* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science Department Physics Review
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
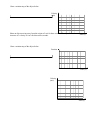
Physics Review! Name: _________________________ Period: ____ Define the following terms: 1. Speed 2. Sir Isaac Newton 3. 1st Law of Motion 4. Inertia (define!!) 5. Force 6. Mass 7. Weight 8. Acceleration 9. Velocity 10. Gravity 11. Newton’s 2nd Law 12. Newton (N) 13. Newton’s 3rd Law 14. Action Force 15. Reaction force 16. Friction “Which Law?” Fill in the law that applies best to each statement: (1, 2, or 3) _____ 21. A book lies undisturbed on a desk. _____ 22. A car does not move until its engine is started and the car is put into gear. _____ 23. A chair with wheels moves back when the secretary pushes on the desk. _____ 24. A girl is able to throw a softball a further distance then a shot put. _____ 25. An opened air-filled balloon flies around the room. _____ 26. A VW bug will accelerate faster uphill than a semi-truck. _____ 27. A rocket does not want to move until a force acts on it. _____ 28. When you turn suddenly to the left in a car your body is pushed to the right. _____ 29. A tractor pulling a full trailer will accelerate slower then a tractor pulling an empty trailer. _____ 30. A rocket lifts because an unbalanced force is acted upon it. _____ 31. The acceleration of the rocket depends on how massive the rocket is and how much force is used to lift the rocket. Short Answer: Answer the following questions in COMPLETE SENTENCES 32. Explain how the lift-off of a rocket (or space shuttle) helps demonstrate the 3rd Law of Motion. 33. Explain how seatbelts & airbags demonstrate the 1st Law of Motion. 34. What is the formula for speed? Time? Distance? Acceleration? Force? Velocity, Acceleration, and Force Problems: SHOW YOUR WORK. LABEL YOUR ANSWER!!!!! 35. A car is driving 130 km in 2 hours. What is the car’s velocity? 36. Calculate the acceleration (in m/sec2) of a missile that goes from 0 km/s to 8.8 km/s in 2 sec. How does this compare to the acceleration of gravity? (about 10 m/s2) 37. A kid on a bicycle rides 12 km in 1.5 hours. What was his velocity? 38. Parker is in a grocery cart that has a mass of 35 kg and is accelerating at a rate of 2 m/s2. What is the strength of the force pushing Parker and wagon? Position (m) Position-Time Graphs Read each scenario then graph it! 39. Show an object moving away from the origin at 1 m/s for 5 seconds, then stopping for 5 seconds. Draw a motion map of the object below. Time (s) Velocity (m/s) Time (s) 40. Show an object starting away from the origin at the 6 meter mark. Then, the object moves in the negative direction back toward the origin at 1 m/s for 3 seconds, stop for 2 seconds, then move away from the reference point at 1 m/s for 5 seconds. Draw a motion map of the object. Position Time (s) Draw a motion map of the object below. Velocity (m/s) . Show an object moving away from the origin at 2 m/s for three seconds. The object then increases it’s velocity to 6 m/s for three more seconds. Time (s) Draw a motion map of the object below. Position Time (s) Velocity (m/s) Time (s)