* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Force - Kuropas 7-4 science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
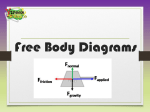
How can the motion of an object can be described? • When an object changes position over time relative to a reference point, the object is in motion – Motion of an object • Always judged with respect to some other object or point How can the motion of an object can be described? • When an object changes position over time relative to a reference point, the object is in motion – Motion of an object • Can be described with a reference direction – North – South – East – West – up or down How can the motion of an object can be described? • When an object changes position over time relative to a reference point, the object is in motion – Speed of an object • Measure of how quickly the object gets from one place to another How can the motion of an object can be described? • When an object changes position over time relative to a reference point, the object is in motion – All motion is relative • Frame of reference chosen • There is no motionless frame from which we can judge all motion Graphing Changes in Motion • Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. – Graphs help make motion easier to picture, and therefore understand. – Remember: • Motion is a change in position measured by distance and time. • Speed tells us the rate at which an object moves. • Velocity tells the speed and direction of a moving object. • Acceleration tells us the rate speed or direction changes. Graphing Changes in Motion Graphing Changes in Motion Graphing Changes in Motion Graphing Changes in Motion Graphing Changes in Motion Graphing Changes in Motion Science Thought 8/29 What causes acceleration? A force applied to an object. Describing Motion Objectives • Explain how the motion of an object can be described by its position, direction of motion, and speed in regard to some other object • Illustrate the motion of an object using a graph to show a change in position over a period of time. Interpret distance versus time graphs for constant speed and variable motion. Today’s class • Get together in group to discuss the questions from the test given on Friday. Submit ONE paper for the group with the group’s correct answers. (Put everyone’s first and last name on the paper.) • Take test home and have parents sign in order to take retest on Wednesday in class. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces objective: Explain the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces acting on an object (including friction, gravity and magnets) https://www.brainpop.com/science/motionsforcesandtime/force/ (3 min) When you ride a bike, your foot pushes against the pedal. The push makes the wheels of the bike move. When you drop something, it is pulled to the ground by gravity. A PUSH or a PULL is a FORCE. So, a good definition for force is a push or pull in a particular direction. Forces affect how objects move. They may cause motion; they may also slow, stop, or change the direction of motion of an object that is already moving What is a force? •In science, a force is a push or a pull. •All forces have two properties: Direction and Size (use VECTOR) •A newton (N) is the unit that describes the size of a force. Science Thought 8/30 What is a force and why do we use a vector to show one? A force is a push or pull and the vector shows the size and direction of the force. What is a force? •In science, a force is a push or a pull. •All forces have two properties: Direction and Size (use VECTOR) •A newton (N) is the unit that describes the size of a force. https://www.brainpop.com/science/motionsforcesandtime/force/ (3 min) Today’s class • Notes on forces (entry # 34) • RETEST on describing motion during class on Wednesday • Need original test signed by parent if under 80 • After the retest – book work – must be completed for Friday notebook check! Forces can affect motion in several ways: → They can make objects start moving → They can make objects move faster → They can make objects move slower → They can make objects stop moving → They can make objects change direction → They can make objects change shape What is a force •The student is pushing down on the chair, but the chair does not move. •The floor is balancing the force by pushing on the chair. Balanced Forces •When the forces on an object produce a net force of 0 N, the forces are balanced. •There is no change in the motion of the object. Since force cause changes in the speed or direction of an object, we can say that forces cause changes in velocity, so.... Forces cause acceleration! Acceleration Measures the change in an object’s velocity over time (Time it takes to change speed) Units include a distance and a time squared Ex: mi/hr2, m/s2 Types of Acceleration: Same Direction of Motion AKA “Speeding Up” + = A force is applied in the same direction causing the bike to speed up. Forces in the Same Direction •When forces are applied in the same direction, they are added to determine the size of the net force. Types of Acceleration: Opposite Direction of Motion AKA “Slowing Down” + = A force is applied in the opposite direction causing the bike to slow down. Forces in Different Directions •When two forces act in opposite directions, you subtract the smaller force from the larger force to determine the net