* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name, Date
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
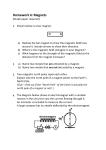
Name: _________________________ Faraday's Electromagnetic Induction Lab Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to help you develop an understanding of how electricity can be generated using a magnetic field. It will also help you understand how varying conditions influence the amount of electricity generated, such as the number of coils, the area of the coils, the speed of the magnet, the polarity of the magnet and the strength of the magnetic field. Procedure: Click on the link below to the simulation “Faraday’s Electromagnetic Lab” on the Physics Education Technology (PhET) website developed at the University of Colorado at Boulder. http://www.colorado.edu/physics/phet/simulations/faraday/faraday.jnlp Bar Magnet – General Magnetism 1. Click on the "Bar Magnet" tab if you are not already there. You should see a bar magnet and compass on the screen. Please note that the color red refers to North Pole of the magnets and white refers to South Pole. Move the compass around the magnet and then move the magnet around the compass. Click and unclick the various controls in the upper right corner of the page to see the different possible views. A. As the compass and magnet are moved around, in what direction does the North Pole of the compass want to point? B. When there are no other magnets around and the compass is only influenced by the Earth’s magnetic field, the red compass needle points in the direction of the Earth’s north geographic pole. From this observation, which magnetic pole is at/near the Earth’s North Pole? Here is a representation of the Earth and its magnetic field from Wiki. Pickup Coil – General Electromagnetic Induction 1. Click on the "Pickup Coil" tab. Observe what happens when you move either the magnet or the light bulb and coil. A. By adjusting the controls on the right hand side of the screen, describe how you should change each of the parameters below to make the bulb grow brighter. - Speed of motion: - Number of loops: - Loop Area: B. Under what conditions does the light bulb not shine? C. What parameter (that causes current to flow and the light to shine) is affected by the speed, number of loops and loop area? D. Write Faraday’s Law. Electromagnet 1. Click on the "Electromagnet" tab. Observe what happens when you move either the magnet or the electromagnet. 2. Align the coils of the electromagnet and the compass, so that the compass is directly to the right of the coils. Using the slider on the batter, change the voltage from +10 V on the right side of the battery to +10 V on the left side of the battery. What is the effect on the compass? Why? 3. Change your current source from DC to AC and describe what the compass does. 4. Observe the electrons in the AC current source and compare their movement to those in the DC current source. Explain the difference between DC and AC in terms of electron movement. Transformer 1. Click on the "Transformer" tab. The last tab showed us that current can create a magnetic field. Move the electromagnetic back and forth and observe what happens. 2. Change the current source to AC source. Observe what happens even while the electromagnet is not moving. Why does the light bulb light up? Generator – Putting it All Together 1. Click on the "Generator" tab. Turn on the water faucet and observe what happens. Adjust the controls to maximize the light’s brightness. Fill in these values below. Turbine (Magnet) Strength Loop Area _______ _______ Number of loops RPMs _______ _______