* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA/RNA
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
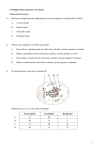
DNA/RNA DNA • Deoxyribonucleic Acid • Organic Category? DNA Structure • Double helix • 1953 • Watson and Crick • Rosalind Franklin Nucleotides • Made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base • Deoxyribose sugar • Nitrogenous bases o o o o Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine Complementary Bases • Nitrogenous bases pair up with each other • Adenine with Thymine • Cytosine with Guanine DNA Replication • Process by which DNA is copied in a cell before a cell divides by mitosis, meiosis, or binary fission • Semi-conservative replication • Makes use of 2 enzymes o Helicase o DNA Polymerase Steps of DNA Replication • DNA is “unzipped” by helicase; results in a replication fork • DNA polymerase adds new complementary bases to the parent strand • DNA polymerase falls off and bonds reform; results in two daughter strands Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic DNA Replication • Prokaryotic: replication in a circle • Eukaryotic: replication begins at many points along chromosome Errors in DNA Replication • DNA polymerase includes enzymes which repair errors • Errors are mutations • A=G Protein Synthesis • • • • Proteins direct most cellular processes Transcription Translation Central Dogma of Biology o DNA RNA Protein RNA • Ribonucleic acid • Organic category? RNA Structure • Single helix Nucleotides • Made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base • Ribose sugar • Nitrogenous bases o o o o Adenine Uracil Cytosine Guanine Complementary Bases • Nitrogenous bases pair up with each other • Adenine with Uracil • Cytosine with Guanine Types of RNA • mRNA – messenger RNA o Carries code from nucleus to ribosomes • rRNA – ribosomal RNA o Part of ribosome structure • tRNA – transfer RNA o Transfers amino acids to ribosome to make protein Transcription • DNA RNA • Can use either DNA strand as template • Only certain regions of DNA are transcribed (genes) • Makes use of 1 enzyme o RNA polymerase Steps of Transcription • RNA polymerase binds to promoter region of DNA • RNA polymerase adds new complementary bases and joins the new bases together • RNA polymerase reaches a termination box and ceases activity Gene Expression • Introns vs. Exons • Translate genes into proteins • Codon – set of three nucleotides that code for an amino acid • 63 codons code for 20 amino acids and specific START and STOP codons Translation • RNA protein • Forms a protein/polypeptide chain Steps of Translation • tRNA and rRNA join together and the ribosome moves to the mRNA coming from the nucleus; the tRNA carries the anticodon for the START codon and does NOT begin until START is found on the mRNA • tRNA continues to bring the appropriate amino acid with the anticodon to the mRNA • Chain continues to grow outside of ribosome Steps of Translation • When the STOP codon is reached, the chain falls off • tRNA leaves the ribosome and the ribosome moves way from the mRNA