* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Static Electricity
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
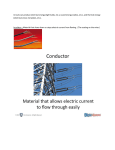
Unit D - Electricity Week 1 STATIC ELECTRICITY I can… • Distinguish between static and current electricity, and identify examples of each Static electricity • Static electricity is a stationary electric charge • What does stationary mean? • The charge is not flowing like a current • Ex. Lightning, static electricity on clothing, “shocking people” by touching them, shock from your car. Electrical charge • Remember that opposites attract which is true of negative charges • Most objects have an equal number of positive and negative charges so they are considered neutral • When an object has more of one charge we say it is charged • Ex. An object with extra electrons is negatively charged Draw this picture in your Notes! Positive Charge = Protons Negative Charge = Electrons Electrical discharge • Static electricity does not continue to flow, but it can undergo electrical discharge • The build up charge on an object can be attracted to another object and jump to that object • We call the spark an electrical discharge Laws of electrical discharge • Opposite charges attract each other • Like charges repel each other Charge separation • Charged objects cause a charge separation when they are brought close to neutral objects • For example, a negatively charged balloon, when brought close to a wall will cause the negative particles in the wall to be repelled, and therefore will be attracted to the positive particles left in the wall. Review Questions • What is the difference between a proton and an electron? • What does it mean to be “statically charged”? • How do like charges interact? • How do unlike charges interact? • A neutral object contains no charge. Is this true? Salt and Pepper Activity • Complete the Salt and Pepper Activity – This is due at the end of class. CURRENT ELECTRICITY I can… • Distinguish between static and current electricity, and identify examples of each • Identify electrical conductors and insulators, and compare the resistance of different materials to electric flow Introduction • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a3sviTa8 hZw • Is the charge on the eel a static charge or a current? Electrical Current • Static charges can discharge but they are not useful for operating electrical devices because they do not flow continually • The steady flow or charged particles is called electrical current • Electrical current can be used to run electrical devices as long as 2 things occur – Need a source of energy – Circuit must be closed The necessary parts to a Circuit • • • • 1) Conductor- wire 2) Energy Source- battery or outlet 3) Load- the thing that uses the electricity 4) Control- often a switch Conductor • A conductor allows electricity to move through it easily • What are examples of conductors? • What is the opposite of a conductor? What are examples of these? Insulators • in an insulator the electrons are bound tightly to the nuclei so they resist movement Conductors and insulators • When would you want to use a conductor in a circuit? • When would you want to use an insulator in a circuit? Conductor and Insulator Sort • Complete the Notebook Activity on Conductors and Insulators • What about wearing a Suit of Armor in a Lightning Storm? Superconductors • Some metals are better conductors than others because they give less resistance to the electrons that are flowing • Superconductors are perfect conductors- they have no resistance to electron flow – Extremely low temperatures help reduce the resistance in the superconductors – What’s the issue to running a superconductor at a low temperature? Circuits • A circuit is a path that controls the flow of electricity • Usually electricity moves through solid wires but it can move through gases or other fluids • Open and Closed Circuits Open and Closed Circuits • Complete the Smart Notebook Activity with Open and Closed Circuits Quick Lab • With a partner do the following lab– you have 20 minutes – 1) Using any materials, make one light bulb light up – 2) Using a battery, one bulb and 1 wire, make the light bulb light up – 3) Using any materials, make 2 light bulbs light up – 4) Make 2 light bulbs light up so that when you unhook one bulb, the other goes out – 5) make 2 light bulbs light up so that when you unhook one bulb, the other stays on CELLS AND BATTERIES I Can… • Investigate and evaluate the use of different chemicals, chemical concentrations and designs for electrical storage cells. (explain functions of parts and diagram) Electrochemical Cells • An electrochemical cell is a package of 2 types of metals and an electrolyte • One metal has more free for electrons than the other metal, so when a wire is attached to create a circuit the electrons get to move from one metal to the next, which creates a current • There are 2 ends on a battery, – Cathode = positive – Anode = negative Types of cells • Cells can power tiny pacemakers, toys, cars or computers • There are 2 types of cells – 1) Dry cells- the electrolyte is a paste – 2) Wet cells- uses a liquid electrolyte Dry Cells • The electrolyte in a dry cell allows ions to flow which completes the circuit • An ion is an atom with a charge • Positive terminal- where electrons travel back to the cell • Negative terminal- where electrons travel from the cell Dry Cells • The 2 metals are called electrodes • One electrode becomes positively charged, and the other becomes negatively charged. • ALKALINE (having a basic electrolyte)- are some of the most common dry cells • What does alkaline mean again? Wet cells • Wet cells often have a liquid such as sulfuric acid as their electrolyte • They are usually cheaper and easier to make than dry cells but are more dangerous • Vehicles use wet cells that need to be disposed of properly • There are individual cells that alternate within the battery • Each cell has a positive and a negative plate • The terminals in the battery are at the top Think about it! • Is it correct to call a car battery a battery? Wet Cell Batteries Answer to Think about It! Primary vs. Rechargeable cells • Primary cells: cells that can only be used one time • Rechargeable cells aka secondary cells- can be reused, the chemical reaction that occurred originally is forced to go back so it can be used again • Ni-Cd batteries are common secondary cells (made up of nickel and cadmium) Battery • Society today does not use the work battery correctly • A battery contains more than one cell Electrochemistry • Alessandro Volta made the first practical battery around 1800 by stacking copper and zinc disks with an electrolyte solution • Other scientists used batteries to split molecules into their elements electrolysis (ex. Water used as a fuel for rockets by breaking into oxygen and hydrogen) • Electrochemistry was begun which is the study of chemical reactions involving electricity • Scientists discovered that by putting more than one cell together they