* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
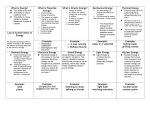
Energy Types & Forms What is Energy? • The ability to do work Types of Energy Potential vs. Kinetic • Potential Energy – Stored energy • Kinetic Energy – Energy of motion Forms of Energy Mechanical Energy • The total energy of motion and position of an object – Mechanical energy = potential + kinetic – Examples: rollercoaster, juggling Thermal Energy • All of the kinetic energy due to random motion of particles that make up an object – Depends on speed & number of particles – Examples: boiling water, rubbing hands together Chemical Energy • Energy stored in the bonds of atoms & molecules – Examples: baking soda, fossil fuels Electrical Energy • Energy of moving electrons – Electrons are negatively charged particles – Examples: appliances Sound/Acoustic Energy • Energy caused by the vibrations of an object – Examples: guitar, speakers Light/Radiant Energy • Energy produced by the vibrations of electrically charged particles – Examples: sun, microwave, radio waves Nuclear Energy • Energy that comes from changes in the nucleus of an atom – Examples: sun, uranium, hydrogen Magnetic Energy • Energy from the attraction of objects made of iron – Examples: magnets, generators