* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Conotruncal Cardiac Defect
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
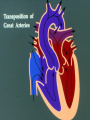
Conotruncal Cardiac Defects: Recognition on Fetal Ultrasound R. Dennis Steed, MD Associate Professor Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology East Carolina University – Brody School of Medicine Greenville, NC Conotruncal Cardiac Defect: A cardiac defect occurring early in development, involving faulty septation or connection of heart’s chambers and/or the major blood vessels leaving the heart. The 4 Most Common Conotruncal Defects: frequency ( per 100,000 live births) Tetralogy of Fallot 38 Transposition of the Great Arteries 25 Double Outlet Right Ventricle 11 Truncus Arteriosus 6 Tetralogy of Fallot: The 4 features typical of tetralogy of Fallot include: 1. Right ventricular (RV) outflow tract obstruction (RVOTO) (infundibular and valvar) 2. A large ventricular septal defect (VSD) 3. Aortic dextroposition resulting in aortic override of the VSD 4. Right ventricular hypertrophy Tetralogy of Fallot: Diagnostic features on fetal ultrasound 1. The main pulmonary artery will be smaller than the aorta. 2. Large outlet VSD. 3. The overriding relationship of the aorta to the VSD. Transposition of the Great Arteries: Diagnostic features on fetal ultrasound: 1. The great arteries are relatively parallel as compared to near perpendicular relationship in a normal heart. 2. Continuity of the anterior mitral leaflet with the posterior wall of the pulmonary artery. 3. The more anterior position of the aorta within the chest results in a rather elongated appearance of the aortic arch. Distinguishing features between the Aorta and the Main Pulmonary Artery: 1. The first branch off the MPA courses directly to the right ( right pulmonary artery) 2. The first branch off the aorta courses superiorly (innominate artery) 3. The MPA is considerably shorter than the ascending aorta, ie. The distance from the pulmonary valve to the right pulmonary artery is considerably shorter than the distance from the aortic valve to the innominate artery. Double Outlet Right Ventricle: 1. Both great arteries arise wholly or predominantly from the morphologic right ventricle. 2. Multiple anatomic variants based on: a. The relationship of the great arteries (normally related or transposed.) b. The relationship of the VSD to the great arteries ( A large subarterial VSD is almost always present). Double Outlet Right Ventricle: Diagnostic features on fetal ultrasound: 1. Both great arteries arise predominantly from the morphologic right ventricle. 2. There is infundibular muscle separating the anterior mitral leaflet from the artery which the artery which is anatomically closest to the left ventricle. 3. A large sub-arterial VSD is present in the vast majority of cases. Truncus Arteriosus: A single arterial trunk arises from the ventricles with a single semilunar valve and typically overides a large VSD. Truncus Arteriosus: Diagnostic Features on Fetal Ultrasound: 1. A single great artery 2. Large subarterial VSD ( the Truncus overides the VSD) 3. A short main pulmonary artery and the branch pulmonary arteries can be identified arising from the truncus just above the truncal valve.