* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Limiting Factors of Population Growth
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Human population planning wikipedia , lookup
Introduced mammals on seabird breeding islands wikipedia , lookup
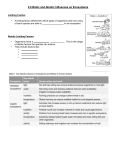
Limiting Factors of Population Growth Pages 98-103 Limiting factors are those factors which, if not suitable enough or abundant enough, affects the distribution and abundance of a population. For instance, trembling aspen (Populus tremuloides) reproduces very quickly, yet they do not live everywhere. Why? As it turns out, after 3.5 billion years of evolution, all life is adapted to live within limits. We call these tolerance limits. That's where individuals of a population will thrive. Tolerance levels are dictated by abiotic and biotic factors Biotic and Abiotic Limiting Factors Classify the factors in the picture as either biotic factors or abiotic factors Cottonwood Trees Along Oldman River · · · Periodic flooding is a natural feature of the cottonwood environment Trees adapted to survive flooded conditions for up to 2 months Increased moisture is timed with the growth of young cottonwood seedlings (critical stage of tree's life cycle) Page 100 -‐ 101 Dammed up the Olman River - what effect will that have on the Cottonwood Population and why? Page 101 -‐ 102 Page 102 - 103 Cheetah Attack Video 2:11 Great White Attack Video 3:17 Page 103 Parasite Video 2:00 Introduced arctic fox taking an auklet, a seabird breeding in the Aleutian Islands, Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. Fox predation decimated seabird populations and reduced the guano supplied by seabirds to the Aleutians, transforming the vegetation on the islands from productive plant communities dominated by grasses to less productive communities dominated by low-lying shrubs. Sea Lamprey 2:05 Introduced Invasive Species 2nd biggest threat to biodiversity after habitat destruction!!! The Canada thistle is capable of crowding out and replacing many native grasses. It is detrimental to natural areas where it occurs, particularly non-forested communities, and it can change the natural structure and species composition where it becomes wellestablished. Prairies, barrens, savannas, glades, sand dunes, fields and meadows are susceptible, particularly those sites that have been disturbed and are reverting naturally to native species, as well as those undergoing manipulative restoration management. This highly invasive thistle prevents the coexistence of other plant species through shading, competition for soil resources and possibly through the release of chemical toxins poisonous to other plants. The overall result is a reduction in plant and animal diversity. Hypothesize why the carp experienced rapid population growth when escaped into the Mississippi River? 1) POISON TH The United St exclusively. Th lethal dose. Re digestive enzy they plan to tes 2) SHOOT TH Silver carp, a t in passing boat boat companie shoot the jump 4) TRAP THE Biologists at th they could be e food stores hav carp-attracting 5) BLOCK T In 2002, the U Sanitary and S basin. But pow researchers fo researching ot mound of soil Population Growth Graphs Characteristics of this planet? These are theoretical factors that can affect human survival and earth's resiliency "Act as if what you do makes a difference. It does."