* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecosystems - Plain Local Schools
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
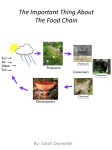
Grade 4, Chapter 3 Ecosystems Summary An ecosystem is all the living and nonliving things in an environment and how they interact. A population is all the organisms of one species that live in an ecosystem. Different populations work together to form a community. A habitat is where an organism lives within an ecosystem. A niche is what an organism eats, how it gets its food, and the other organisms that use it for food. The Sun is the main energy source for plants to make food. Plants are producers. Consumers include herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. The energy that producers store moves through a food chain. Food chains overlap to form food webs. Activate Prior Knowledge Provide background for students by previewing the book. Discuss the text features and preview the key vocabulary and concepts. Vocabulary carnivores, community, decomposers, ecosystem, herbivores, niche, omnivores, population Comprehension Skill: Sequence Tell students that when they read about different food chains, it is important to pay attention to the order in which things happen in the process of decay. During Reading Think Critically Have students answer the What Did You Learn? questions located on the inside back cover of their book. 1. What are some living things in an ecosystem? What are some nonliving things? Living—animals, plants, fungi, protists, and bacteria. Nonliving—air, water, soil, sun, climate, and landforms. 2. What is the major source of energy for life on Earth? The Sun is the major source of energy for life on Earth. Leveled Reader Teacher’s Guide 3. Why are decomposers important in an ecosystem? Without decomposers plants couldn’t get the nutrients they need from the soil. Decomposers break down the plant and animal remains into minerals and nutrients. These are then put back into the water, air, and soil. After Reading Writing in Science Food webs are made of several food chains. Look at the food web on pages 18 and 19. Describe on your paper how the energy moves through a food web. Use examples from the book to support your answer. Organize Information Graphic Organizer: Sequence Have students complete the Sequence chart on the BLM for this Leveled Reader to describe the process of decay. Related Resources Vocabulary Cards Every Student Learns Activity Flipchart Graphic Organizer Transparencies Quick Activity Transparency www.pearsonsuccessnet.com Equipment Kit LabZone Quick Study Grade 4 Chapter 3 Below-Level © Pearson Education, Inc. Before Reading 13 ____________________________________ Name _______________________________ Ecosystems Write your answers. 1. Name five kinds of ecosystems. Which is the driest? Five ecosystems are desert, tundra, forest, tropical rainforest, and grassland. The desert is the driest ecosystem. 2. Describe how habitat, population, and community are related. A population is all the organisms of one species that live in a habitat. Different populations make up a community. 3. What are some adaptations that help animals live in their habitats? Possible answer: Herbivores have flat teeth for tearing leaves. Carnivores have sharp teeth for eating their prey. 4. Describe the steps involved in the process of decay. Use the graphic organizer to help you. Possible answer: Sequence First Scavengers eat parts of dead organisms. Then © Pearson Education, Inc. Decomposers break down dead organisms. 14 Finally The broken down organisms return nutrients and minerals to the ecosystem.