* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 9.1 How and where volcanoes form
Mono–Inyo Craters wikipedia , lookup
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Lascar (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Potrillo volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
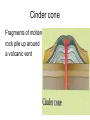
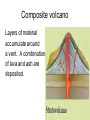
Section 9.1 How and where volcanoes form Please write any information that you feel is important. volcano Any area where molten rock, ash, and gasses can erupt volcanic ash Volcanic Lapilli Volcanic bombs • Iceland imovie How magma forms 3 ways to form magma • Decrease the pressure • Increase the temperature • Increase the amount of water in the asthenosphere Volcanic activity at different boundaries Observe an animation of volcanism at a subduction zone. Observe an animation of volcanism along a rift zone. Observe an animation of volcanic islands forming over a hot spot. Something to ponder. How are the 3 different boundaries connected to volcanoes? What is one of the biggest reasons that we are able to observe volcanic activity? Why was learning plate tectonics important for this chapter and the coming chapters? Section 9.2 Erupted materials Write down information that you feel is important Different types of magma What are some ways that magma could be different? Silica content Gas content Viscosity Melting temperature Conditions that lead to more explosive eruptions High silica content – they resist flow viscosity the resistance of a liquid to flow Higher gas concentration Lower melting point Location Lava flows on land Pahoehoe smooth rope like lava that flows very easily Lava flows on land AA basaltic lava that cools quickly into rough jagged rock Underwater lava flows Pillow lava rounded lumps of lava that crack forming pillow shapes because of the drastic temperature change in the ocean. http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?gu idAssetId=54BFD59D-FB25-435B-B5DF926F5CBA7E9F&blnFromSearch=1&productcod e=US# Ash and rock fragments Pyroclastic flow A dense superheated eruption of gases and pyroclastic material. Travels down hill at speeds over 100 kilometers per hour. Ash and rock fragments Pyroclastic material gases and solid fragments of solid rock that is ejected from a volcano Volcanic landforms Section 9.3 3 types of volcanoes • Shield volcano • Cinder volcano • Composite volcano Shield volcano Lava flows out of the earth creating a broad base and gentle slopes Cinder cone Fragments of molten rock pile up around a volcanic vent Composite volcano Layers of material accumulate around a vent. A combination of lava and ash are deposited. Other formations associated with volcanic activity Lahar Fast-moving mud flow that is associated with volcanic activity. Caldera Large crater at the top of a volcano. Usually caused by a collapse in the magma chamber. Lava plateau Large flat area where lava spills out onto the Earth’s surface.