* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carson ECG presentation
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
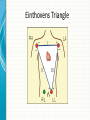
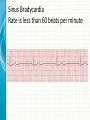
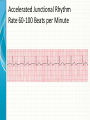
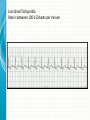
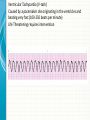
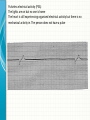
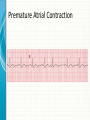
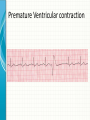
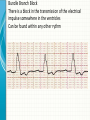
THE CARDIAC CYCLE AND THE ECG Carson Vandiver Einthovens Triangle The Normal ECG Sinus Rhythms • The Impulse is Originating in the SA node (Sinus Node) • Characterized by: – One P wave for Every QRS Complex – Rhythm is Normally Spaced out Regularly – PR interval is between .12-.20 Seconds – QRS is less than .12 Seconds • Classified by Rate Normal Sinus Rhythm Rate is Between 60-100 Sinus Bradycardia Rate is less than 60 beats per minute Sinus Tachycardia Rate is between 100 and 150 Sinus Arrhythmia Impulse is still originating in SA node but QRS complexes are spaced out unevenly (Usually related to breathing pattern) Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Has all the characteristics of sinus Arrhythmia but P waves have different Morphology AV Blocks • AV blocks means that there is an issue with the conduction of the Impulse through the AV node • Characterized by: – By an Abnormal PR interval – Or More than 1 P wave associated with Every QRS First Degree AV Block Impulse is being held for too long at AV Node Usually Benign (Very Common in Elderly) Second Degree Type 1 AV Block PR Interval gets longer until QRS is Dropped Commonly associated with Myocardial infarctions (Heart Attack) or infections of the heart such as myocarditis Second Degree Type 2 AV Block Impulse is blocked at AV Node Commonly associated with extensive damage to the bundle branches usually caused by an anteroseptal Myocardial infarction (heart attack) Third Degree AV Block Total disassociation between the electrical activity in the Atria and Ventricles Very critical requires immediate intervention because they are normally hypotensive and Bradycardic Junctional Rhythms • Av Junction is the secondary pacemaker site for the heart if the impulse fails to start in the SA node the AV junction will start firing • Junctional Rhythms are Characterized by: – The Absence of a P wave – Regularly spaced out QRS Complexes – QRS that is less than .12 seconds in length • The are classified by Rate • Can be caused by drug toxicity from Digoxin, Myocardial infarctions and a number of other physiological issues Junctional Escape Rhythm Rate is 40-60 Beats per Minute Accelerated Junctional Rhythm Rate 60-100 Beats per Minute Junctional Tachycardia Rate is between 100-150 beats per minute Atrial Arrhythmias • Impulse is originating in the SA node • Characterized by • QRS that is less than .12 seconds • Can be benign or life threatening Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib) No organized atrial contraction Atria is Fibrillating (Pulsating) Atrial Flutter Well defined pacemaker within atria firing at a rate of 250-350 times Suparventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Occurs when a Pacemaker site develops within the Atria and fires very quickly (Greater than 150 beats per minute) Life Threatening Ventricular Dysthymias • Caused by a pacemaker site developing somewhere in the Ventricles • Characterized by: – QRS complex that is greater than .12 • Can Be life threatening Ventricular Tachycardia (V-tach) Caused by a pacemaker site originating in the ventricles and beating very fast (100-250 beats per minute) Life Threatening requires intervention Cardiac Arrest Rhythms • With these rhythms the patient does not have a pulse • Very life threatening • If the person does not have a pulse you should be doing CPR • Depending on the rhythm these patients require drugs and defibrillation to correct Ventricular Fibrillation (V-Fib) No organized electrical rhythm Ventricles are Fibrillating (Pulsating) Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) The lights are on but no one is home The heart is still experiencing organized electrical activity but there is no mechanical activity ie. The person does not have a pulse Asystole No electrical activity Ectopic Beats • An Ectopic beat is premature heart beat • They are broken down by the origin of the electrical impulse • Most of the time they are benign Premature Atrial Contraction Premature Junctional Contraction A beat originates in the AV Junction early Premature Ventricular contraction Bundle Branch Block There is a block in the transmission of the electrical impulse somewhere in the ventricles Can be found within any other rythm 12-Lead ECG • Much more complicated to read • Used in the pre-hospital setting to Identify ST elevation Myocardial Infarctions • Used in the hospital setting to aid in the diagnosis various cardiac related conditions • Uses the 4 limb leads plus 6 precordial leads to take pictures of the heart from different angles 12-Lead ECG patches placement 12-Lead ECG