* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Biology Unit 5 – The Cell Cycle, Cell Division, Cell Signaling
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
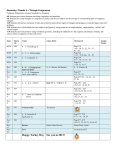
AP Biology Unit 5 – The Cell Cycle, Cell Division, Cell Signaling Name____________________________________ Block ____ Date______________________ Timeline: Oct 31st to Nov 18th; see calendar for no school days and mini-unit leading up to Thanksgiving Textbook readings (Unit 5): Parts of Ch 6 (read over summer), Ch 11, 12, Sec. 40.1 and Sec. 18.5 Labs: Mitosis & Cell Cycle, flowers and fruits for next unit; Continue artificial selection lab, phenology Essential Questions • • • • • • • • • • What are some key structures in organization of the animal body? What factors limit cell size? What is the structure and organization of the cytoskeleton? What are its functions in cellular life, especially during cell division? How does the cell cycle assure genetic continuity? How does mitosis allow for the even distribution of genetic information to new cells? How is the cell cycle regulated, and what happens when the cell cycle is not properly regulated? How are external signals converted to cellular responses? What are some common types of molecules involved in signal transduction? How does cell signaling involving ras and p53 proteins play a role in cancer? What is apoptosis and how is it regulated? Monday Oct 31 Chapter 12 reading, notes, study guide, and h.w. questions due Nov 7 Quiz On 40.1 and chapter 12 Then Cn3D 3min presentations Tuesday Nov 1 “unit 5 overview” due in google classroom in class: finish mitosis lab A block 2nd block: animal tissues lab Nov 8 Chapter 11 reading, notes, study guide, and h.w. questions Wednesday Nov 2 Thursday Nov 3 Mitosis lab due Friday Nov 4 Chapter 6 and 40.1 reading, notes, study guide, and h.w. questions; finish up chapt 12 Tonight: optional E.C. documentary and Q&A see info on google classroom Work on Cn3D Protein research Nov 9 Nov 10 Nov 11 Parent-Teacher conferences No school Veteran’s Day No School Signal transduction POGIL 3 Bozeman videos: G block 2nd block: animal tissues lab Begin signal transduction group mini-posters Signal transmission, Evolutionary significance of cell signaling, Effects of changes in signaling pathways Nov 14 Nov 15 Nov 16 Nov 17 Nov 18 Chapter section 18.5 notes, vocab, study guide Finish up all notes, study guide, vocab, signal transduction mini-posters Present signal transduction miniposters Review for test Unit 5 Test A block Lab: Flowers & Fruits Nov 21 Global warming mini unit Nov 22 Guest speaker Ms. Appel Nov 23 Half day; Flowers and fruits lab due G block Lab: Flowers & Fruits Nov 24 Thanksgiving No School Nov 25 No school Unit Outline I. II. Animal Form and Function a. Organs and Organ Systems b. Tissue Types The Cell Cycle a. Why are cells small? b. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes c. Chromosome structure d. Mitosis and cytokinesis III. e. Regulation of the cell cycle Cell Signalling a. Regulation of the cell cycle b. Review of DNAàRNAàprotein c. Cancer and the cell cycle d. Apoptosis The “Big Ideas” of AP Biology: In each unit, consider how these themes relate to what you learn. 1 - The process of Evolution drives the diversity and unity of life 2 - Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow and to maintain dynamic homeostasis 3 - Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life 4 - Biologic systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Why are cells small? 2. Briefly describe the structure and functions of the cytoskeleton, with focus on its role in cell division. Chapter 40.1. – Animal form and function 1. What are constraints on animal size and shape? 2. What are some general roles of interstitial fluid? 3. How is the body organized? What are the main functions of the organ systems of mammals? 4. What are the four different types of animal body tissues? Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle 1. Describe the functions of cell division. 2. Using a typical animal cell as an example, describe the complete cell cycle, including all of the stages of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. 3. Compare and contrast the cell cycle in plants and animals. In prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 4. Briefly describe the regulation of the cell cycle in terms of the three cell cycle checkpoints including the roles of cyclins and Cdks (ex. MPF) 5. Describe what happens when the cell cycle is not properly regulated. Chapter 11: Cell Communication 1. What are uses of local and long-distance signaling between cells in prokaryotes? In eukaryotes? 2. What is an example of a plant hormone? An animal hormone? 3. Describe the three stages of cell signaling. 4. How does testosterone activate cells? [Note: this is a model that we can generalize, since many cell signals result in activating or inhibiting transcription of specific genes.] 5. Detail the function of G protein-coupled receptors, receptor tyrosine kinases, and ion channel receptors 6. What are protein kinases? Describe the effects of a signal transduction cascade (shown in Fig. 11.9) 7. What are the roles of second messengers like cAMP, calcium ions, and IP3? 8. Describe how cell signals initiate nuclear and cytoplasmic responses. 9. What is apoptosis? Why do organisms need this process? Section 18.5: Cancer Study Guide: Interactive Q’s 18.9, Multiple Choice 9, 10, 11, 13, 21 1. What is the role of viruses in cancer? 2. What are oncogenes and how are they related to proto-oncogenes? 3. How do mutations in the ras gene contribute to cancer? What kind of protein is encoded by ras? 4. How do mutations in p53 gene contribute to cancer? What kind of protein is encoded by p53? 5. What is meant by the multistep model of cancer development? 6. How does genetics contribute to cancer?