force. •The net force will be in the same direction as the larger force. Types of Acceleration: At angle to motion AKA “Turning” + = A force is applied at an angle causing the bike to change direction. The speed may not change! FORCE FACTS: → Forces are measured in Newtons (N) → Forces usually act in pairs → Forces act in a particular direction → Forces usually cannot be seen, but their effects can Combining Forces •More than one force often acts on an object. •When all the forces acting on an object are added together, you determine the net force on the object. •An object with a net force more than 0 N on it will change its state of motion. Net Forces More than one force can act on an object at a time. The forces can push or pull in any direction. What happens to the object when the forces act depends on two things: → How strong the forces are → The direction of the forces Unbalanced Forces •When the net force on an object is not 0 N, the forces on the object are unbalanced. •Unbalanced forces produce a change in motion of an object. In summary! If the effects of the forces don't cancel each other, if one force is stronger than others, the forces are unbalanced forces. Unbalanced forces cause a change in motion; speed and/or direction. • When two forces act in the same direction on an object, the net force is equal to the sum of the two forces. • When two unequal forces act in opposite directions on an object, the net force is the difference of the two forces The final force and its direction are called a resultant. Science Thoughts 8/31 What happens when there are unbalanced forces acting on an object? The object moves Today in class • Retest for describing motion –Go to my page of the team website –Click on the link –Complete then submit the test • Complete bookwork – sections 2.1&2.2 • Thurs – more notes • Fri – Bill Nye video, quiz and INB check Science Thoughts 9/1 What is net force? Combining all the forces acting on a object. (add same direction, subtract opposite direction) How do balanced and unbalanced forces affect an object? • An unbalanced force that acts on an object changes its speed or direction of motion, or both. – Newton’s law • Inertia – Tendency of objects to resist any change in motion – Reason a moving object stays in motion with the same velocity unless a force changes its speed or direction or both. What is inertia? Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. Inertia tells us the we need a force to get an object to move or stop an object from moving. How do balanced and unbalanced forces affect an object? • An unbalanced force that acts on an object changes its speed or direction of motion, or both. – Newton’s law • An object will not start moving until a force acts upon it • An object will stay in motion forever unless an unbalanced force acts upon it How do balanced and unbalanced forces affect an object? • An unbalanced force that acts on an object changes its speed or direction of motion, or both. – Change in motion (direction or speed) of an object is • Proportional to the applied force • Inversely proportional to the mass. How do balanced and unbalanced forces affect an object? • An unbalanced force that acts on an object changes its speed or direction of motion, or both. – Change in motion (direction or speed) of an object is • Proportional to the applied force • Inversely proportional to the mass. Exploring Forces We will look at three examples of forces: - Friction - Gravity - Magnets How do balanced and unbalanced forces affect an object? • An unbalanced force that acts on an object changes its speed or direction of motion, or both. – Friction • Force that opposes motion • Between two surfaces that are in contact • Amount depends on factors – Roughness of the surfaces – Force pushing the surfaces together Friction •Friction is the force that opposes the motion between two surfaces that touch. •The surface of any object is rough. •Even an object that feels smooth is covered with tiny hills and valleys. •The contact between the hills of valleys of two surfaces causes them to stick, resulting in friction. Friction •The amount of friction depends on: –Roughness of the surfaces –Force pushing the surfaces together Types of Friction Kinetic friction occurs when force is applied to an object and the object moves. Examples: Sliding Friction: pushing an object across a surface Rolling Friction: between wheels and a surface Fluid Friction: opposes the motion of objects traveling through a fluid (air or water) Types of Friction Static friction occurs when force applied to an object does not cause the object to move. Reducing Friction •To reduce the amount of friction, apply a lubricant between two surfaces. Ex) Motor oil, wax, and grease •Friction can also be reduced by rolling, rather than pushing, an object. Increasing Friction ● Friction increases ● when the surface area of an object increases. ● as surfaces are made rougher. ● when the force between two objects increases. Gravity Gravity is the force of attraction between matter. Gravity depends on: mass and distance How do balanced and unbalanced forces affect an object? • An unbalanced force that acts on an object changes its speed or direction of motion, or both. – Newton’s law • Describes the relationship between – Gravitational force – Mass – Distance Mass and Gravity The more massive an object the more it can attract objects to