* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download R Ch 37 Electric Induction pg 1
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
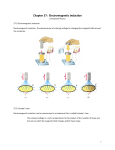
R Ch 37 Electromagnetic Induction pg 1 Text Qs pg 592 RQ 2, 3, 7, 9-14, 16-18, 20, 21 R Ch 37.1 Electromagnetic Induction pg 2 • In 1831 Faraday found you could produce an electric current moving a magnet and wire. • Electromagnetic Induction – causing a voltage by changing the magnetic field around a coductor R Ch 37.1 Electric Induction pg 3 • The voltage that can be induced depends on; • 1) the speed of the motion (fast motion = big voltage) • 2) the wire motion is at a right angle to the magnetic field • 3) more loops of wire crossing the magnetic field = more voltage & more current R Ch 37.2 Faraday’s Law pg 4 • Faraday’s Law – move a conductor through a magnetic field and create a voltage & current. • move an insulator through a magnetic field and create a voltage but no current R Ch 37.3 Generators & Alternating Current pg 5 • Generators – convert mechanical energy to electric energy • Motors – convert electric energy to mechanical energy • A generator spins a coil of wire inside a magnet, and as it spins the N pole & S pole pull the electrons back and forth causing AC (alternating) current R Ch 37.3 Generators & Alternating Current pg 6 • Batteries have DC (direct) current • In North America the voltage & current change in strength 60 times a second and it is called 60 cycle or 60 Hertz current R Ch 37.4 Motor & Generator Comparisons pg 7 • Motors spin around because a current in the wire feels a force from a magnet • Generators spin around because something, wind, water or steam pushes the wire around inside a magnet R Ch 37.5 Transformers pg 8 • Transformers are squares of iron used to increase or decrease the voltage and current of AC circuits only. • Step-up Transformer – increases v & c • Step-down Transformer – decreases v & c • Primary coil – wire into transformer • Secondary coil – wire out of transformer R Ch 37.6 Power Transmission pg 9 • All electric energy sold today is AC because it is easy to step up and step down • Power ->Tall -> Backyard ->House • Plant tower pole • 6,000 v 100,000 v 6,000 v 120 v R Ch 37.6 Power Transmission pg 10 • Electromagnetic induction is all that current electricity is and it turns out it is all that TV & radio are, controlled electromagnetic induction R Ch 37.7 Induction of Electric & Magnetic Fields pg 11 • Faraday said – an electric field is created where a magnetic field changes with time • Maxwell said – an magnetic field is created where an electric field changes with time • These two ideas created the technology that we live with today R Ch 37.8 Electromagnetic Waves pg 12 • Electromagnetic waves move at the speed of light 300,000 km/s or 186,000 miles/s • Because a changing electric field is creates a magnetic field & a changing magnetic field is creates a electric field the two fields regenerate each other. R Ch 37.8 Electromagnetic Waves pg 13 • Electromagnetic Waves have an magnetic half and an electric half that; • 1) move as a wave • 2) are at 90 degrees to each other • 3) they can move through a vacuum (space)