* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Objective bits
Dynamic insulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-equilibrium thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Thermal radiation wikipedia , lookup
Heat capacity wikipedia , lookup
R-value (insulation) wikipedia , lookup
First law of thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Countercurrent exchange wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Calorimetry wikipedia , lookup
Thermoregulation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Temperature wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conduction wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamic system wikipedia , lookup
Second law of thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Adiabatic process wikipedia , lookup
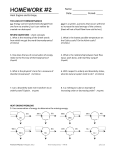
UNIT – I 1. A path function quantity is ___________ (A)Pressure (B) Temperature (C) Enthalpy [D] (D) Heat 2.The sequence of processes that eventually return the working substance to its original state is known as _________________ [C] (A) Process (B) property (C) cycle (D) state 3. In a reversible process, the change in entropy is ____ [ A] (A) Zero (B) minimum (C) maximum (D) unity 4. A thermodynamic system is referred to be an isolated system when there is transfer of __________ across the boundaries. [D] A) Only mass B) only energy C) both mass and energy D) neither mass nor energy 5. Which one of the following is the extensive property of a thermodynamic system? A) Volume B) pressure C) temperature D) density [ A] 6. The thermometric property for a constant volume gas thermometer is [ A] A) Pressure B) volume C) resistance D) length 7. Quantity of matter is called as ………… [A] (a)System (b) Surroundings (c) Boundary (d) None of the above 8. It is an intensive property …………… [C] (a)Volume (b) Energy (c) Pressure (d) All the above 9. The relation among entropy, enthalpy and pressure is given by : [A] (a)TdS=dH+VdP (b)dH=VdP-TdS (c)TdS=dH-VdP (d)Vdp=dH/TdS 10. Which one is not the intensive property of a thermodynamic system ?[ B ] (a)temperature (b)total (d)density 10. A PMM I is _____ (A)Impossible according to second law of thermodynamics (B) possible according to first law of thermodynamics (C) Impossible according to first law of thermodynamics (D) Possible according to second law of thermodynamics 11. Quantity of matter is called as ………… (a)System (b) Surroundings (c) Boundary [C] [A] (d) None of the above 12. The temperature of a gas is the measure of _________ [ A] (A)Average kinetic energy of gas molecule (B) Average distance between gas molecules (C) Average potential energy of gas molecules (D) None 13. The first law of thermodynamics is the law of (a)conservation of energy (b) conservation of mass (c) conservation of heat (d) conservation of momentum [ A] 14. The basis for measuring thermodynamic property of temperature is given by [D] (a)first law of thermodynamics (b)second law of thermodynamics (c)third law of thermodynamics (d)zeroth law of thermodynamics 15. Energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another. This statement is known as [ B] A) Zeroth law of thermodynamics B) first law of thermodynamics C) second law of thermodynamics D) kinetic theory of gases 16. A perpetual motion machine of first kind is represented by [C] (A) Fully reversible engine B) an engine with 100% thermal efficiency (C) A machine that continuously creates its own energy (D) A machine that is capable of transferring heat energy from a system at low temperature to a System at high temperature 17. Which law states that heat and work are mutually convertible ?