* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
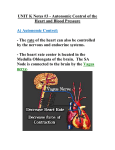
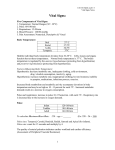
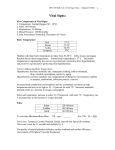
:::Index>Profound Human World>Knowledge Acquisition>Material Circulation> Blood Pressure and Pulse Blood Pressure and Pulse The measurements of blood pressure and pulse are the basic tests of blood circulation. Now let’s see that principles and methods in the following : Blood pressure Fig.1:The heart contraction Blood pressure is the force that blood flow exerts on the walls of the blood vessels, especially arteries, in the systemic circuit and it is directly related to the power of the heart contraction. When the ventricles contract, the blood pressure gets up to the highest value, called systolic pressure. When the ventricles relax, the blood pressure diminishes to the lowest value, called diastolic pressure. Blood pressure read as mmHg is measured on the brachium by the blood pressure monitor and indicated with the systolic/diastolic pressure formula. The following table shows the normal pressure of a person when resting: Adult 90~130/60~90(mmHg) Teenager 100~110/65~75(mmHg) If a person with the systolic pressure usually above 140/90 mmHg when resting will be supposed to have hypertension; if below 60 mmHg, then it is low blood pressure. Too high blood pressure will increase the load of the heart and may cause the blood vessels to break; too low blood pressure will slow the blood flowing to decrease the efficiency of blood transportation and further effects the normal operation of tissues and organs. So maintaining the normal blood pressure is important for health. All rights reserved by National Taiwan Science Education Center Pulse When the ventricles contract, the blood in the left ventricle infuses to the aorta with its wall expanding and when the atria relax, the aorta will reverberate. The pulse is the rhythmic stretching of the arteries caused by the powerful contractions of the ventricles during systole, it is strongest proximally to the heart and getting weak far away from the heart, finally disappears in the capillaries. It is easy to find the pulse on the arteries closing to the body surface or crossing over the bones and the solid tissues. Besides the radial artery of the wrist, we can fell the pulse on other places of the body such as superficial temporal artery in front of the ear, facial artery in front of the mandible masseter muscle, common carotid artery in front of the neck, brachial artery along both sides of the biceps muscle, femoral artery of the groin and popliteal artery behinds the knee. Since the pulse is caused by the heartbeat, so they have the same value, about 70~90 per minute when resting, in a normal adult. If the heartbeat is over 100, called tachycardia, if under 50, called bradycardia. Reviewed by:Zhang, Yong-Ta、Lu, Yu-Ling professor All rights reserved by National Taiwan Science Education Center