* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Body - Riverdale Middle School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
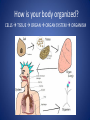
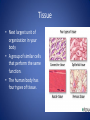
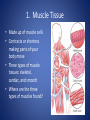
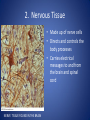
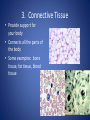
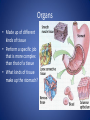
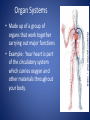
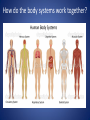
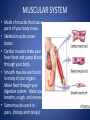
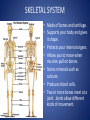
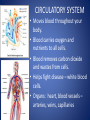
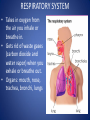
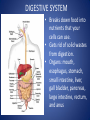
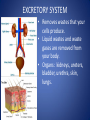
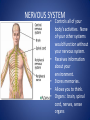
The Human Body GLE 9 – Relate features of organs to their functions in major systems. GLE 10 – Describe the way major organ systems in the human body interact to sustain life. How is your body organized? CELLS TISSUE ORGAN ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM Cells • Basic unit of structure and function in a living thing • Carry out processes that keep organisms alive • Contain about 100 trillion tiny cells SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS Tissue • Next largest unit of organization in your body • A group of similar cells that perform the same function. • The human body has four types of tissue. 1. Muscle Tissue • Made up of muscle cells • Contracts or shortens making parts of your body move • Three types of muscle tissues: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth • Where are the three types of muscles found? 2. Nervous Tissue • Made up of nerve cells • Directs and controls the body processes • Carries electrical messages to and from the brain and spinal cord NERVE TISSUE FOUND IN THE BRAIN 3. Connective Tissue • Provide support for your body • Connects all the parts of the body • Some examples: bone tissue, fat tissue, blood tissue 4. Epithelial Tissue • Covers the outside surfaces of your body and the inside surfaces of your body • Protects delicate structures that lie beneath it CHEEK CELLS GROUPED TOGETHER MAKE UP EPITHELIAL TISSUE. Organs • Made up of different kinds of tissue • Perform a specific job that is more complex than that of a tissue • What kinds of tissue make up the stomach? Organ Systems • Made up of a group of organs that work together carrying out major functions • Example: Your heart is part of the circulatory system which carries oxygen and other materials throughout your body. How do the body systems work together? How Do You Move? Muscles and bones work together, making your body move. The nervous system tells your muscles when to act. MUSCULAR SYSTEM • Made of muscles that cause parts of your body move. • Skeletal muscles move bones. • Cardiac muscles make your heart beat and pump blood through your body. • Smooth muscles are found in many of your organs. Move food through your digestive system. Make you breathe, cough, and sneeze. • Some muscles work in pairs. (biceps and triceps) SKELETAL SYSTEM • Made of bones and cartilage. • Supports your body and gives it shape. • Protects your internal organs. • Allows you to move when muscles pull on bones. • Stores minerals such as calcium. • Produces blood cells. • Two or more bones meet at a joint. Joints allow different kinds of movement. Which Systems Move Materials in Your Body? The circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and excretory systems play key roles in moving materials in your body. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM • Moves blood throughout your body. • Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to all cells. • Blood removes carbon dioxide and wastes from cells. • Helps fight disease – white blood cells. • Organs: heart, blood vessels – arteries, veins, capillaries RESPIRATORY SYSTEM • Takes in oxygen from the air you inhale or breathe in. • Gets rid of waste gases (carbon dioxide and water vapor) when you exhale or breathe out. • Organs: mouth, nose, trachea, bronchi, lungs DIGESTIVE SYSTEM • Breaks down food into nutrients that your cells can use. • Gets rid of solid wastes from digestion. • Organs: mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, large intestine, rectum, and anus EXCRETORY SYSTEM • Removes wastes that your cells produce. • Liquid wastes and waste gases are removed from your body. • Organs: kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, skin, lungs. Which Systems Control Body Functions? The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to control body functions. NERVOUS SYSTEM • Controls all of your body’s activities. None of your other systems would function without your nervous system. • Receives information about your environment. • Stores memories. • Allows you to think. • Organs: brain, spinal cord, nerves, sense organs ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Controls growth, development, and energy processes by releasing chemicals called hormones. • Helps maintain homeostasis. • Structures: glands (thyroid, pancreas, adrenals, pituitary, and others)