* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
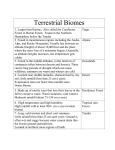
Name 4 Class Ecosystems and Communities Date Chapter Test B Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 1. How does an area’s weather differ from the area’s climate? a. Weather involves temperature and precipitation and climate involves only temperature. b. An area’s weather depends on where it is located on Earth and the area’s climate does not. c. An area’s weather does not change very much and an area’s climate changes many times. d. Weather is the area’s day-to-day conditions and climate is the area’s average conditions. _____ 2. The greenhouse effect is a. something that has only occurred for the last 50 years. b. a natural phenomenon that maintains Earth’s temperature range. c. the result of the differences in the angle of the sun’s rays. d. an unnatural phenomenon that causes heat energy to be radiated back into the atmosphere. _____ 3. The tendency for warm air to rise and cool air to sink results in a. global wind patterns. b. ocean upwelling. c. the seasons. d. regional precipitation. _____ 4. Which of the following is a biological aspect of an organism’s niche? a. the water in the area c. the way it gets food b. amount of sunlight d. composition of soil _____ 5. Several species of warblers can live in the same spruce tree ONLY because they a. have different habitats within the tree. b. don’t eat food from the tree. c. occupy different niches within the tree. d. can find different temperatures within the tree. _____ 6. An interaction in which an animal feeds on plants is called a. carnivory. c. predation. b. herbivory. d. symbiosis. _____ 7. A symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit is a. commensalism. c. predation. b. mutualism. d. parasitism. _____ 8. Primary succession would most likely occur after a. a forest fire. c. farm land is abandoned. b. a lava flow. d. a severe storm. 117 Name Class Date Figure 4-1 _____ 9. Figure 4–1 shows succession in an ecosystem. What organisms are found in the climax community for this ecosystem? a. lichens and moss c. weeds and grasses b. trees and shrubs d. volcanoes and soil _____ 10. Which biome is characterized by very low temperatures, little precipitation, and permafrost? a. desert c. tundra b. temperate forest d. tropical dry forest _____ 11. The North Pole and the South Poles are a. classified as tundra biomes. c. not classified into major biomes. b. not home to any animals. d. part of aquatic ecosystems. _____ 12. The nutrient availability of aquatic ecosystems is the a. amount of nitrogen, oxygen, and other elements dissolved in the water. b. number of other organisms present in the water. c. amount of rainfall the water receives. d. number of different animal species living in the water. _____ 13. Freshwater ecosystems that often originate from underground sources in mountains or hills are a. estuaries. c. lakes and ponds. b. rivers and streams. d. wetlands. _____ 14. A wetland that contains a mixture of fresh water and salt water is called a. an estuary. c. a river. b. a stream. d. a pond. _____ 15. Which of the following statements is NOT true about the open ocean? a. The open ocean has low levels of nutrients. b. Organisms in the deep ocean are exposed to frigid temperatures and total darkness. c. The open ocean begins at the low-tide mark and extends to the end of the continental shelf. d. Most of the photosynthetic activity on Earth occurs in the open ocean within the photic zone. 118 Name Class Date Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the underlined word or phrase to make the statement true. _____ 16. Two kinds of birds eat the same food and nest in the same area. These two species of birds are in symbiosis. _____ 17. A series of more-or-less predictable changes that occur in a community over time is ecological succession. _____ 18. The temperate forest biome is typically warmer and has more rainfall than the boreal forest biome. Completion Complete each statement on the line provided Figure 4–2 19. As shown in Figure 4–2, the climate zone that receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year lies between and latitudes. 20. Predator is to prey as herbivore is to . 21. Abandoned farmland in North America usually returns to its original . 22. Mountain ranges are not usually classified into biomes because conditions within them vary by ____________________. 23. A freshwater ecosystem that can purify water by filtering pollutants and help to prevent flooding by absorbing large amounts of water is a . Short Answer In complete sentences, write the answers to the questions on the lines provided. 24. How are microclimates related to climates? 25. Give three examples of resources that a plant would need in its niche in order to live. 26. Explain what would happen if two mouse species tried to occupy the same niche in a meadow. 119 Name Class Date 27. How do predators affect the population of their prey? 28. Why is there little plant life near the source of a river or stream? Using Science Skills Use the diagram below to answer the following questions on the lines provided. Figure 4–3 Characteristics of Different Biomes Biome Temperatures Precipitation Soil Quality Tropical Rain Forest hot year-round wet year-round thin, nutrient-poor Tropical Dry Forest warm year-round alternating wet and dry rich seasons Tropical Grassland/ warm seasonal rainfall compact variable low precipitation rich in minerals but poor Savanna/Shrubland Desert in organic material Temperate Grassland warm to hot summers; moderate and seasonal fertile thin, nutrient-poor cold winters Temperate Woodland hot summers, cool dry summers; moist and Shrubland winters winters Temperate Forest warm summers; cold to stable year-round fertile dry summers; abundant rocky, acidic moderate winters Northwestern mild temperatures Coniferous Forest precipitation in the fall, winter, and spring Boreal Forest short mild summers; moderate precipitation acidic, nutrient-poor low precipitation poorly developed long cold winters Tundra short summers; long, cold, dark winters 29. Interpret Tables Which biomes in Figure 4–3 have a relatively stable amount of precipitation all year long? 28. Analyze Data Which biomes in Figure 4–3 have little variation in temperatures during the year? 120