[ D] (a) zeroth law of thermodynamics (b)first law of thermodynamics(II) (c)second law of thermodynamics (d)third law of thermodynamics 18. One reversible heat engine operates bet ween 1600oK and T2.Another reversible heat engine operates between T2 and 400oK.If both the engines have the same heat input and output,then the temperature T2 must be equal to: [A] (a)1200o K (b)1400o K (c)800o K (d) 1000o K 19. For an irreversible process,entropy change is : (a)greater than dQ/T (b)equal to dQ/T (c)less than dQ/T [B] (d)less than dT/Q 20. A closed system undergoes a process 1-2 for which the values of Q1-2 and W1-2 are +20 kJ and +50 kJ, respectively. If the system is returned to state, 1, and Q2-1 is - 10 kJ, what is the value of the work W2-1? [ B] (a) + 20 kJ (b) –40 kJ (c) –80 kJ (d) +40 kJ UNIT-II 1. Which one of the following is correct on basis of the second law of thermodynamics? [] (a) For any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases (b) ¨S =qrev/T at constant temperature (c) Efficiency of the Stirling cycle is more than that of a Carnot cycle (d) ¨E=q+w (The symbols have their usual meaning) 2. Heat transfer takes place according to (a) Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics (c) Second Law of Thermodynamics [C] (b) First Law of Thermodynamics (d) Third Law of Thermodynamics. 3. Consider the following statements: [] 1. Slow heating of water from an electric heater. 2. Isentropic expansion of air. 3. Evaporation of a liquid from a heat source at the evaporation temperature. 4. Constant pressure heating of a gas by a constant temperature source. Which of these processes is/are reversible? (a) 3 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 2 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 4. Consider the following statements: [] 1. Boiling of water from a heat source at the same boiling temperature. 2. Theoretical isothermal compression of a gas. 3. Theoretical polytropic compression process with heat rejection to atmosphere. 4. Diffusion of two ideal gases into each other at constant pressure and temperature. Which of these processes are irreversible? (a) 1, 2, 3 and 4 (c) 2, 3 and 4 only (b) 1 and 4 only (d) 3 and 4 only 5. Consider the following statements: [] 1. Temperature is due to Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics. 2. Entropy is due to First Law of Thermodynamics. 3. Internal energy is due to Second Law of Thermodynamics. 4. Reversibility is due to Kelvin-Planck's statement. Of these statements (a) 1, 2 and 3 are correct (b) 1, 3 and 4 are correct (c) 1 alone is correct (d) 2 alone is correct 6. An inventor states that his new engine rejects to the sink 40% of heat absorbed from the source while the source and sink temperatures are 327º C and 27º C respectively. His engine is therefore equivalent to [] (a) Joule engine (c) Impossible engine (b) Stirling engine (d) Carnot engine 7. A reversible engine operates between temperatures 900 K & T2 (T2 < 900 K), & another reversible engine between T2 & 400 K (T2 > 400 K) in series. What is the value of T2 if work outputs of both the engines are equal? [] (a) 600 K (b) 625 K (c) 650 K (d) 675 K 8. An engine operates between temperature limits of 900 K and T2 and another between T2 and 400 K. For both to be equally efficient, the value of T2 will be [] (a) 700 K (b) 600 K (c) 750 K (d) 650 9. An inventor says that his new concept of an engine, while working between temperature limits of 27°C and 327°C rejects 45% of heat absorbed from the source. His engine is then equivalent to which one of the following engines? [] (a) Carnot engine (b) Diesel engine (c) An impossible engine (d) Ericsson engine 10. A series combination of two Carnot’s engines operates between the temperatures of 180°C and 20°C. If the engines produce equal amount of work, then what is the intermediate temperature? [] (a) 80°C (b) 90°C (c) 100°C (d) 110°C 11. An engine working