* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download structure of human heart - external features
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
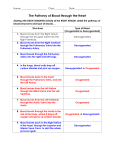
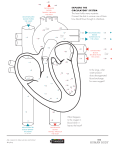
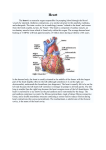
STRUCTURE OF HUMAN HEART - EXTERNAL FEATURES CONCEPTS: • The heart is a hallow organ. It is situated slightly towards left side in the middle of the thorasic (chest) cavity. It is made up of CARDIAC MUSCLE • PERICARDIUM: Heart is enclosed in a double layered, transparent, thin sac called PERICARDIUM. The space between the inner and outer layers is called PERICARDIUM SPACE. It is filled with a fluid, PERICARDIAL FLUID. Pericardium and the pericardial fluid protect the heart from physical shocks or blows. • The heard is internally divided into four chambers – Two upper chambers called AURICLES and lower chambers called VENTRICLES. VENA CAVAE OR CAVAL VEINS • Very large veins that bring blood to the heart are called vena cavae or caval veins. AORTAE Very large arteries that carry blood away from the heart are called AORTAE. • SUPERIOR VENA CAVA: Collects deoxygenated blood from the upper parts of the body (such as head and neck). • INFERIOR VENACAVA/ POST CAVAL VEIN: Brings deoxygenated blood from lower parts of the body. (Such as abdomen, hands and legs.) • PULMONARY VEIN : Which brings oxygenated blood from the lungs and opens into the left auricle • CORONARY VEINS: In addition to these major veins, a pair of veins called coronary veins bring deoxygenated blood from the walls of the heart. These also open into right auricle. • SYSTEMIC AORTA: Heart received oxygenated blood from lungs and pumps it various organs in the body through large aorta called systemic aorta. • PULMONARY AORTA: Pulmonary aorta originates in the right ventricle. Out side the heart, it divides into two branches – RIGHT AND LEFT PULMONARY ARTERIES which carry blood to right and left lungs. • CORONARY ARTERIESI: There is a pair of coronary arteries. They carry oxygenated blood to the heart. • HEART ATTACK: In some people, the Coronary arteries get blocked with age. when this happens, muscle cell in the heart do not receive oxygenated blood and stop working. This is called heart attack and if not treated immediately the patient may die due to the failure of hearty muscle 1 -MARK QUESTIONS 1. Name the artery that carries deoxygenated blood? (June 07) Ans. The artery that carries deoxygenated blood is pulmonary artery. 2. What is the function of pericardial fluid? Ans. Pericardial fluid protects of the heart from physical shocks or blows. 3. Name the Skeletal structures that protect the human heart? Ans. Heart is protected on all sides by ribcage and by vertebral column on the back (March 2008) side. 4. Ans. Which vein carries oxygenated blood? Pulmonary vein 5. Name the artery that carries deoxygenated blood? Ans. Pulmonary artery 6. Which chambers of the heart have thicker walls? Ans. The walls of ventricles are thicker. 7. De-Oxygenated blood from heart goes to lungs and oxygenated blood from lungs returns to heart. What do you call this circuit? Ans. (March 2005) Pulmonary Circuit 2- MARKS QUESTIONS 1. Write short notes on external features of human heart? Ans. 1. The heart is a hallow organ. (June 2004) 2. It is situated slightly towards left side in the middle of thoracic cavity. 3. It is made up of cardiac muscles. 4. Heart is conical in shape with apex facing downwards and the broad base directed upwards 5. Generally it is the size of the fist of the person. 6. It is protected by the ribcage and vertebral column 2. Write a short not on pericardium? Ans. 1. Heart is enclosed in a double layered transparent thin sac called pericardium. 2. The space between the inner and outer layers is called pericardial space. 3. The pericardial space is filled with a fluid called pericardial fluid. 4. Pericardium and pericar5dial fluid protects the heart from physical shocks and blows. IV 4 MARKS QUESTIONS 1. How is the human heart protected from physical shocks and injuries? Ans. 1. Heart is enclosed in a double layered transparent thin sac called pericardium 2. The space between the inner and outer layers is called pericardial space. 3. It is filled with a fluid called pericardial fluid. 4. Pericardium and pericardial fluid protect the heart from physical shocks and injuries. V Fill in the blanks 1. Pulmonary aorta arises from _______. 2. When the _______artery is chocked, the muscle cells of heart don’t get blood. 3. The blocking of ______ artery results in heart attack. 4. ______ collect de oxygenated blood from the upper parts of the body. 5. The inferior vena cava or post cava vein brings de-oxygenated blood from ____ parts of the body 6. In human body ______ is the biggest artery. 7. Systemic aorta originates from ____. Key 1. Right Ventricle 2. Coronary, Oxygenated 4. Superior vena cava 5. Lower 3. Coronary artery. 6. Systemic aorto 7. Left ventricle. VI Multiple choice Questions 1. Incompletely divided ventricles occurs in ______ animals. a) Fish 2. 3. 4. b) Frogs d) Aves. Heart attack is caused by the blocking of a) Pulmonary artery b) Coronary artery c) Coronary vein d) Pulmonary vein Four chambered heart is present in which animals a) Fishes, Aves b) Amphibians, Reptiles c) Reptiles, mammals . d) Aves, Mammals Pulmonary vein bring blood from a) Heart 5. c) Reptiles b) Brain c) mixed blood d) Lungs Systemic aorta carries a) Oxygenated blood b) lymph c) deoxygenated blood d) mixed blood. Key 1. c VII 2. b 3. d 4.d 5. a Match the following Group – A 1 Superior Vena cava Group – B ( ) A. Deoxygenated blood boom the walls of the heart. 2. Interior vena cava ( ) B. Oxygenated blood from the walls of the heart. 3. Pulmonary vein ( ) C. Collects Deoxygenated blood from the upper parts of the body. 4. Coronary vein ( ) D. Brings deoxygenated blood from lower parts of the body 5. Systemic aorta ( ) E. carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart F. Large aorta Key 1. C 2. D 3. E 4.A 5. B