* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pedigrees and Autosomal Inheritance - Emery
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic studies on Bulgarians wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
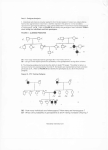
Pedigrees and Autosomal Inheritance Pedigree – a chart that shows the genetic relationships between individuals in a family -using a pedigree chart and Mendelian genetics, you can determine whether the allele for a given trait is dominant, recessive, autosomal or sex-linked female – unaffected female – affected male – unaffected male – affected Autosomal Inheritance = the inheritance of traits determined by genes found on autosomal chromosomes (chromosomes 1-22 in humans). Autosomal genes are responsible for many inherited genetic disorders, such as Huntington disease and cystic fibrosis. These disorders may be classified as either autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Autosomal dominant = the inheritance of a dominant phenotype whose gene is on an autosomal chromosome. Therefore this type of disorder occurs when the disease-causing allel is dominant and the individual has one or both copies of the allele. An example is Huntington disease. Here is an example of a pedigree with an autosomal dominant disorder: Characteristics of pedigrees showing an autosomal dominant disorder: 1) The disorder is present in every generation (children with trait have at least one parent with trait). 2) Affects males and females equally. 3) Once a trait is no longer in the family, it will not reappear. Autosomal recessive = the inheritance of a recessive phenotype whose gene is on an autosomal chromosome. Therefore this type of disorder occurs when the disease-causing allele is recessive and an individual has both copies of the allele. An example is cystic fibrosis. Here is an example of a pedigree with an autosomal recessive disorder: Characteristics of pedigrees showing an autosomal recessive disorder: 1) The disorder can (but not always) skip a generation, therefore children with the trait have parents without trait. 2) Affects males and females equally. 3) Two unaffected parents can have an affected child. Check your understanding: The following is a pedigree chart illustrating the occurrence of an autosomal trait in family. Q: Is the trait dominant or recessive? Task – Identify any heterozygous individuals. Do so by writing Ho or He under each circle or square. Now answer questions 1 – 4. Write your answers here. 1) For each pedigree below, tell if the trait can be autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. If the pedigree cannot fit a mode of inheritance, tell why. Pedigree A Pedigree B Pedigree C 2) Albinism is inherited as an autosomal recessive. In the figure below, assuming that persons from the general population are not heterozygous for albinism (Aa), what are the genotypes of all persons whose genotypes are known? (i.e., indicate the genotypes on the figure for all known AA, Aa, and aa individuals) 3) Which type of inheritance pattern, autosomal domiant or autosomal recessive, is likely to remain hidden in a family, only to appear in a future generation? Explain your answer. 4) Construct a pedigree below using the following information. Albinism, a lack of skin pigmentation, is a recessive phenotype. An individual with this disorder is referred to as albino. Two parents with normal pigmentation have four children, three girls and a boy. The eldest girl and the boy are both albino. Determine the genotypes of all the members of the family. For those whose genotype cannot be determined, what is the probability that they are heterozygous? (Hint: Since you know they are not albino, do not count that probability in your calculation).