* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Landforms and VA regions
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
Sierra Madre Occidental wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Cartographic propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
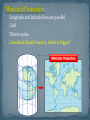
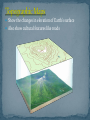
Views of Earth Section 1 – Landforms/ Virginia Provinces Video of 5 regions of Virginia Landforms are the natural shapes or features of Earth’s surface. There are many different types of landforms found on the earth. 3 major landforms shaped by weathering and erosion. Plains Coastal plains Mountains Interior plains Plateaus Mountains Folded Mountains Upwarped Mountains Fault-Block Mountains Volcanic Mountains Plateau A plain is a flat area on Earth’s surface. Large, flat areas, often found in the interior regions of continents Good for agriculture Thick fertile soil Makes up half of United States Plains near the ocean Formation: Sediment deposited from erosion of Appalachian Mountains Sea level dropped, sea floor was exposed The central portion of the United States from the Rocky Mountains to the Appalachian Mountains A plateau is a flat area higher than the land around it. Flat, raised areas of land with nearly horizontal rocks lifted by forces within Earth A mountain is a place on Earth’s surface that is much higher than the land around it. Highest Mountain – Mt. Everest in the Himalayas (8,800 m) U.S. - Mt. McKinley (Alaska) – 6,194 m VA – Mt. Rogers – 1,747 m Amherst County – Mt. Pleasant – 1,222 m Mr Lee Song about Crust and Mantle How Mountains are Formed Video Mountains formed when horizontal rock layers are squeezed from opposite sides, causing them to fold Like a rug being pushed up against a wall Characteristics: Folded horizontal rock layers Ex: Appalachian Mountains Appalachians formed 480 million and 250 million yrs ago one of the oldest and longest mtn. ranges in N. America Once were higher than the Rockies What could have caused them to shrink to less than 2,000 m above sea level? Form when blocks of Earth’s crust are pushed up by forces inside Earth Characteristics: High peaks and sharp ridges Ex: Adirondack Mountains in New York, Southern Rocky Mountains, Black Hills of South Dakota Are made of huge, tilted blocks of rock that are separated from surrounding rock by faults. Faults – large fractures in rock along which mostly vertical movement has occurred One block is pushed up while adjacent is dropped down Characteristics: Causes steep slopes Grand Tetons in Wyoming Form when molten material reaches the surface through a weak area of the crust. Deposition of materials causes cone shape to form. In the continental U.S. – Mount St. Helen in Washington, Mt. Shasta in California Hawaiian Islands Iceland, volcanic mtn born 3 sisters peak, OR A valley is a lowland area between higher lands such as mountains. A canyon is a deep valley with very steep sides. An island is land that is completely surrounded by water. A lake is water that is completely surrounded by land. Oceans are the largest bodies of water on earth. A coast is the area where the ocean touches the land. A desert is a hot dry place with little or no rainfall. A river is a long flowing body of water. A peninsula is a piece of land that has water on ONLY THREE sides and attached to another piece of land. A good example of a peninsula is FLORIDA. Sea floor spreading video Google Image Result for http://howard.nebrwesleyan.edu/hhmi/fellows/gbran d/images/larrow.jpg 1 2 3 4 Produced by Virginia’s geologic activity Coastal Plain Piedmont Blue Ridge Valley and Ridge Appalachian Plateau Google Image Result for http://www.radford.edu/~swoodwar/CLASSES/GEOG 202/physprov/physprov.gif A flat area that is underlain by young, unconsolidated (loose) sediment and at one time was covered by ocean Sediment from erosion of Appalachian Mountains YELLOW Flat, low Marine fossils Sedimentary rocks wetlands Sudden drop in elevation between the coastal plains and the piedmont Cliffs created many waterfalls that fueled industry of major cities like Washington and Richmond An area of rolling hills underlain by mostly ancient igneous and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rock come from the volcanoes near subduction zones that occurred before the formation of the Appalachian Mountains RED Gently rolling land Where we are Igneous and metamorphic rocks A high ridge separating the Piedmont from the Valley and Ridge Province BLUE Billion of year old rocks Oldest rocks in state Igneous and metamorphic rocks An area with long parallel ridges and valleys that formed during a collision between Africa and North America Collision also produced the Appalachian Mountains GREEN Karst topography –caves, sinkholes Sedimentary rocks – limestone Limestone used for concrete An area with rugged, irregular topography; a series of plateaus separated by faults Sedimentary rock underneath Most of VA coal is found here PURPLE rugged, irregular topography Coal mined here Sedimentary rocks James River – Chesapeake Bay Watershed