* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 14.0 Describe Principles of Plant Growth Production 14.2 Explore
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
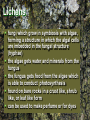
Plants Two Groups of Plants Nonvascular - most primitive, rely on water coming to them. Vascular - contain vascular tissue that transports water. And Fungi – which are not plants Vascular Plants Have vascular tissue – tissue that moves food and nutrients around plant Xylem and phloem Leaves, stems, and roots Produces food for plant in leaves May have a long life span – one season or many grows tall and wide Has chlorophyll for photosynthesis examples: ferns, trees, grasses and flowering plants Non-vascular Plant Nonvascular no vascular tissue no leaves, stems, or roots low growing, close to the ground reach maturity quickly can grow in varying climates Produce food in every cell Mosses a flowerless plant lies flat and grows in moist areas (carpet like appearance) reproduces sexually Economics - used by gardeners as a mulch because it helps keep moisture close to the plants roots. And Non Plants Fungi most primitive; do not have true roots, leaves, stems do not contain chlorophyll in their cells Obtain their food from other sources – heterotrophs or parasites Reproduce asexually - spores Example: Mushrooms, molds, puffballs, lichens Mushrooms and Toadstools Found in damp, shady places Very short lifespan Most are poisonous (if it is red it is poison) Some grown for commercial use Lichens fungi which grow in symbiosis with algae, forming a structure in which the algal cells are imbedded in the fungal structure (hyphae) the algae gets water and minerals from the fungus the fungus gets food from the algae which is able to conduct photosynthesis found on bare rocks in a crust like, shrub like, or leaf like form can be used to make perfume or for dyes Two Groups of Vascular Plants Gymnosperms - naked seed Angiosperms - vessel seed Gymnosperm vs. Angiosperm Gymnosperm expose their seeds examples-pine, spruce, ferns and conifers trees Angiosperm produce and store their seeds in an ovary – often called fruit examples - roses, elm trees, geraniums, apple trees, etc. Subclasses of Angiosperms A. Monocots – single seed leaf (cotyledon) flowers/petals grow in groups of three leaves have parallel veins Flowers often small, overlooked Usually grow for only one year Examples: corn, grasses, onions, lilies and many grains Dicots two seed leaves (cotyledons) flowers/petals grow in groups of four or five leaves have network veins that branch out Greatest number of plants are dicots Tend to live a long time – one season or many Produce food, clothing, housing Examples: trees, sunflower, beans, pumpkins and clover. Review: Vascular or Non-vascular? Moss Review: Vascular or Non-vascular? flowering tree Review: Gymnosperm or Angiosperm? Rose Review: Gymnosperm or Angiosperm? Pine Tree Review: Monocot or Dicot? Corn Review: Monocot or Dicot? Bean