* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
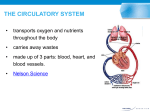
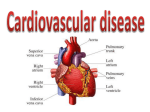
Medical Terminology - Cardiovascular Disease angi/o arteri/o brad/y—slow cardi/o cereb/o cor—heart cyan/o—blue gram/o hemangl/o my/o—muscle orrhex’s phleb/o scler/o—hard tach/y—fast thromb/o—clot vas/o varix—swollen vein vena—vein xanta/o—yellow C.V. Diagnostic Terms Aneurysm – weakened portion of a blood vessel wall Arteriosclerosis – thickening/hardening of blood vessels and restricts blood flow Atheroma – fatty deposit in the inner lining of an artery (occurs in atherosclerosis) Atherosclerosis – refers to the build-up of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in artery walls (plaques) Cardiac arrest – sudden stop in blood circulation due to failure of the heart to contract Cardiac cachexia – CVD associated malnutrition or wasting syndrome characterized by extreme skeletal muscle wasting, fatigue Cardiomegaly – enlarged heart Cerebrovascular accident (CVA) – sudden death of some brain cells due to lack of oxygen by blocked blood flow to the brain Congestive heart failure – weakening of the heart to pump blood throughout the body Coronary heart disease (CHD) – disease in which plaque builds-up within the coronary arteries and restricts blood and oxygen flow through the narrowing of vessels Dyslipidemia – disorder of lipoprotein metabolism (abnormal amount of lipids in blood) Embolism – obstruction of an artery by a blood clot or air bubble Fatty streaks – earliest form of atherosclerosis (cholesterol deposits in the walls of arteries; visible lesions) Homocysteine – amino acid found in the blood that is a breakdown product of protein metabolism Hypercholesterolemia – excess of cholesterol in the bloodstream Hyperlipoproteinemia – inability to break down lipids, especially cholesterol and triglycerides Hypertension (HTN) – chronically elevated blood pressure (140/90mmHg or higher) Ischemia – inadequate blood supply to an organ, especially the heart muscle Myocardial infarction (MI) – heart attack (when blood flow is blocked to the heart) Myocarditis – inflammation of the heart muscle Plaque – semi-hardened accumulation, usually cholesterol plaque that builds-up and blocks blood flow to the arteries Thrombus – blood clot C.V. Symptomatic Terms Angina syndrome; angina pectoris – chest pain due to lack of blood flow to the heart Anoxia – absence or deficiency of oxygen to an organ or tissue Asystole – no cardiac electrical activity, contractions, or blood flow (no heart rhythm) Bradycardia – abnormally slow heart beat Cardia edema – swelling of soft tissues of the heart, causing pressure by increased interstitial fluid resulting from congestive heart failure Claudication – pain in arms and legs due to inadequate blood flow to those muscles Ischemia – condition when there is a lack of blood flow to the brain to meet metabolic demand Palpitation – rapid, strong, or irregular heartbeat Systole – phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle contracts and pumps blood from the chambers into the arteries Tachycardia – faster than normal heart rate (>100 beats/min when resting) Vasoconstriction – narrowing of blood vessels that results from contraction of the muscular walls of the vessels Vasodepression – reduction of tone in the blood vessels with vasodilation and resulting in lowered blood pressure (hypotension) Xanthoma – skin condition in which certain fats build-up under the skin due to high blood lipids C.V. Chart Abbreviations CABG AHA AI ASHD atr AV BP brady BV CAD cardio CBC CCCR CCU CHD CHF Chol CP CPR CVA ECG, EKG FFA fib HCVD HTN, HPN MI MS MVR HTG OHS PA PT RHD SOB tach TG Throm vent