fruit is dominant to hairy fruit. A plant homozygous for both dominant traits is crossed with a plant homozygous for both recessive traits. The F1 progeny are testcrossed with the following results: 78 tall, smooth fruit parental 82 dwarf, hairy fruit parental 22 tall, hairy fruit recombinant 18 dwarf, smooth fruit recombinant Total 200 Parental = 78+82= 160/200 = 0.8 Recombinants = (22+18)/200 = 0.20 Linked and 20 map units apart 13