* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review/Study Guide Chapter 15 Quiz: Independent
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Antisymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sloppy identity wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
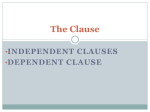
Review/Study Guide Chapter 15 Quiz: Independent and Subordinate Clauses, Adjective and Adverb Clauses A clause is a group of related words. A clause has both a subject and a predicate. There are two types of clauses. Independent Clause - An independent clause contains a subject and its verb and can stand alone as a sentence. Here is an example: We walk to school. This sentence expresses a complete thought and can stand alone. Subordinate Clause - A subordinate clause contains a subject and its verb but cannot stand alone as a sentence. Here is an example: when the cake is done baking. This clause does not express a complete thought and cannot stand alone. Adjective Clause – An adjective clause is a subordinate clause that functions as an adjective, modifying nouns and pronouns. It will usually begin with a relative pronoun. Here is an example: The boy who loves to play soccer tried out for the school team. This clause begins with who and modifies boy. NOTE: Adjective clauses will always modify the noun that directly precedes the clause. Adverb Clause – An adverb clause is a subordinate clause that functions as an adverb, modifying verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. It will begin with a subordinate conjunction. Here is an example: The boy plays soccer when he gets home from school. This clause begins with when and modifies plays. Relative Pronouns who whom whose which Common Subordinating Conjunctions after if unless although in order that until as since when as if so that whenever as long as than where as much as that wherever as soon as though while as though because before even if even though that