* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plate tectonics post-test
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
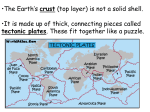
PLATE TECTONICS STUDY GUIDE 1. Which of the following is associated with transform boundaries? Earthquakes Volcanoes or Sea floor spreading 2. Continental-oceanic collisions can also be called: Subduction Zones 3. Mid-ocean ridges occur at what type of boundary Divergent 4. The sinking of Earth’s crust to lower elevations is called subsidence 5. Sea-floor spreading occurs at which type of tectonic plate boundaries? Divergent 6. Tectonic plates consist of which two types of crust? Continental and oceanic 7. Wegener thought that all the continents were once together in one large continent called: Pangaea 8. New oceanic lithosphere forms as a result of: Sea floor spreading 9. A possible result of plates moving along a transform boundary is: earthquake 10. What type of fault usually occurs because of tension? Normal fault 11. What type of fault usually occurs because of compression? Reverse Fault 12. What is the area where two tectonic plates meet called? A boundary 13. What type of boundary is formed when plates separate? Divergent 14. What type of boundary is formed when plates slide past each other? Transform 15. Where does sea-floor spreading take place? Mid Ocean Ridge 16. What happens at mid-ocean ridges? Sea floor spreading 17.How do mid-ocean ridges support both the idea of continental drift and the theory of plate tectonics New crust forms at mid ocean ridge, divergent boundary, sea floor spreading 18.Which compositional layer makes up the greatest percentage of Earth’s mass? Mantle 19. How does fossil evidence support Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift? Similar fossils of plants and animals have been found on continents where they were once connected. 20. Most of the world’s folded mountains formed as a result of: Continental-Continental collision at convergent boundaries 21. Which fault occurs as a result of shearing? Strike –slip fault 22.Scientists think that all of the present-day continents were once joined in a single supercontinent called: Pangaea 23.Be able to state 5 pieces of evidence proving the theory of continental drift. 1. The continents fit together like a puzzle 2. Sea floor spreading 3. Fossils of the same animals and plants found on different continents 4. Similar types of rocks found on different continents 5. Evidence of the same climatic conditions on different continents PLATE TECTONICS STUDY GUIDE Which of the following is associated with transform boundaries? Continental-oceanic collisions can also be called: Mid-ocean ridges are the most common type of: Be able to state 5 pieces of evidence proving the theory of continental drift. The sinking of Earth’s crust to lower elevations is called: Sea-floor spreading occurs at which type of tectonic plate boundaries? Tectonic plates consist of which two types of crust? Wegener thought that all the continents were once together in one large continent called: New oceanic lithosphere forms as a result of: Evidence for sea-floor spreading (name 3): A possible result of plates moving along a transform boundary is: What type of fault usually occurs because of tension? What type of fault usually occurs because of compression? What is the area where two tectonic plates meet called? What type of boundary is formed when plates separate? What type of boundary is formed when plates slide past each other? Where does sea-floor spreading take place? What happens at mid-ocean ridges? How do mid-ocean ridges support both the idea of continental drift and the theory of plate tectonics? Which compositional layer makes up the greatest percentage of Earth’s mass? How does fossil evidence support Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift? Most of the world’s folded mountains formed as a result of: Which geologic features forms as a result of tension? Scientists think that all of the present-day continents were once joined in a single supercontinent called:









![jeopardy_platetectonics[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008388988_1-c1f7a56df21131a376d1ab2c8c0b8111-150x150.png)