* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Competition
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
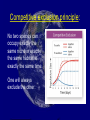
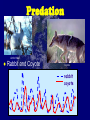
Community Interactions EQ: How do the three types of symbiosis differ? Types of Interactions Competition Predation Symbiosis Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Competition (-/-) Organisms of the same or different species compete for the same resource in the same place at the same time. Elk Herd Bison Moose Competition Intraspecific competition: Competition among members of the same species Tiger Swallowtail butterfly Interspecific competition: Competition between members of different species Blue Butterfly Competitive exclusion principle: No two species can occupy exactly the same niche in exactly the same habitat at exactly the same time. One will always exclude the other. Predation (+/-) Interaction in which one organism captures and feeds on another organism predator Falcon prey Herbivory: • Type of predation • Interaction in which an herbivore feeds on producers. Ground Squirrel Predation Keystone species: a single species that is vital to the ecosystem stability. Ex. Otters/kelp/sea urchins Predation Arctic Hare Rabbit and Coyote Coyote rabbit coyote Symbiosis Any relationship in which two species live closely together. Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Mutualism (+/+) Both organisms benefit Bee on Purple Flower o Examples: o Flowers and insects o Ants and aphids Ant and Aphid Mutualism (+/+) Lichen Lichen Algae and fungus living together Commensalism (+/0) One organism benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed. Spanish Moss Commensalism (+/0) Whales & Barnacles Barnacles on Whale Commensalism (+/0) Epiphytes “air plants” Epiphyte in Tree Epiphyte Parasitism (+/-) One organism benefits while the other is harmed Examples: tapeworms inside mammals; fleas, ticks, and lice on mammals Female Head Lice Parasitism (+/-) Ticks Before After The parasite obtains all or part of its nutritional needs from the other organism, the host. Blacklegged Tick: An adult female blacklegged tick, engorged after a blood meal, rests on a leaf. Black Legged Tick