* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy and Work - Stanley Teacher Prep
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
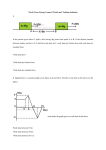
Physical Science What background knowledge do you need to get the joke? • What gravity does. • That “keeps me down” means bums you out! What is Physical Science • Physics: the science of matter and energy and their interactions – Sciences such as physics, chemistry, astronomy, – studies of matter, electricity, magnetism, sound, and light – designed to observe behaviors of physical objects Matter Topics • States of Matter • Changes in state of matter • Behaviors of Gasses and Fluids Matter - anything that takes up space and has mass Four States of Matter • Solid • Liquid • Gas • Plasma » Mass - amount of matter in an object Amorphous solids • Amorphous without a definite form – Some scientists think they should be classified as very thick liquids Chemistry Topics • Atoms • Elements • Mixtures vs Compounds* • Polarity of Water – Chemical Bonds – Acids and Bases Thermal Expansion - matter expands as it warms, contracts as it cools • As heat a substance, give more E to molecules • As cool a substance, take away molecule’s E Energy and Forces Topics • Energy and Work • Motion and Forces • Newton’s 3 Laws Energy-An Agent of Change • When an object can change its environment, it has energy (e.g baseball breaking window) – Energy: ability to cause change (E) Two types of energy: 1. Kinetic Energy 2. Potential Energy Kinetic Energy (KE) • Kinetic energy: energy in the form of motion – E.g. spinning bicycle wheel, sprinting, flying Frisbee Potential Energy (PE) • Potential energy: stored energy Conservation of Energy • Law of conservation of energy: energy is neither created or destroyed, only changes state – As you move back and forth, energy is converted from kinetic to potential back to kinetic energy continuously – So why does the swing eventually stop? What is work? • Work: transfer of energy through motion – In order to take place, force must be exerted Force - push or pull • Balanced forces - forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction – Do not change an object’s motion • Unbalanced forces force that changes the motion or position of an object – Cause it to accelerate Motion - change in position • Speed - distance traveled in a certain amount of time – Rate of motion Newton’s First Law - object moving at a constant velocity keeps moving at that velocity until acted upon by an unbalanced force • Object in motion stays in motion – E.g. Air hockey puck glided until hits wall • Object at rest stays at rest – E.g. Hockey puck stays on ice until hit it • Also called law of inertia • Inertia - tendency of an object to resist changes in motion Momentum - measures the amount of inertia (mass x velocity) • High velocity = more momentum • High mass = more momentum Friction • Friction - force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching each other • Depends on: – Type of surfaces – Force pressing surfaces together Types of Friction • Sliding friction - when solids slide over each other – Strongest friction • Rolling friction - when objects roll over a surface – Medium strength • Fluid friction - when object moves through a fluid – Least strong Steps of the Scientific Method • • • • • • • Observe Question Hypothesize Experiment Record Data Analyze Data Conclude The Science Circle Experiment and Bloom’s Taxonomy: Science’s Natural Progression