* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pharmacology PT020D - Porterville College Home
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Plateau principle wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
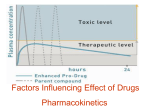
Pharmacology PT020D Lecture 2 Course Objective #14 • Identify medications commonly prescribed for D.D. clients by both generic and trade names. Commonly prescribed meds • • • • • Vitamins Cardiac meds Muscle relaxants Anti-anxiety Anti-convulsants Course Objective #15 • Describe the following mechanisms of drug action: – Altering existing cellular functions – Altering cellular environment Alteration in Cellular Function • Drugs CANNOT create new function! • Drugs CAN alter existing cellular function Receptor-mediated drug action • Agonist –Enhances • Antagonist –Blocks What are the 2 types of Antagonists? • Competitive • Non-competitive Drug Action Alter function Agonist Competitive Alter environment Antagonist Noncompetitive Physically Chemically Alteration in Cellular environment Physically • • • • Chemically Osmotic pressure • Alter body fluids Lubrication Absorption Surface conditions Course objective #16 • Differentiate between commonly used drugs according to: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Name Classification Mechanism of action Indications for use Contraindications Adverse drug effects Drug interactions Drug incompatibilities The name game • • • • Chemical name Generic name Official name Trade name / brand name The NAME game Chemical Scientific terms – describes the molecular structure Generic General name used by any company “non-proprietary” Official Name given by FDA Trade Specific company – marketing name Classification “Class” • Common action • Frequently common –Side-effects –Adverse reactions Mechanism of Action • Pharmacodynamics – “The study of the drug mechanism that produce biochemical or physiologic changes in the body” Mechanism of Action / Pharmacodynamics • Admin. Rx • Systemic circulation • Entire body Mechanism of Action • 1o Effect – Desired / therapeutic • 2o Effect – All other effects –+/– “side-effects” – expected Mechanism of Action Affinity for certain organs “Target Sites” Alt. function Alt environment Course Objective #17 • Describe the following indications for use of drugs: – Primary – Adjunctive – Non-labeled use – Investigative use Indications for Use • Valid reason • What is the opposite of indication? – Contraindication Indications • Primary –Main use Indications • Adjunctive –Used along with Indication • Non-labeled use –Supported by research Indications for use • Investigative use • Only in FDA approved studies Contraindication • Published • When to Avoid or D/C Adverse Drug Reactions • Undesirable Rx effects Types of Adverse Rx effects • Allergic Adverse Drug Reactions • Allergic Reaction –Hypersensitivity –Immune response • “antigen” – Anaphylactic Shock S&S Anaphylactic Shock Resp C/V Skin G/I Dyspnea, bronchospasm B/P + h P = Cardiac Arrest Urticaria + Pruritus N/V Adverse Drug Reactions • Rx Idiosyncrasy – Unusual reaction Adverse Drug Reactions • Rx Tolerance – response to Rx Adverse Drug Reactions • Cumulative Rx Effect – metabolism of Rx –h levels Adverse Drug Reactions • Toxic Reaction – h levels – Toxic / harmful Adverse Drug Reactions • Teratogenic – Rx + PG = – Congenital defects Drug interactions • Drug – Drug – When 1 Rx interacts with other Rx • Drug - Food Drug-to-drug • Additive Rx reaction –1 + 1 = 2 Drug-to-drug • Synergistic Rx reaction –1 + 1 = 3 Drug-to-drug • Antagonistic Rx reaction –1 + 1 = 0 (or 1) What should you do? • You are mixing drugs in a syringe to give a parenteral injection when you notice white particles forming in the syringe. • What should you do? • Do NOT give the drug! Drug-to-Food • Food –+/- absorption Rx bottle reads: Take on an empty stomach • What are the rules???? • (tell your neighbor) – 1hr ac – 2hr pc Rx bottle reads: Take with meals • Minimize GI irritation Insoluble Food-Rx mix • Rx + Food = Insoluble –(Cannot be absorbed) – absorption effect Course Objective #18 • Explain how absorption, distribution, biotransformation and excretion effect: – The concentration of drug at body sites – The concentration of drug metabolites at body sites – The time for drug concentration to develop or change Pharmacokinetics • What the body does to the Rx – Absorption – Distribution – Metabolism • Half-life – Excretion Biotransformation Absorption • How Rx is “made available” • Most PO Rx are absorbed into the body from the…. – Small intestine Factors that Affect Absorption • Route • Solubility Distribution • Rx carried from absorption site tissue – *C/V system! Course objective #20 • Explain how distribution of a drug is effected by the blood-brain barrier. Blood-brain Barrier • Selective permeability • Impermeable to MOST Rx • • • • • • Hypertension Hyperosmolar Radiation Infection Trauma Development • Blood-Brain Barrier makes the brain impermeable to Most drugs Metabolism • What is the other name for Rx metabolism? –Biotransformation –Breakdown of the drug Half-life • Time required for body to eliminate 50% of the drug Excretion • Elimination of Rx from body Explain how… • Absorption • Distribution • Biotransformation • Excretion Effect • Rx concentration in the body Course Objective #19 • Describe how the rate of absorption of a drug is affected by: – Route of administration • • • • • • Oral Sublingual Parenteral Subcutaneous Intramuscular Intravenous – Interfering factors • Stomach contents and acids • Tissue problems at site of injection, topical, inhalant 2 biggest variables affecting absorption? • Route • Circulation Categories of Rx administration • Enteral • Parenteral • Percutaneous Enteral • Directly into GI –Oral –Rectal –Nasogastric Parenteral • Bypasses GI –Subcutaneous (Subcut) –Intramuscular (IM) –Intravenous (IV) Percutaneous • Skin –Inhalation –Sublingual –Topical Enteral • With fluids – 8 oz water • Food Parenteral • • • • Correct tissue Reconstitute Assess tissue Heat – h absorption • Cool – absorption Percutaneous • Topical – Skin thickness – Hydration – Newborns • h absorption • Inhaled – Depth of breath – Fineness of droplet – Hydration Course Objective #21 • Describe how biotransformation facilitates elimination of drug metabolites. Turn to your neighbor… • Define the term biotransformation – Metabolism Course objective #22 • List the four body processes through which drugs or their metabolites are eliminated. Course Objective #23 • Explain how the following factors which influence individual pharmacological response: – – – – – – Age Gender Body weight Basal metabolic rate Disease states Genetic factors – – – – Time/route Tolerance Nutrition Smoking Age • Infant / Child –< dose • Elderly –< dose –Polypharmacy Gender • Male vs. Female –Dose amount??? • Male > Female –WHY???? –Fat:Water Body Weight • Dosing based on – 170 lbs Basal Metabolic Rate • h BMR – __?___ dose – h Disease State • What diseases might effect pharmacological responses the most? – C/V • Distribution – Liver • Metabolism – Kidney • Excretion Genetic Factors Time/Route • Place the following in order of Speed: – IV – PO – IM – Subcut Time/Route • Place the following in order of Speed: – 1. IV – 4. PO – 2. IM – 3. Subcut Tolerance • What is the difference between drug tolerance and drug dependence? Tolerance • Requires h dose to produce same effect Dependency • AKA: Addiction –Cannot control ingestion –Physical • Withdrawal –Psychological • Emotionally attached Nutrition Smoking • What effect does smoking have on BMR? –__?___ dosing Course Objective #24 • Calculate accurate medication dosages using dimensional analysis.