* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electromagnet
Magnetorotational instability wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
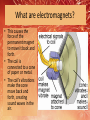
Electromagnetism Unit Standards 5.P.5A.1 Use mathematical and computational thinking to describe and predict the motion of an object (including position, direction, and speed). 5.P.5A.2 Develop and use models to explain how the amount or type of force (contact and non-contact) affects the motion of an object. 5.P.5A.3 Plan and conduct controlled scientific investigations to test the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces on the rate and direction of motion of objects. 5.P.5A.4 Analyze and interpret data to describe how a change of force, a change of mass, or friction affects the motion of an object. 5.P.5A.5 Design and test possible devices or solutions that reduce the effects of friction on the motion of an object. What are electromagnets? • Electromagnet- an electric circuit that produces a magnetic field. • The moving electrons in electricity generate magnetic fields. When the current stops the magnetic field disappears. What are electromagnets? • The simplest electromagnet is a straight wire. • The magnetic field circles around the wire when current is flowing. • When you wrap a wire into a loop, you increase the strength of the magnetic field. What are electromagnets? • Many loops together can make a coil. • The magnetism from each loop adds up to make the coil a stronger electromagnet. • The shape of its magnetic field is like a bar magnet’s. What are electromagnets? • Placing a rod of iron in a coil will magnetize the iron. This adds to the strength of the electromagnet’s magnetic field. Increasing the current also strengthens the field. What are electromagnets? • An iron rod in an electromagnet’s coil is pulled toward the center of the coil. If you try to pull it out, it will spring back. This action is used in a number of devices, such as doorbells. What are electromagnets? • A voice coil operates audio speakers. The voice coil sits in a permanent magnetic field. Current changes in the coil alter its magnetic field. What are electromagnets? • This causes the force of the permanent magnet to move it back and forth. • The coil is connected to a cone of paper or metal. • The coil’s vibrations make the cone move back and forth, creating sound waves in the air. What are electromagnets? • If several voice coils were placed in a circle, changes in electric current would cause them to rotate back and forth. • Something very similar happens in electric motors. What are electromagnets? • An axle is attached to many coils which are between two permanent magnets. • Forces between the permanent magnets and the coils acting as electromagnets cause the coils to rotate. What are electromagnets? • Electric motors are used in many devices, from ceiling fans to cars.