* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thursday, February 19, 2015
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
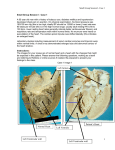
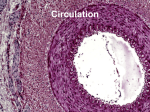
Monday, February 6, 2017 • Grab a sheet of scrap paper out of the basket. • Get out something to write with. Bellringer – answer on the scrap paper 1. How are plasma and the formed elements of blood different? 2. What are the steps of hemostasis? Are you correct? 1. The formed elements include the RBCs, WBCs, and platelets, or the cells found in the blood. The plasma is the liquid portion of blood that is mostly water. 2. Hemostasis: 1) vascular spasm; 2) platelet plug formation; 3) coagulation LEQs • What is the structure of the heart? • What path does blood take through the heart and body? • What are the differences and similarities in the functions of the systemic system, pulmonary system, hepatic portal, and coronary circulation? Read pgs. 362-366 1. What are the layers of the heart from outermost to inner-most? 2. What is the difference between atria and ventricles in terms of location, structure and function? 3. Starting with the vena cava, what is the path of blood through the heart? Include the trip to the lungs, blood vessels & specific valves. Get out CVS Notes Cardiovascular System Notes Part 1 Basics • Cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels • Cardio- = heart • -vascular = refers to the blood vessels • Basic path: arteries – arterioles – capillaries – venules - veins Pulmonary circuit •Sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs to get O2 and get rid of CO2 Systemic Circuit •Sends O2 rich blood and nutrients all over body •Removes wastes Path of blood 1. O2- poor blood to right atrium 2. Right atrium to right ventricle 3. Right ventricle pumps to lungs 4. Lungs to left atrium 5. Left atrium to left ventricle 6. Left ventricle to body Structure of heart • Hollow, cone-shaped, muscular pump • In thoracic cavity, on top of the diaphragm • Size: approx. 14 cm long by 9 cm wide • Pericardium = covering around heart • Heart wall = epicardium (outer layer); myocardium (muscular middle layer); endocardium (inner layer) Chambers • 2 atria on top; thin walls; receive blood • 2 ventricles on bottom; thicker walls; pumps blood out into arteries • Septum; wall that separates left and right sides Valves • • • • • Function: to ensure one-way blood flow AV (atrioventricular) valves: tricuspid & mitral Tricuspid: on right, 3 cusps (flaps) Mitral: on left, a.k.a. bicuspid; only 2 cusps Pulmonary valve: between right ventricle and pulmonary artery; 3 cusps • Aortic valve: at base of aorta and top of left ventricle; 3 cusps Blood Supply • Coronary arteries: 1st 2 branches of aorta; provide for the capillaries of the myocardium • Cardiac veins: remove blood from myocardial capillaries • Coronary sinus: empties into right atrium Cardiac cycle • Systole = contraction • Diastole = relaxation • Cycle = atrial systole / ventricular diastole – ventricular systole / atrial diastole – both relax; equals a complete heart beat Beating heart • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p1xEvCzs vTM Heart sounds • Through a stethoscope sounds like “lubb – dupp” • Lubb = ventricular contraction; AV valves closing • Dupp = ventricular relaxation pulmonary & aortic valves closing • Murmur = abnormal heart sounds Functional Syncytium • Mass of merging cells that function as a unit • Atrial walls and ventricular walls Cardiac conduction system • Fibers that initiate and distribute impulses throughout the myocardium • Coordinates cardiac cycle Sinoatrial node (S-A node) • In right atrium near superior vena cava • Initiates impulses that spread into myocardium and cause cardiac contractions • A.k.a. the pacemaker The Path • S-A note atrial syncytium junctional fibers A-V node A-V bundle bundle branches Purkinje fibers ventricular syncytium Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) • Recording of electrical changes during cardiac cycle • Muscle fibers are polarized between cycles • P wave = depolarization of ventricles • T wave = ventricles repolarizing • P-Q interval = time between beginning of P wave and beginning of QRS complex; time for impulse to travel from S-A node through A-V Regulation of Cardiac Cycle • cells need more blood during certain times, like strenuous exercise • parasympathetic or sympathetic nerve fibers “tell” the heart to increase heart rate • Temperature changes can affect HR (colder = slower HR) • Ions affect HR (CA+2, K+) Blood Vessels • Closed circuit • Tubes that carry blood from the heart to the cells and back • Includes: arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins Arteries & Arterioles • • • • • • • • Carry blood away from the heart Under high pressure Arteries are larger Arterioles are smaller and branched Contain muscle in the artery wall Vasoconstriction: contraction of the artery Vasodilation: increase diameter of the vessel Aorta = largest-diameter artery Capillaries • Smallest-diameter blood vessel • Connect to arterioles and venules • Where exchange of gases and nutrients happens between blood and cells • Happens by osmosis, diffusion and filtration Veins and venules • Carry blood back to heart • Veins are larger than venules • Lower pressure than in arteries and arterioles • Less muscle in the wall than arteries • Many contain valves Blood pressure • Force blood exerts against the inner walls of blood vessels • Systolic pressure: max pressure during ventricular contraction • Diastolic pressure: lower pressure during ventricular relaxation • Influenced by stroke volume / cardiac output, blood volume, peripheral resistance, viscosity • Normal = 120 / 80 (+/- 20) Tuesday, February 7, 2017 • • • • Turn in homework (3 questions) Grab a copy of the Pulse / BP Lab Get a ruler Get out several sheets of paper & something to write with • READ THROUGH THE ENTIRE PACKET Set Up Paper • Put your first & last name in upper right corner of your paper • Put the title on the top line & underline it – BP & Pulse Lab • Set up for answers; leave space to answer • Activity 1 – 3. _______ sec – (question) – (question) • Activity 2 – – – – – – – (question) (question) (question) count 1 count 2 count 3 average • Activity 3 – apical count _____ beats / min – radial count _____ pulses / min – pulse deficit _____ pulses / min • Activity 4 – First trial: systolic pressure _____ diastolic pressure _____ – Second trial: systolic pressure _____ diastolic pressure _____ Activity 5 • Copy Charts 1 & 2 – Use a ruler & make it neat – leave room to answer 2 questions • Activity 6 – – – – – 3. (question) 4. (question) 5. (2 questions) 7. (3 questions) Effects of Venous Congestion • color of raised arm: • color of dependent arm: • (question) • Effect of Mechanical Stimulation – (question) – (question) • You will complete the entire lab procedure tomorrow & Thurs. / Fri. in class. Lab directions • Before using, clean off ear pieces of stethoscope w/ alcohol-soaked cotton ball; throw cotton ball in trash • read & follow all directions • Ask if you have any questions