Roanoke River – North Carolina Sounds Watershed New River – Ohio River – Gulf of Mexico Section 2 Brain Pop Latitude and Longitude lines Imaginary line running all the way around Earth halfway between the north and south poles Splits Earth into Northern and Southern Hemisphere Longitude and Latitude Song Lines that are running parallel to the equator Measures North and South Never intersect or cross one another The equator is O˚ latitude, and the poles are 90˚ latitude Imaginary line representing O˚ longitude and runs from the North pole through Greenwich, England to the South pole. East lines of longitude meet west lines of longitude at the 180° meridian, which is opposite the prime meridian Distances in degrees east or west of the prime meridian - Models of Earth The lines of latitude and longitude form a grid that can be used to find locations anywhere on Earth. Lat – Flat – First North or South comes first then East or west Ex: 60° North 30° West Review Questions Each day is 24 hrs. so there are 24 time zones that are 15˚ longitude wide, or one hour different that the zone on each side Why do we have time zones? Because different parts of the country don’t experience dusk at the same time because the Earth rotates Time zones are not perfectly straight, they take cities in to consideration Move to EAST you ADD Move to WEST you SUBTRACT Is the transition line for calendar days Traveling west, move calendar forward one day Traveling east, move calendar back one day Located around the 180˚ meridian Section 3 To locate various places and to show the distribution of various features of types of material Example: Virginia Geological Map Made when points and lines on a globe’s surface are transferred onto paper All types of projections distort Example: Antarctica Mercator Projection – project correct shapes of continents, but sizes are distorted Robinson/Equal-Area Projection – shows accurate continent shapes and more accurate land sizes Conic Projection – road maps or weather maps Longitude and latitude lines are parallel Grid Distorts poles Greenland/South America, which is bigger? Good Bad Correct shapes of Areas are distorted continents Areas near the poles appear bigger than they are Because longitude lines are drawn parallel to each other Shows sizes more accurately Latitude lines are parallel, longitude lines are curved More accurate Robinson Projection Good Bad Accurate continent Still slightly distorted shapes More accurate land areas Because longitude lines are curved on the globe near the poles A conic projection is based on a cone that covers part of Earth and is then rolled out flat. A conic projection’s grid is formed from straight lines of longitude and curved lines of latitude. Good Bad Well suited for middle Not very useful for latitude regions mapping polar or equatorial regions Show the changes in elevation of Earth’s surface Also show cultural features like roads Quadrangle 7.5 minutes of longitude 7.5 minutes of latitude Contour lines - lines on a map that connect points of equal elevation Contour interval – the difference in elevation between two side-by-side contour lines Index contours – contour lines marked with their elevation 1. Contour lines close around hills and basins. Look at numbers or hachures 2. Contour lines never cross. 3. Close contour lines = steep terrain Far away contour lines = flat terrain 4. Contour lines form V’s that point upstream when they cross streams. Streams flow in depressions that are beneath the surrounding land surface. - Topographic Maps The map shows the elevation data points on which the contour lines are based. Study the map and the map key, then answer the questions. - Topographic Maps Reading Maps: What is the contour interval on this map? 100 feet - Topographic Maps Reading Maps: What color are the lowest points on the map? What range of elevations do these points represent? Yellow; points below 1,200 feet. - Topographic Maps Reading Maps: What color are the highest points on the map? What range of elevations do these points represent? Red; 1,500 feet or above. - Topographic Maps Applying Concepts: What is the elevation of the contour line labeled A? 1,300 feet - Topographic Maps Inferring: Is the area between B and C a ridge or a valley? How can you tell? Valley; contour lines curve uphill. - Topographic Maps Interpreting Data: Describe how elevation changes along the trail from point D to point C. At point D, elevation is above 1,500 feet. It then decreases to about midway along the trail where elevation is less than 1,400 feet. Elevation then increases again to point C, which is above 1,500 feet. The relationship between the distances on the map and distances on Earth’s surface Expressed as ratio 1:80,000 1 cm = 80,000 cm Explains what the symbols used on the map mean. Pg. 806 Raised Relief Maps Landsat Satellites that take pictures of the Earth’s surface using different wavelengths of light A satellite-based, radio-navigation system that allows users to determine their exact position anywhere on Earth 24 satellites 20,200 km above planet Triangulation geocaching