* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Canada`s Geologic
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
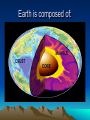
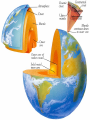
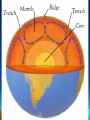
Canada’s Geologic History Exploring Earth’s Structure and Surface CGC1D1 THINK-‐PAIR-‐SHARE Have you ever wondered? • What it would be like to journey to the center of the Earth? • What do you think it would be like? Journey to the Centre of the Earth Journey to the Centre of the Earth Earth is composed of: MANTLE CRUST CORE Earth’s Composition – Act It Out! • In your group, create a short skit that will illustrate the characteristics of your part of the earth’s interior • Now let’s compare our skits to the real characteristics and definitions of the earth’s interior. THERE ARE FOUR MAIN LAYERS THAT MAKE UP THE EARTH: 1.The Inner Core is… • Mass of iron, about 3500C • Solid due to immense pressure 2. The Outer Core is… • Mass of molten iron and nickel, surrounding inner core, 5000C • The entire core is about 3500km thick 3. The Mantle is… • A rock layer about 2900km thick, surrounding the outer core • Outer layer is known as the asthenosphere, slow moving molten rock • Where convection currents get energy to move plates Earth has a radius of about 6500km from inner core to the surface Earth’s Structure cont’d 4. The Crust is… • A layer of rock between 35-75 km in depth • Made of oceanic and continental crust • Outer mantle and crust together are called the lithosphere THE EARTH AS AN EGG • Compare the earth’s layers to an egg • The shell is much like the thin crust called the lithosphere • The white of the egg is like the mantle – a layer of molten rock • The yolk is the core of the Earth Your Turn • Think of another object that could be compared to the earth’s composition • A chocolate cherry bomb candy • A peach Systems/Spheres on Earth Recall! What are the four main spheres on Earth? 1. Atmosphere 2. Lithosphere 3. Hydrosphere 4. Biosphere Individual Exploration – Point-Form Note Taking • Use page 51 in Encounter Canada to complete your chart • You must read the information and identify the MOST important information to record on your chart • HINT: You should include 1 point/box and each sphere has about 7-8 points Spheres – Mix and Match • Place the card you have been given in the correct location on the whiteboard • Compare your notes to the board and make any necessary changes Check-In • Add new terms from today’s lesson to your glossary • Class Shout-Out: Tell me 1 new thing you learned today 1 question you still have Geologic Time • Geologists have divided the earth’s history into 4 periods called eras. Each era represents a time of major sediment deposition and earth movement • Why do you think we divide the earth’s history into eras? Geologic Eras • • • • Precambrian Paleozoic Mesozoic Cenozoic Acronyms • P • P • M • C Geologic Time – Decode the Puzzle • In your group, arrange the puzzle pieces into the correct order to create an accurate timeline based on what you currently know • Now, compare your timeline to that on the handout provided by your teacher. How did you do? Your Task • Read pp.118-119 and define the following terms in your notebook. Use them in a sentence to demonstrate your understanding: - Geologic Time - Erosion - Eras • Use the chart on page 119 to complete your own Geologic Timeline in your notebook • Only record major geologic events Create a song/rap/jingle • In your groups, create a song, rap or jingle that identifies the major geologic events of each of the four eras.