itself. For example, the Sun has a larger gravitational effect than the Earth. Distance and Gravity The further away objects get from one another, the less gravitational attraction can be found. https://www.brainpop.com/science/motionsfor cesandtime/gravity/ (2:43) Magnets A magnet is an object with a north and south pole that produces a magnetic field and exerts a magnetic force. Magnets A magnetic field is the force field that surrounds the magnet. A magnetic force can cause objects to attract or repel without needing to touch the magnet! Poles Like poles will repel or move away from one another. Opposite poles will attract or move towards one another. https://www.brainpop.com/sci ence/motionsforcesandtime /magnetism/ Compass A compass uses the Earth’s magnetic field and magnets to help a person determine direction. The magnet’s poles will line up with the Earth’s north magnetic pole and south magnetic pole. Science Thoughts 9/2 What is the difference between kinetic friction and static friction? Friction – force that keeps object from moving Kinetic – objects move Static – objects don’t move Today in class • Quiz • Net Force/Vectors worksheets (#37) • Study Jams (#38) – Complete activity (video & quiz) – While score on screen – raise hand so I can sign that you have completed – Continue to next activity • KE and PE Nerd Words (#39) Science Thoughts 9/6 What is inertia? An object’s resistance to change of motion Sept 6 in class both of these sites are on the team web page (science weebly) must be completed for homework if not finished in class 1. Complete Study Jams – Get each of the 5 quizzes signed – leave score on screen until I sign (not simple machines) 2. Complete Forces and Motion – Get quiz score signed – fill in chart and questions Science Thoughts 9/7 What is gravity and what 2 factors effect its strength? Gravity is the attraction between 2 objects and effected by mass and distance. Sept 7 in class Log into Discovery Education –Username: wcp and lunch # Password: lunch # –Complete "Slippery Slope" exploration –Fill in data chart and answer questions on worksheet –Any work not completed in class must be completed for homework Science Thoughts 9/8 What causes friction? Contact between surfaces – the rougher the surface – the more friction. Sept 8 in class Log into Discovery Education – Username: wcp and lunch # Password: lunch # – Complete “Magnets" exploration • • • • • Mad about magnets (read and timeline) Everyday use of magnets (video and list) * real world What is a magnet (use vocabulary list) Animal magnetism (video and list) *physical science Attraction is mutual (exploration, data, question) – Watch Real World Science: Magnetism (15:42 min) – Watch Physical Science: Magnetism (20 min) – Complete at home Science Thoughts 9/9 In our labs this week, why did the car/block go farther when it started higher on the ramp? Had more potential energy that converted to kinetic energy. Sept 9 in class • Finish all labs –Study jams –Friction and motion –Slippery slope –Magnets webquest –Watch 2 magnets videos (15 minutes and 20 minutes) Science Thoughts 9/12 What is energy? The ability to do work. (in physics – work is movement) Modeling Kinetic and Potential Energy Explain how kinetic and potential energy contribute to the mechanical energy of an object. Explain how energy can be transformed from one form to another (specifically potential and kinetic) using a model or a diagram of a moving object (roller coaster, pendulum, or cars on ramps as examples). 9/12 in class Complete the guided notes using the power point that follows. Science Thoughts 9/13 How can energy be transformed between systems? Give an example. Changes to be used and passed to the next need. How do kinetic and potential energy contribute to the mechanical energy of an object? • An object that possesses mechanical energy is able to do work. – Mechanical energy • Possessed by an object due to its –Motion –Stored energy of position Energy Transfer Objective Recognize that energy can be transferred from one system to another when two objects push or pull on each other over a distance (work) and electrical circuits require a complete loop through which an electric current can pass. Getting started What do you already know? (KWL, true/false) Reading • Read and annotate 3 page article. • Review true/false and make the false ones true based on the information in the reading. Science Thoughts 9/14 Why is electricity in a circuit a force? Electrons are being pushed and/or pulled through a circuit. LAB DAY • 3 circuit kits to be completed. • 15 minutes per kit. • Finish all of the activities on the instruction sheet. • Everyone gets a turn. Science Thoughts 9/15 What is needed for electricity to be useful in our homes and for our appliances and devices? A Circuit How can energy be transformed from one form to another? The workings of the universe plus all of present day technology can be viewed from the perspective of energy flowing from one place to another and changing back and forth from one form to another. How can energy be transformed from one form to another? • Energy appears in different forms such as motion and heat • Energy can travel in different forms, such as light, sound or electricity How is energy transferred from one system to another? Energy is one of the fundamental building blocks of our universe. –Energy can be transferred from a system