* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Irregular Verb Forms, Subject-Verb Agreement, Conjunctive Adverbs
Chichewa tenses wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sanskrit grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Germanic weak verb wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Germanic strong verb wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Kagoshima verb conjugations wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish verbs wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Hungarian verbs wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
English grammar wikipedia , lookup
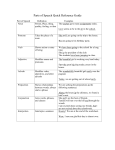
Irregular Verb Forms, Subject-Verb Agreement, Conjunctive Adverbs Irregular Verb Forms An irregular verb does not conform to the rules that govern how regular verbs are stated in past tense or as a past participle. Consider the past tense form of the regular verb botch, which is botched; the past participle of botch is have botched. An irregular verb does not follow the simple, linear construction of a regular verb. The various tenses of an irregular verb are expressed through entirely different words that do not always bear a resemblance to the present tense form. One example is the verb fly—in its past tense form, it is written as flew, and its past participle is have flown. If unsure about the correct spelling of an irregular verb, consult a dictionary. Subject-Verb Agreement In sentences, subject and verbs should be in agreement. There should be an agreement in the singular and plural form and in subject and verb tenses. If your sentence uses a singular subject, then the verb should also be singular. Subject-verb agreement An employee is giving a picnic for the first-floor sales team. If you make the subject plural, the verb should be also made plural. To make it plural, change it to read the following: The employees are giving a picnic for the first-floor sales team. Verbs have to match in tense in the same sentence. The past tense for one of the verbs has to be kept consistent for the rest of the verbs in the sentence. Singular and plural forms for verbs must be consistent. The sports car has been parked outside the building all night. Several sports cars have been parked outside the building all night. Present and past tense usage for verbs have to be consistent. She will bring in the data report and ring up the sales receipts tomorrow. She brought in the data report and rang up the sales receipts. Remember to write and edit your work with consistency. Your verb forms and tenses should agree with your subject matter. This also applies to pronoun usage. Your pronouns should match the subject that they are referring to and the verb form. He is going to be late. They are going to be late. John is the best office manager, and he works very hard. Sarah and John are the best people to place on a team; they work well together. Writing to keep subject agreement with verbs and pronouns that match the antecedent helps to avoid confusion in your writing. Conjunctive Adverbs An adverb functions in much the same way as an adjective. While adjectives modify or describe nouns, adverbs do the same to verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. An adverb may come before or after the word(s) it modifies; adverbs tell how, when, or where an action is performed. Adverbs come in different forms: descriptive and conjunctive. Conjunctive adverbs express relationships between two things; those relationships include addition, contrast, comparison, result, time, and emphasis (Troyka 316). Conjunctive adverbs that express a relationship of addition are also, furthermore, moreover, and besides. The sentence, I am leaving; furthermore, I will not return, contains the conjunctive adverb furthermore. Conjunctive adverbs that express a relationship of contrast are however, still, nevertheless, conversely, nonetheless, otherwise, and instead. The sentence, She chose to stay home instead, expresses a contrast between staying home and another activity through usage of the conjunctive adverb instead. Conjunctive adverbs that express relationships of comparison are similarly and likewise. The sentence, Like you, I similarly enjoy opera music, provides a comparison between another person (you) and the writer of the sentence (I). Conjunctive adverbs expressing a relationship of result are therefore, thus, consequently, accordingly, and hence. The sentence, The boy fell off his bike; consequently, he scraped his knee, shows a result—scraping a knee as a result of falling off a bike. Conjunctive adverbs showing a relationship of time are next, meanwhile, finally, and subsequently. The sentence, David finally asked Jan to marry him, shows the passage of time—David could have asked Jan to marry him long ago, but he did not. By asking her now, he is finally (or at last) doing so. Lastly, conjunctive adverbs that show an emphasis are indeed and certainly. The sentence, Jan certainly didn’t expect it, emphasizes the fact that she did not hold any expectations. Descriptive adverbs add more information to a verb. Descriptive adverbs are words like happily, clearly, quickly, and loudly. The sentence, The rabbit scurried away quickly, contains the descriptive adverb quickly. Quickly tells the reader how the rabbit ran. The sentence, The man loudly shouted at the dog, contains the descriptive adverb loudly. It tells the reader how the man shouted—loudly. Reference Troyka, L. Q. (2004). Quick access reference for writers (4th ed). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.