* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendel`s Pea experiments Why did Mendel choose pea plants? Pea
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
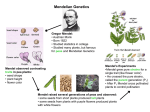
Mendel's Pea experiments Why did Mendel choose pea plants? Pea plants grow and reproduce quickly. They have a wide variety of different ____________, and were easy to breed and cross-pollinate. What are the 7 genetic traits Mendel looked at? (pg. 157) _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ What did Mendel do? First, he transferred ________ from flowers on short-stemmed plants to the _________ of flowers on other short-stemmed plants and found out that all the offspring were short-stemmed. Mendel called these plants ___________ plants, plants that always produce offspring with the ___________ traits as their parents. When he crossed tall-stemmed plants with other tall-stemmed plants, he found that both tall and short plants resulted. What were Mendel's conclusions? Mendel realized that each plant must contain _______ factors for a particular trait. He called these factors genes. Alternative forms of a gene (tall and short) are now called alleles. When he crossed two true-breeding plants with opposite traits (for example tall with short), the offspring showed only one of the traits, which Mendel called the ________ trait. He called the “weaker” trait which did not appear in those offspring ________. How are the genes inherited? Mendel realized that each parent could only contribute _______ of the factors (genes) to the plant in the offspring generation, so the offspring in the first filial generation would get one factor from the female parent and one from the male parent. Mendel Rap There was an Austrian Monk called Gregor. He looked at something never done before. I say Gregor Mendel was his name. He wondered why sometimes we look the same. Using peas he looked at their height. He worked all day and all night. The first he crossed was a tall and a dwarf one. Their offspring were all tall F1 He was at no loss He went for a second cross He did it, two of these tall What did he see? I said, what did he see? F2 – 1 dwarf and tall ones there were 3 Now what was his conclusion? To him there was no confusion. Features came in hereditary units. This was his message. One was dominant, and the other recessive. His work turned out to be quite prophetic. This was the start of modern genetics. Word to the Brother, Peas. Mendel's Pea experiments Why did Mendel choose pea plants? Pea plants grow and reproduce quickly. They have a wide variety of different ____________, and were easy to breed and cross-pollinate. What are the 7 genetic traits Mendel looked at? (pg. 157) _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ What did Mendel do? First, he transferred ________ from flowers on short-stemmed plants to the _________ of flowers on other short-stemmed plants and found out that all the offspring were short-stemmed. Mendel called these plants ___________ plants, plants that always produce offspring with the ___________ traits as their parents. When he crossed tall-stemmed plants with other tall-stemmed plants, he found that both tall and short plants resulted. What were Mendel's conclusions? Mendel realized that each plant must contain _______ factors for a particular trait. He called these factors genes. Alternative forms of a gene (tall and short) are now called alleles. When he crossed two true-breeding plants with opposite traits (for example tall with short), the offspring showed only one of the traits, which Mendel called the ________ trait. He called the “weaker” trait which did not appear in those offspring ________. How are the genes inherited? Mendel realized that each parent could only contribute _______ of the factors (genes) to the plant in the offspring generation, so the offspring in the first filial generation would get one factor from the female parent and one from the male parent. Mendel Rap There was an Austrian Monk called Gregor. He looked at something never done before. I say Gregor Mendel was his name. He wondered why sometimes we look the same. Using peas he looked at their height. He worked all day and all night. The first he crossed was a tall and a dwarf one. Their offspring were all tall F1 He was at no loss He went for a second cross He did it, two of these tall What did he see? I said, what did he see? F2 – 1 dwarf and tall ones there were 3 Now what was his conclusion? To him there was no confusion. Features came in hereditary units. This was his message. One was dominant, and the other recessive. His work turned out to be quite prophetic. This was the start of modern genetics. Word to the Brother, Peas.