to its environment • Thermal - A warmer object is in contact with a cooler one • Mechanical - Two objects push or pull on each other over a distance How is energy transferred from one system to another? • Energy is one of the fundamental building blocks of our universe. – Energy can change from one form to another • Some energy is always converted to heat • Some systems transform energy with less loss of heat than others How is energy transferred from one system to another? – Energy can be transferred from a system to its environment • Electrical –An electrical source (for example, a battery or generator) is connected in a complete circuit to an electrical device • Electromagnetic Waves (light, heat, UV, X-rays, etc.) How is energy transferred from one system to another? – Electrical energy • Produced from a variety of energy sources • Can be transformed into almost any other form of energy • Batteries –Store energy –Transfer energy to components in a circuit –Energy comes from chemical reactions How is energy transferred from one system to another? – Electrical energy • Important because we can use it to make so many things work –A bulb converts it into light energy –A speaker converts it into sound energy How is energy transferred from one system to another? – Electrical energy • Primary source of electrical energy is the heat generated by –Burning fossil fuels –Water power –Wind power How is energy transferred from one system to another? – Electrical energy • Secondary sources of energy –Windmills –Waterfalls –Power plants • A natural form = lightning How is energy transferred from one system to another? –Green energy • Solar • Water • Wind • Does not pollute the environment Reading Complete the two reading assignments Science Thoughts 9/16 What is green energy? Energy that does not harm the environment. Circuit Lab • Answers to yesterday’s reading (1 – AAB, 2 – DDA) • https://www.brainpop.com/science/energy/electriccircuits/ • • • • Draw FIVE circuits Build FIVE circuits Write up lab observations/answer questions Remember – lab is written as SERIES CIRCUIT but we are also doing parallel (additional questions) – 8. Compare brightness of lights in series circuit to parallel circuit – 9. What happened when the circuit was set up in formation 4? Formation 5? Why? Science Thought 9/19 What is the difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit? A series circuit has 2 or more loads on the same “loop” while a parallel circuit has a separate loop for each load. UNIT TEST • Balance and Unbalanced Forces –Net forces –Gravity, friction, magnets • Potential and Kinetic Energy • Energy Transformation and Electric Circuits Balanced and Unbalanced Forces a force is a push or a pull forces have two properties: direction and size (use VECTOR) forces can affect motion in several ways: faster, start, slower, stop, change direction Net forces: add if same direction subtract if different directions Newton’s Laws First inertia – oppose change (not moving – stay not moving, moving – stay moving) Second force = mass * acceleration (Proportional and inversely proportional) Third equal and opposite force (for every action there is an opposite and equal reaction) Friction Force that opposes motion Objects in contact with each other 2 factors effect amount of friction roughness of surface force pushing objects together 2 types kinetic – rolling, sliding, fluid static – no movement Increases with more force, more surface, rougher surface Lab answers • Forces and Motion • More friction – less distance • More mass – less distance • Big parachute – less distance • Slippery Slope • Steel & steel went farther – less friction • Slide into base to stop faster – on base Gravity the force of attraction between two objects depends on: mass and distance In a vacuum – no resistance so all objects fall at the same rate Magnets Objects with north and south pole Magnetic field surrounding Force strongest At poles Like poles repel Unlike poles attract Magnets Lab answers • Magnetic field surrounds magnet – attract and repel without touching • Magnets strongest at poles • North up for all three – all attract • North – south – north – all repel • South – north – north – repel and attract • Conclusion – – Opposites attract and same repels Energy • The ability to do work • What is work? – Cause object to move • Mechanical - movement – Kinetic – movement – Potential – stored • Transferred from one object to another • Transformed from one type to another Electricity and Circuits • Electricity is a force because – – Electrons being pushed and pulled through circuit • Two things needed for electricity to be used – – Current (steady) and circuit (path to travel) • Circuit – Power source, load, switch, conductor • Electricity is made from energy – transferred through power lines – made back into energy • Green – Doesn’t harm environment Today in class • https://www.schooltube.com/video/c74a9a49 5e7544dba30a/bill%20nye%20-%20motion (25 minutes) Circuits Lab answers Science Thought 9/20 Unit Test Turn to Circuit Lab in INB Log into google classroom 25 questions Then physics scavenger hunt How do kinetic and potential energy contribute to the mechanical energy of an object? • An object that possesses mechanical energy is able to do work. – Mechanical energy • Kinetic –Energy of motion • Potential –Energy of position • Involved in the operation of simple machines