* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cardiac pacemaker
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
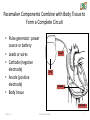
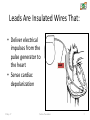
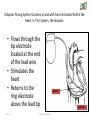
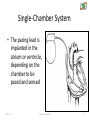
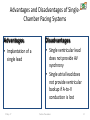
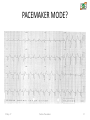
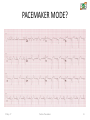
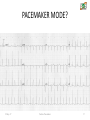
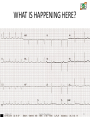
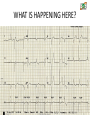
CARDIAC PACEMAKER Ms. Saranya N 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 1 Implantable Pacemaker Systems Contain the Following Components: Lead wire(s) Implantable pulse generator (IPG) 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 2 Pacemaker Components Combine with Body Tissue to Form a Complete Circuit • Pulse generator: power source or battery • Leads or wires • Cathode (negative electrode) • Anode (positive electrode) • Body tissue Lead IPG Anode Cathode 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 3 The Pulse Generator: • Contains a battery that provides the energy for sending electrical impulses to the heart • Houses the circuitry that controls pacemaker operations 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker Circuitry Battery 4 Leads Are Insulated Wires That: • Deliver electrical impulses from the pulse generator to the heart • Sense cardiac depolarization 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker Lead 5 During Pacing, the Impulse: • Begins in the pulse generator • Flows through the lead and the cathode (–) • Stimulates the heart • Returns to the anode (+) 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker Impulse onset * 6 A Unipolar Pacing System Contains a Lead with Only One Electrode Within the Heart; In This System, the Impulse: • Flows through the tip electrode (cathode) • Stimulates the heart • Returns through body fluid and tissue to the IPG (anode) 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker + Anode Cathode 7 A Bipolar Pacing System Contains a Lead with Two Electrodes Within the Heart. In This System, the Impulse: • Flows through the tip electrode located at the end of the lead wire • Stimulates the heart • Returns to the ring electrode above the lead tip 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker Anode Cathode 8 Most Pacemakers Perform Four Functions: • Stimulate cardiac depolarization • Sense intrinsic cardiac function • Respond to increased metabolic demand by providing rate responsive pacing • Provide diagnostic information stored by the pacemaker 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 9 Types 1. Asynchronous/Fixed Rate 2. Synchronous/Demand 3. Single/Dual Chamber Sequential (A & V) 4. Programmable/nonprogrammable 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 10 Single-Chamber System • The pacing lead is implanted in the atrium or ventricle, depending on the chamber to be paced and sensed 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 11 Advantages and Disadvantages of SingleChamber Pacing Systems Advantages Disadvantages • Implantation of a single lead • Single ventricular lead does not provide AV synchrony • Single atrial lead does not provide ventricular backup if A-to-V conduction is lost 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 12 Dual-Chamber Systems Have Two Leads: • One lead implanted in the atrium • One lead implanted in the ventricle 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 13 Benefits of Dual Chamber Pacing • • • • Provides AV synchrony Lower incidence of atrial fibrillation Lower risk of systemic embolism and stroke Lower incidence of new congestive heart failure • Lower mortality and higher survival rates 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 14 PACEMAKER MODE? 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 15 PACEMAKER MODE? 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 16 PACEMAKER MODE? 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 17 WHAT IS HAPPENING HERE? 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 18 WHAT IS HAPPENING HERE? 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 19 THANK YOU 2-May-17 Cardiac Pacemaker 20