on Carnot cycle rejects 40% of absorbed heat from the source, while the sink temperature is maintained at 27°C, then what is the source temperature? [] (a) 750°C (b) 477°C (c) 203°C (d) 67.5°C 12. A Carnot engine rejects 30% of absorbed that to a sink at 30º C. The temperature of the heat source is [] (a) 100º C (b) 433º C (c) 737º C (d) 1010º C 13. A reversible heat engine rejects 50 percent of the heat supplied during a cycle of operation. If this engine is reversed and operates as a heat pump, then what is its coefficient of performance? [] (a) 1.0 (b) 1.5 (c) 2.0 (d) 2.5 14. A heat engine is supplied with 250 kJ/s of heat at a constant fixed temperature of 227°C; the heat is rejected at 27°C, the cycle is reversible, then what amount of heat is rejected? [] (a) 250 kJ/s (b) 200 kJ/s (c) 180 kJ/s (d) 150 kJ/s 15. One reversible heat engine operates between 1600 K and T2 K, and another reversible heat engine operates between T2K and 400 K. If both the engines have the same heat input and output, then the temperature T2 must be equal to: [IES-1993] (a) 1000 (b) 1200 (c) 1400 (d) 800 16. A heat engine is supplied with 250 KJ/s of heat at a constant fixed temperature of 227°C. The heat is rejected at 27°C. The cycle is reversible, if the amount of heat rejected is: [] (a) 273 KJ/s (b) 200 KJ/s (c) 180 KJ/s (d) 150 KJ/s 17. Consider the following statements: [] 1. Amount of work from cascaded Carnot engines corresponding to fixed temperature difference falls as one goes to lower absolute level of temperature. 2. On the enthalpy-entropy diagram, constant pressure lines diverge as the entropy increases. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 18. In a cyclic heat engine operating between a source temperature of 600°C and a sink temperature of 20°C, the least rate of heat rejection per kW net output of the engine is: [IAS 1994] (a) 0.460 kW (b) 0.505 kW (c) 0.588 kW (d) 0.650 kW 19. Second law of thermodynamics gives the concept of ____ (A) Work (B) heat (C) internal energy (D) entropy [D] 20. For any irreversible process the change in entropy is ______ (A)Negative (B) positive (C) zero (D) none [ B] UNIT – III 1. At triple point of a pure substance [ D] A) Liquid and vapour phases coexist B) Solid and vapour phases co-exist C) Liquid and solid phases coexist D) Solid, liquid and vapour phases co-exist 2.Mollier diagram is drawn between A) p-V B) T-S C) h-s D) p-T 3. Phase change occurs at …………. (a) Constant pressure (b) Constant temperature [C] [C] (c) Constant pressure and temp 4. A pure liquid at a given pressure will transform into vapor at …………….. [ A ] (a)Saturation temperature (b) critical temperature (c) boiling point (d) None 5. At critical point the enthalpy of vaporisation is: [A] (a)maximum (b)a function of temperature (c)a function of pressure (d)zero (d) None 6.According to Clausius statement [A&D] (a)heat flows from hot substance to cold substance. (b) heat flows from cold substance to hot substance. (c) heat cannot flows from cold substance to hot substance. (d) heat can flows from cold substance to hot substance with the aid of external work. 7.For dry saturated steam, dryness fraction is…………….. [B] a) <1 b) =1 c) >1 d) none 8. Solid, liquid and vapour phases co-exist at …………….. point [A] A)Triple b) boiling point c) maximum d) none 9.The temperature of water at its triple point is …………….. [C] a)201.0K b)190.12K c)273.16 K d)144K 10.The isotherm passing through the critical temperature is …………….. a)Critical Isotherm. b) unity c) Zero d)none 11.Heat supplied to a system equals the work done in case of a non-flow process carried out [ C ] (A)Isochoric ally (B) Isobaric ally (C)Isothermally (D)Adiabatically 12. Only throttling calorimeter is used for measuring [B] (A)very low dryness fraction up to 0.7 (B) very high