* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download here - Holy Spirit High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
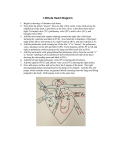
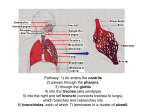
Sample Test -Biology 2201 Respiration/Circulation Systems 1. Food and liquids are prevented from entering the esophagus in humans by a flap of skin called the: A. tongue B. bicuspid valve C. tricuspid valve D. epiglottis 2. The process of maintaining a constant internal environment despite changing external conditions is known as: A. weathering B. climate control C. plasmolysis D. homeostasis 3. What is the purpose of cilia in the respiratory system? A. To remove dirt and bacteria from the bronchial tubes B. To make the air cool. C. To enable the larynx to produce sound. D. To lubricate the trachea so it can stay flexible. 4. When the diaphragm and the rib muscles contract; what happens? A. The volume of the chest cavity decreases. B. The volume of the chest cavity increases. C. The pressure inside the chest cavity increases. D. Exhalation occurs. 5. What are the tubes of the respiratory system called? A. bronchioles B. bronchi C. bronchial tubes D. trachea 6. Which is NOT a direct health risk of smoking? A. lung cancer B. emphysema C. heart disease D. pneumonia 7. The rate of breathing in an individual is controlled by: A. The medulla oblongata monitoring the amount of oxygen in the blood. B. The medulla oblongata monitoring the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood. C. The hypothalamus monitoring the amount of oxygen in the blood. D. The hypothalamus monitoring the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood. 8. The sequence of structures through which air passes into the human lung is: A. trachea, pharynx, alveolus, bronchiole, and bronchus. B. Bronchiole, bronchus, pharynx, trachea, and alveoli. C. Pharynx, trachea, bronchiole, bronchus, and alveoli. D. Pharynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchiole, and alveoli. 9. Air is moved in and out of the lungs by: A. the diaphragm and rib muscles working together to expand or decrease the size of the chest cavity. B. The diaphragm moving up and down, forcing air into the lungs. C. The rib muscles relaxing during inhalation, and the diaphragm contracting during exhalation. D. The rib muscles and the diaphragm contracting during exhalation. 10. When the diaphragm relaxes, the pressure in the (thorax) chest cavity: A. rises. B. Does not change. C. Falls D. First falls then rises. 11. Long exposure to irritating, airborne chemicals may cause a breakdown of the alveolar walls in the lungs. This is known as: A. emphysema B. bronchitis C. pleurisy D. bronchial asthma 12. The volume of air inhaled in normal breathing is known as the A. inspiratory reserve B. expiratory reserve C. tidal volume D. vital capacity 13. During swallowing, the human epiglottis A. closes of the larynx B. closes of the esophagus C. prevents food from passing through the esophagus D. allows food to pass through the windpipe 14. The exchange of gases between the blood and the body cells is called A. breathing B. internal respiration C. external respiration D. circulation 15. For the most part, breathing is controlled by the A. brain B. lungs C. diaphragm D. heart Use the above diagram to answer questions 16,17 and 18. 16. 17. 18. 19. Which letter indicates the trachea? A) X B) Y C) W D) Z Which structure does pneumonia effect? A) X B) W C) Y D) Z Which letter indicates the lung? A) X B) Y C) W D) Z What is the volume of air that you take in and push out when you are sitting at your desk in class? A. B. C. D. tidal volume residual volume vital capacity total capacity 20. Which of the labelled structures prevents blood from re-entering the right atrium from the right ventricle? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 21. Through how many heart valves must a blood cell pass as it moves from the brain to the lungs? A. 2 B. 4 C. 6 D. 8 22. A. What blood vessel supplies blood directly to the heart muscle? the aorta B. C. D. the carotid artery the coronary artery the pulmonary artery 23. Which of the labelled structures is the inferior (anterior) vena cava? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 24. What is the volume of air that you take in and push out when you are breathing at you maximum volume? A. tidal volume B. residual volume C. D. 25. vital capacity total capacity What structure does blood flow through immediately after leaving the right ventricle? A. the aorta B. the AV valve C. the pulmonary vein D. the pulmonary trunk The diagrams above illustrate cross-sectional views of three different types of blood vessels. Which of the following correctly describes the characteristics of each blood vessel? 26. 27. A. B. C. Which of the following statements is true? Arteries have thinner walls than veins. Veins have greater elasticity than arteries. Arteries have one-way valves and veins do not. D. Veins have a larger internal diameter than arteries. 28. Which of the following are characteristics of the blood vessel that carries blood from the arterioles to the venules? thin walls with valves thin walls, one cell layer thick thick walls to withstand pressure a thick middle layer of elastic tissue A. B. C. D. 29. A. B. C. D. 30. A. B. C. D. What structures are shown in the diagram? platelets and red blood cells platelets and white blood cells red blood cells and white blood cells white blood cells and plasma proteins Which of the following correctly compares the blood in the pulmonary arteries to the blood in the aorta? The blood in both vessels has low concentrations of oxyhemoglobin. The blood in both vessels has a high concentration of oxyhemoglobin. The blood in the pulmonary arteries has less oxyhemoglobin than the blood in the aorta. The blood in the pulmonary arteries has more oxyhemoglobin than the blood in the aorta. 31. A. B. C. D. What is produced by white blood cells that inactivates bacteria or viruses? antigens platelets antibodies hemoglobin 32. What valve opens when the heart chamber producing the highest blood pressure contracts? the aortic semi-lunar valve the pulmonary semi-lunar valve the left atrioventricular valve the right atrioventricular valve A. B. C. D. 33. A. B. C. D. Contraction of which heart chamber forces blood into the aorta? left atrium right atrium left ventricle right ventricle 34. What is the function of structure X? to carry oxygenated blood to the body from the heart to return oxygenated blood to the heart from the lungs to carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs from the heart to return deoxygenated blood to the heart from the body A. B. C. D. 35. A. B. C. D. Which heart structure is not functioning properly if an electrical device is needed to stimulate the atria to contract? septum SA node AV node chordae tendineae SECTION B: Answer all questions from this section. 1. What are the 2 phases of breathing? Describe the step by step actions that must occur to move a breath of air into and out of the lungs. 2. Differentiate between internal respiration and external respiration. 3. State the major difference between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. 4. Completely describe two diseases of the respiratory system? 5. Completely describe two diseases of the circulatory system?