* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year 10 TRIPLE Biology Learning Cycle 3 Overview
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
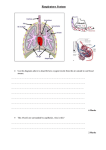
Year 10 TRIPLE Biology Learning Cycle 3 Overview How do organisms interact with one another as well as the environment and what is their impact? Learning Cycle Overview: Line of enquiry 1: Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 What impact do organisms have on the environment? Biomass is how much energy there is in an organism Dead organisms decay on their own Organic matter can decay at different rates Line of enquiry 2: Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Oxygen is vital for all life process Breathing produces carbon dioxide Deforestation is a bad thing for the carbon cycle Respiration is vital for all life Respiration rate increases when you do exercise Anaerobic respiration is important when resting Week 1 Week 1/2 Year 10 TRIPLE Biology | Learning Cycle 3 | Medium Term Plan | Science 2015/16 How do organisms interact with one another as well as the environment and what is their impact? Line of enquiry one: What impact do organisms have on the environment? Intentions for learning AQA schemes of work/specification: ENERGY IN BIOMASS Be able to construct and interpret pyramids of biomass. Describe how energy and mass is transferred along a food chain. Explain why energy and biomass is reduced at successive stages in a food chain. Home Learning Week 1: Pupils to be given a short exam paper consisting of biology, chemistry and physics questions from LC1 & 2. These are marked weekly by the member of staff not on Y10 timetable and handed back the following week. DECAY PROCESS Describe how plants and animals return materials to the environment. Describe the role of microorganisms in decay. Be able to name the type of living organism that causes leaves to decay? Describe factors affecting the rate of decay. Explain how decay is useful to plants. Evaluate the necessity and effectiveness of recycling organic kitchen or garden wastes. Lesson 1: Biomass is how much energy there is in an organism Key words: biomass, pyramid of biomass, consumer, producer, urea Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding of: what biomass is, how it is transferred between organisms and how its levels change through a food chain. Success Criteria: Recall how to construct and Interpret pyramids of biomass Describe how energy and mass is transferred along a food chain Explain why energy and biomass reduces at successive stages in a food chain Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Self assessed activity in class Lesson 2: Dead organisms decay on their own Lesson 3: Organic matter can decay at different rates Key words: decomposers, detritus feeders Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: Animals return organic matter to the environment and it is used by other organisms (microorganisms) Key words: sewage treatment, compost Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: The organic matter returned by animals and plants has a use for other organisms Success Criteria: Recall the type of living organism that causes leaves to decay Describe the role of microorganisms in decay Describe how plants/animals return materials to the environment Success Criteria: Recall and describe factors that affect rate of decay Explain how decay is useful to plants Evaluate the necessity/effectiveness of recycling organic kitchen matter/garden waste Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Extended writing exam question provided and will be tutor marked Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Act on feedback given by tutor and improve work Year 10 TRIPLE Biology | Learning Cycle 3 | Medium Term Plan | Science 2015/16 How do organisms interact with one another as well as the environment and what is their impact? Line of enquiry two: Oxygen is vital for all life process Intentions for learning AQA schemes of work/specification: THE CARBON CYCLE Explain the carbon cycle in terms of photosynthesis, respiration, feeding, death and decay, combustion of wood and fossil fuels. Explain the role of microorganisms and detritus feeders in decay. Explain why deforestation increases the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. AEROBIC RESPIRATION Describe the word equation for aerobic respiration. Define the term ‘aerobic’. Describe some uses of energy in animals and in plants. Explain why respiration has to occur continually in plant and animal cells. State the site of aerobic respiration and be able to give examples of cells that contain a lot of mitochondria. Describe the test for carbon dioxide. State that all animals and plants produce carbon dioxide all the time as a by-product of aerobic respiration. Describe the test for carbon dioxide. Design an investigation to find out the effect of exercise on heart and breathing rates. Plot the results in a graph. Explain why heart rate and breathing rate increase during exercise. Interpret data relating to the effects of exercise on the body, e.g. spirometer tracings. Write equations and explain the conversion between glucose and glycogen in liver and muscle cells ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION Write the equation for anaerobic respiration in animal cells. Explain the effect of lactic acid build up on muscle activity. Explain why anaerobic respiration is less efficient than aerobic respiration. Define the term oxygen debt. Write the equation for the Breakdown of lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water. Home Learning Week 2: Pupils to be given a short exam paper consisting of biology, chemistry and physics questions from LC1 & 2. These are marked weekly by the member of staff not on Y10 timetable and handed back the following week. Lesson 4: Breathing produces carbon dioxide Key words: fossil fuels, combustion, respiration, decay Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: A variety of chemical reactions add carbon dioxide into the environment Success Criteria: Recall the equation for photosynthesis and respiration Describe which process add carbon dioxide to the environment Explain the role of microorganisms and detritus feeders in decay Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Peer marked exam question on slide with rubric provided for pupil-given formative feedback Lesson 5: Deforestation is a bad thing for the carbon cycle Lesson 6: Respiration is vital for all life Lesson 7: Respiration rate increases when you do exercise Key words: photosynthesis, algae Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: Some chemical reactions can remove carbon dioxide out of the environment Key words: mitochondria, respiration Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding: Of the importance of respiration in living things Key words: glycogen, exercise Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: x Success Criteria: Define the term aerobic and where this type of respiration happens in cells Describe the test for carbon dioxide Explain why respiration must occur continuously in plant and animal cells Success Criteria: Interpret basic data relating to the effects of exercise on the body Explain why heart rate and breathing rate increase during exercise Design an investigation to find out the effect of exercise on heart and breathing rates Success Criteria: Recall the equation for photosynthesis and respiration Describe which process removes carbon dioxide from the environment Explain why deforestation increases the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Self assessed activity in class Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Extended writing exam question provided and will be tutor marked Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Act on feedback given by tutor and improve work Year 10 TRIPLE Biology | Learning Cycle 3 | Medium Term Plan | Science 2015/16 How do organisms interact with one another as well as the environment and what is their impact? Lesson 8: Anaerobic respiration is important when resting Key words: anaerobic, lactic acid Learning Intentions: Students should develop an understanding that: cells can still respire when there is little/no oxygen available Success Criteria: Recall the equation for anaerobic respiration Describe the breakdown of lactic acid in muscles Explain the effect of lactic acid build up on muscle activity Explain why anaerobic respiration is less efficient than aerobic Feedback Focus Knowledge input | Check | Development | REACH | Improvement Details: Peer marked exam question on slide with rubric provided for pupil-given formative feedback