dryness fraction up to 0.98 (C) dryness fraction of only low pressure steam (D) dryness fraction of only high pressure steam 13.Gas laws are applicable to _________ (A)gases as well as vapours (B)gases alone and not to vapours (C) gases and steam (D) none of the above [B] 14.During a refrigeration cycle heat is rejected by the refrigerant in______[ B ] 15.Specific heat of air at constant volume is equal to _____ (A) 0.71 (B) 0.21 (C) 0.24 (D) 1.4 [A] 16.Dew point temperature is the temperature at which condensation begins when the air is cooled at constant (a) pressure, (b) volume, (c) enthalpy (d) entropy [A] 17.Vander Waals equation may be written as _____ (a) (p+a/v )(v-b)=RT (b) (p+a/v2 )(v-b)=RT (c) (p+a/v 2)(v2-b)=RT (d) (p+a/v )(v-b)=RT2 [B] 18. Heat supplied to a gas at constant volume: [D] (a)decreases the pressure of the gas (b)increases the internal energy of gas (c)external work is done (d)decreases the internal energy of gas 19. The order of thermal efficiency of SI, CI and GT(gas turbine) is: [D] (a)SI>GT>CI (b)GT>CI>SI (c)CI>GT>SI (d)SI>CI>GT 20. The value of n=1 in the polytropic process indicates (a)adiabatic process (b)isobaric process (c)isochoric process [D] (d)isothermal process UNIT – IV 1. The Clausius-Clapeyron equation is given by: (a)(dT/dP)sat= (hfg/T vfg) (b) (dP/dT)sat = (hfg/T vfg) (c) (dP/dv)sat= (vfg/T hfg) (d) (dv/dP)sat = (Thfg/ vfg) [B] 2. Which of the following variables controls the physical properties of a perfect gas [ D ] (A) pressure (B)temperature (C) volume (D)all of the above 3. The statement that molecular weights of all gases occupy the same volume is known as (A)Avogadro’s hypothesis (B)Dalton’s law (C) Gas law (D) Joule’s Law [A] 4. During the adiabatic cooling of moist air ____ [ D ] (a) dry-bulb temperature remains constant (b) specific humidity remains constant (c) Relative humidity remains constant (d) specific enthalpy remains constant 5. Boyle's law states that when temperature is constant, the volume of a given mass of a perfect gas [ B ] (a) Varies directly as the absolute pressure (b) varies inversely as the absolute pressure (c) varies as square of the absolute pressure (d) does not vary with the absolute pressure 6. Change of entropy depends upon (a)change of mass (b)change of temperature (c)change of heat (d)change of specific heat 7. The ratio of molar specific heats for monoatomic gas is (a)1 (b)1.4 (c)1.67 (d)1.87 [C] [C] 8. In mollier diagram the pressure lines are straight in the wet region, because (a)(dg/ds) is constant (b)Tds is constant (c) (d) [B] 9.With increase in temperature the specific heats for gases(except monoatomic)______ [A] a) Increases b)decreases c)constant d)zero 10.Relative C.O.P. is equal to _______ [A] a)Actual C.O.P/Theoretical C.O.P b) Actual C.O.P-Theoretical C.O.P c) Actual C.O.P*Theoretical C.O.P d) Actual C.O.P+Theoretical C.O.P 11. The specific heats of an ideal gas depend on its (a) Temperature (b) Pressure (c) Volume (d) Molecular weight and structure [A] 12. Which one of the following statements applicable to a perfect gas will also be true for an irreversible process? (Symbols have the usual meanings). [C] (a) dQ = du + pdV (b) dQ = Tds (c) Tds = du + pdV (d) None of the above 13. The number of degrees of freedom for a diatomic molecule (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5 𝐶𝑝 14. The ratio 𝐶 for a gas with n degrees of freedom is equal to: 𝑣 (b) n – 1 (a) n + 1 (c) 2/n -1 (a) (c) 𝑑𝑃 𝑠𝑎𝑡 𝑑𝑇 𝑑𝑃 𝑠𝑎𝑡 𝑓𝑔 = 𝑇𝑣 = 𝑓𝑔 𝑇 𝑓𝑔 𝑣𝑓𝑔 [D] (d) 1+2/n 15. The Clapeyron equation with usual notations is given by: 𝑑𝑇 [D 𝒅𝑷 (b) (d) 𝒅𝑻 𝒔𝒂𝒕 𝑑𝑃 𝑑𝑇 𝑠𝑎𝑡 [B] 𝒉𝒇𝒈 = 𝑻𝒗 = 𝒇𝒈 𝑇 𝑓𝑔 𝑣𝑓𝑔 16. Clausius-Clapeyron equation gives the 'slope' of a curve in (a) p–v diagram (b) p–h diagram (c) p–T diagram [C] (d) T–S diagram 17. Number of components (C), phase (P) and