could increase the current and the power of the battery • http://www.edumedia-sciences.com/en/media/670electrolytic-conduction • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8oeUE6dlP2A Electroplating • Electroplating uses the technology of a battery in reverse to create a layer of silver or gold on an object How to electroplate • The metal that is to be coated is immersed in an electrolyte solution with metal bar in it. • The metal ions bond on the object and become a solid metal deposited on top of the less expensive materials • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z7f7dQF2 KLA CONTROLLING THE FLOW OF ELECTRICAL CURRENT I can… • Draw and troubleshoot circuit diagrams for a variety of specific purposes. • Explain how switches and resistors can control electrical flow, and predict the effects of these changes on output in a circuit. A Unique circuit • Neon signs have neon gas in them, when electricity is run through them they glow. • The circuit needs to be complete and needs to be controlled carefully Resistors • Resistance is a measure of how difficult it is for electrons to flow through a substance • A resistor uses power (a load can be a resistor) • Resistance is measured in ohms –symbol Ω (omega) • The more resistance a substance has the more energy it takes from the electrons that pass through it Switches and Variable resistors • Switches allow the control of a circuit by simply shutting it “on” or “off” • A variable resistor or a rheostat can adjust the resistance in an object that the current flows through • Ex. Volume control on stereos, dimmer light switch ANALYZING AND BUILDING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS I Can… • Draw and troubleshoot circuit diagrams for a variety of specific purposes. • Explain how switches and resistors can control electrical flow, and predict the effects of these changes on output in a circuit. Types of circuits • The most economical way to design a circuit is in a loop • However, we do not always want every part of the circuit being dependent on the others in the circuit • Ex. Would it be convenient for a plug-in to only work if the light switch was on? Other types of Circuits • Series Circuits • Parallel Circuits • http://www.edumediasciences.com/en/media/2 29-series-and-parallelcircuits Series circuit • In a series circuit there is only one pathway for the current • If the pathway is interrupted the circuit cannot function • Problem: adding more things increases the total resistance light bulb will get dimmer as we add more Parallel circuit • Parallel circuits have a current path for each section of the current • A break in one pathway does not affect the others • Adding more pathways decreases the total resistance Parallel vs Series • Complete the Smart Notebook Activity using Series and Parallel Circuits • http://cashmancuneo.net/flash/parallel.swf Circuit drawing • We use special (easy to draw) symbols to represent parts in a diagram • An electrical diagram is called a schematic • 4 parts of a circuit – Source – Conductor – Switch or control – Load Lets draw parts for our Schematic Diagram Tips for drawing schematics • Conductors are always drawn in straight lines with 90 degree angles • The symbols are made the same size • Conductor lines are not allowed to cross Example Complete the Circuit Assignment in your notes. 1. A closed circuit with a two-cell battery, a bulb and a switch. 2. An open circuit with a three-cell battery, a bulb and a switch. 3. A closed circuit with a three-cell battery, two bulbs, a switch and an voltmeter 4. A circuit with a two-cell battery and two bulbs that can are controlled by one switch. 5. A circuit with a three-cell battery and two bulbs, each of which are controlled independently by a switch. Practice 1 • Draw a schematic in a circuit made from: – A battery – 2 light bulbs – A switch – Conductors (Wires) Practice 2 • Draw a schematic diagram in a series including these things – Resistor – Switch – Voltmeter – Fuse – Battery made of 3 cells Practice 3 • Draw a schematic diagram in parallel with the following: – 2 cells that power the whole circuit – A light turned on by one switch – 2 more lights turned on by a switch together – A third switch that turns on or off all the lights together Lets read! • As a class read about House Wiring and Microcircuits in your notes. • What is a transistor? • What is a microcircuit? ELECTRICAL SAFETY I can… • Assess the potential danger of electrical devices, by referring to voltage and current rating (amperage) of the devices, and distinguish between safe and unsafe activities. Review • What is the difference between static and current electricity? • What are some examples of conductors and insulators? • What four things do we need to have in a circuit? • Electricity moves through the path of least resistance– where it is the easiest to flow • A short circuit is a circuit where there isn’t any protection and the electricity moves quickly and can cause damage • The 3rd prong on a cord leads to the ground and is called a ground wire • http://www.edumediasciences.com/en/media/486-grounding-earthing • The number of amps of a current is more important in terms of the danger of being shocked • Current from 0.015 A to 0.020 A will cause a painful shock and loss of muscles control • What does this mean for a person being shocked? The dangers of electrical shock • To protect yourself from electric shock you never want to allow electricity to run through you • Why are you safe in your car if a power line fell on it? • When are you not safe? Factors affecting electrical shock • Different situations affect how bad an electrical shock is • One a dry day with running shoes on you may just feel a tingle from an electrical fence, but the same fence on a rainy day when you are barefoot could really hurt Protecting yourself from Electrical Shock • Every plug in device in Canada must have a label on it showing what voltage it requires and what current it can use • The higher these numbers the more harm it can do • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n6DXkVY8fzs • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DtoQbXzNqk g&list=PLyxsgbmjwCCkYdJ6Y2anojKwKXJVqiu9V Plugs, Fuses and breakers • Fuse: contain a very thin piece of metal that will melt if too much current flows through it stopping the circuit – Need to be replaced (like in a car) • Breakers- they “ short out” when too much current is sent through them – Need to be cooled (like in your home) Danger of lightning • A lightning strike can give a current up to 30 000 A and it can kill • Lightning usually strikes at the highest point on a horizon • Lightning rods are connected to the ground through a wire to allow the discharge to dissipate to the ground • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RLWIBrweSU8 • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XKMdYbOfFzI Demonstration • Blow a Fuse! • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZT3HhDj8 bRk • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pJ9e4eaOi Ek