* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 Day 3 – Electric Field Properties
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
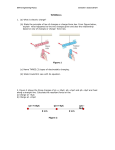
Day 3: Electric Fields Objectives • Static Electricity • Electric Field Properties • 1 & 2 –Dimensional Electric Field Calculations of Point Charges Static Electricity • The electrostatic Force, like gravity, is a field force & is an inverse square law with the radial distance away • Michael Faraday (1791-1867) was the first to develop the idea of an electric field 21-6 The Electric Field • An electric field surrounds every point charge • It extends radially outward for positive (+) charges • It extends radially inward for negative (-) charges • The Electric Field felt at a point at some position P, away from the point charge is: 21-6 The Electric Field For a point charge: 21-6 The Electric Field • The Electric Field is a Vector Quantity • The net Electric Field at a point P due to the presence of multiple electric charges is the vector sum of the Electric Field generated by each charge: E E1 E2 E3 . . . . (Law of Superposition) 21-6 The Electric Field Example 21-7: E at a point between two charges. Two point charges are separated by a distance of 10.0 cm. One has a charge of -25 μC and the other +50 μC. (a) Determine the direction and magnitude of the electric field at a point P between the two charges that is 2.0 cm from the negative charge. (b) If an electron (mass = 9.11 x 10-31 kg) is placed at rest at P and then released, what will be its initial acceleration (direction and magnitude)? 21-6 The Electric Field Example 21-8: E above two point charges. Calculate the total electric field (a) at point A and (b) at point B in the figure due to both charges, Q1 and Q2. 21-6 The Electric Field Problem solving in electrostatics: electric forces and electric fields 1. Draw a diagram; show all charges, with signs, and electric fields and forces with directions. 2. Calculate forces using Coulomb’s law. 3. Add forces vectorially to get result. 4. Check your answer!