degrees of freedom (F) are related by Gibbs-phase rule as: [D] (a) C – P – F = 2 (b) F – C – P = 2 (c) C + F – P = 2 (d) P + F – C = 2 18. As per Gibb's phase rule, if number of components is equal to 2 then the number of phases will be: [c] (a) ≤ 2 (b) ≤ 3 (c) ≤ 4 (d) ≤ 5 19. Gibb's phase rule is given by: [D] (F = number of degrees of freedom; C = number of components; P = number of phases) (a) F = C + P (b) F = C + P – 2 (c) F = C – P – 2 (d) F = C – P + 2 20. Gibb's free energy 'c' is defined as: (a) G = H – TS (b) G = U – TS (c) G = U + pV [A] (d) G = H + TS UNIT – V 1. For same compression ratio and for same heat added ottocycle is ___________efficient than dieselcycle [B] (A)less (B) more (C)equally (D) none 2. For same compression ratio the efficiency of dual combustion cycle is ______ Otto cycle [A] (A)less than (B)more than (C)equal to (D) none 3. Diesel cycle consists of following four processes _____ [C] (A)two isothermals and two isentropics (B) two isentropics and two constant volumes (C) twoisentropics and one constant volume and one constant pressure (D) twoisentropics and two constant pressures 4. For the same compression ratio and for same heat added ___ [A] (a) Otto cycle is more efficient than Diesel cycle (b) Diesel cycle is more efficient than Otto cycle (c) both Otto and Diesel cycles are equally efficient (d) none 5.Otto cycle consists of following four processes______ [ B ] (a) Two isothermal and two isentropic (b) two isentropic and two constant volume (c) Two isentropic, one constant volume and one constant pressure (d) Two isentropic and two constant pressure 6. The efficiency of Diesel cycle with decrease in cut off ____ (a) Increases (b) decreases (c) remains unaffected (d) first increases and then decreases [A] 7. Air standard efficiency of theoretical otto cycle [A] (a)increases with increase in compression ration (b) increases with increase in isentropic index of compression only (c)dose not depend upon the pressure ratio (d)depends on the temperature after expansion 8. In an air compressor an after cooler is used to: [C] (a)reduce volume of air (b)remove impurities from air (c)cool the air (d)cause moisture and oil vapour to drop out 9. A heat engine is supplied heat at the ratio of 30,000 j/s and gives an output of 9kW.The thermal efficiency of the engine is [A] (a)30% (b)33% (c)40% (d)50% 10.Work done in afree expansion process is: [A] (a)zero (b)always positive (c)always negative (d)non-zero quantity either positive or negative 11. In the expression of brake power BP= (2πnT/60),for a four stroke engine ‘n’ should be taken as:[B] (a)N (b)N/2 (c)2N (d)N/4 Where , N=speed of the crankshaft in rpm 12. The constant pressure gas turbine works on BRAYTON_cycle (A) Otto (B) Joule (C) stirling (D) Atkinson 13.Thermal power plant works on _________ [C] (a) Carnot cycle (b) Joules cycle (c) Rankine cycle (d) Otto cycle 14. Bell-Coleman cycle is a reversed ____ [ B ] (a) Carnot cycle (b) Joules cycle (c) Rankine cycle (d) Otto cycle 15. The constant pressure gas turbine works on the ____[B ] (a) Reversed-Braytron cycle (b) Braytron cycle (c) Rankine cycle (d) Otto cycle 16. Steam power plant works on______ cycle. [A] a)Rankine b) Otto c) Carnot d) Atkinson 17. According to ______law the specific c internal energy of a gas depends only on the temperature of the gas and is independent of both pressure and volume. [C] a) Atkinson b) Turbo-jet c)Joule’s d) stirling 18. Rankine cycle consists of_____ number of processes. [D] a)two b)four c)one d)five 19. The efficiency of RANKINE _______cycle is closer to that of Carnot cycle [A] a)cycle b)process c)system d)none 20. The ratio of actual cycle efficiency to that of the ideal cycle efficiency is called_____ [A] a)Efficiency ratio b)COP ratio c)power ratio d)speed ratio