* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blood Pressure ppt
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
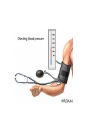
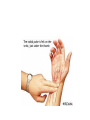
Blood Pressure • Pressure in arteries exerted by the left ventricle when it undergoes systole (contraction) and the pressure remaining in the arteries when the ventricle is in diastole (relaxation) • Taken in the left brachial artery Systolic Pressure • First sound – corresponds to systolic blood pressure. • The force when blood is pushing against the arterial walls • Normal – 100 + age Diastolic • Last sound – when the sound becomes faint • Measure the force of blood remaining in the arteries during ventricular relaxation • Normal – 60-80 • Normal Blood Pressure – 120 / 80 Pulse • Alternate expansion and elastic recoil of an artery with each contraction of the left ventricle. • • • • Radial artery – wrist Carotid artery – next to voice box Popliteal artery – behind knee Dorsalis pedis artery – above the instep of foot Pulse • Average Pulse – 70-80 beats/min at rest • Tachycardia – rapid heart/pulse over 100/min • Bradicardia – slow heart/pulse under 60/min Factors that determine blood Pressure • Stroke Volume Output– the amount of blood pumped out per beat • Average – 70 ml per beat • As SVO goes up, blood pressure goes up • As SVO goes down, blood pressure goes down Elasticity • Constricted arteries – (narrow) blood pressure goes up • Dialated arteries – (wide) blood pressure goes down Things that make BP go up • Constricted Arteries • Quick, small heart beats • Blood transfusions • Areteriosclerosis Things that cause BP to go down • Blood loss • Slow, strong heart beats • Large, dialated arteries • Kidney loss of fluids