* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Skin and Body Membranes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
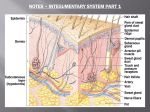
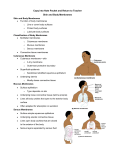
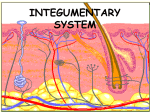
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Connective tissue membranes Cutaneous Membrane Cutaneous membrane = Superficial epidermis is composed of Underlying dermis is mostly Mucous Membrane Surface epithelium type depends on site Underlying loose connective tissue ( Often adapted for Serous Membranes Surface is a layer of Underlying layer is a thin layer of ) Lines open body cavities that are Serous membranes occur in pairs separated by serous fluid Specific serous membranes Connective Tissue Membrane Synovial membrane Integumentary System Skin ( Skin derivatives ) Skin Functions (see image) Skin Structure (see image) Epidermis— Often keratinized ( Dermis Skin Structure (see image) Subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) is deep to dermis ) Layers of the Epidermis Stratum basale (stratum germinativum) Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum Stratum corneum Summary of layers from deepest to most superficial Stratum basale Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum (thick, hairless skin only) Stratum corneum Melanin Pigment (melanin) produced by Melanocytes are mostly in the Color is yellow to brown to black Amount of melanin produced depends upon Dermis Two layers Papillary layer ( ) Reticular layer ( ) Overall dermis structure Collagen and elastic fibers located throughout the dermis Blood vessels play a role in Normal Skin Color Determinants Melanin Carotene Hemoglobin Skin Appendages Cutaneous glands are all exocrine glands Produce oil Most have ducts that others Glands are activated ; Sweat glands Two types Open via duct to pore on skin surface Ducts empty into hair follicles Sweat and Its Function Composition Function Odor is from Hair Hair anatomy Most heavily keratinized Associated hair structures Hair follicle Arrector pili muscle Sebaceous gland Sweat gland Nails Scale-like modifications Stratum basale extends Lack of pigment makes them Nail structures Skin Homeostatic Imbalances Infections Athlete’s foot ( Caused by Boils and carbuncles Cold sores Infections and allergies Contact Impetigo Psoriasis Triggered by Burns Tissue damage and cell death Associated dangers ) Rule of Nines Way to determine the extent of burns Body is divided into Each area represents Severity of Burns First-degree burns Second-degree burns Third-degree burns Critical Burns Burns are considered critical if Over 25% of body Over 10% of the body There are third-degree burns of Skin Cancer Cancer— Classified two ways (encapsulated) Malignant Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer Skin Cancer Types Basal cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Malignant melanoma Detection uses ABCD rule ABCD Rule A= B= C= D=