* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download states - Issaquah Connect
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Missouri in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
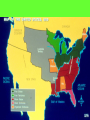
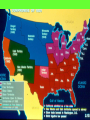
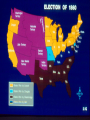
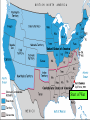
Major Events Leading to The Civil War 1. New additions to America (1820-1850): As new states are added to the Union (Louisiana Purchase territory slowly becoming individual states), congress had to decide if each state would be a free or slave state. Each new addition threatened the delicate balance of free and slave states, infuriated one side or the other, and led to heated debate. For a good example, let’s take a look at The Missouri Compromise 1820 and the Compromise of 1850: The decision as to whether a state should be free or slave becomes an issue of state vs. federal power. The decision as to whether a state should be free or slave becomes an issue of state vs. federal power. How to keep representation in Congress balanced Popular Sovereignty: The idea that political authority belongs to the people; principle that would allow voters in a territory to decide whether to ban or permit slavery. It did accomplish the following: •Added Missouri as a slave state. •Added Maine as a free state. •This made the balance of power in the Senate at 12 states each. •A line across the Louisiana Territory at 36°30’ North of this line, slavery was to be forever banned (except in Missouri). South of this line, slaveholding was permitted. The Compromise of 1850 It did accomplish the following: •California is admitted as a free state. North is happy. •New Mexico & Utah would be organized into territory open to slavery. South is happy. •Slave trade (not slavery) would be abolished in Washington, D.C. Both happy? •A strong fugitive slave law was created. South is happy. 2. Fugitive Slave Law (1850): Law stating that all citizens had to help catch runaway slaves or face a $1000 fine or 6mos in jail. Northerners resented being forced to help capture runaway slaves, and Southerners were elated to get slaves back but angry at lack of Northern support. (Judges who sent slaves back to the South were awarded with $10 for their work; but only $5 if person in question was freed!!) 3. Uncle Tom’s Cabin (1852): Outraged by the Fugitive Slave Law, Harriet Beecher Stowe addressed the cruelty of slavery in the book Uncle Tom’s Cabin. It sold over 300,000 copies in its first year. This book created more abolitionists. “Bleeding Kansas” Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854): The remainder of the Louisiana Purchase was divided into two separate territories, Kansas and Nebraska. Several other proposed causes: 4. In each territory, popular sovereignty (voters) would decide the question of slavery. • • This act repealed the earlier Missouri Compromise where slavery was banned North of Missouri. • The Kansas-Nebraska Act led to violence between proslavery and anti-slavery groups who each rushed to the new territory to support their cause. Over 200 people died in pro-slavery vs. anti-slavery skirmishes-- some call the Kansas-Nebraska Act the official start of the Civil War. • Federal Government continued to recognize the proslavery legislature as government of Kansas. EFFECT: Fourth Convention in July 1859 Kansas adopts a free state Constitution and applies to become a state. Only after Confederate states seceded did Kansas become a free state and join Union. Fallout •Got rid of the Missouri Compromise by making both Kansas and Nebraska open to slavery. •Northerners had nightmares of slavery spreading. •In May of 1856, an army of 800 pro-slavery settlers invades Lawrence. •John Brown gets revenge, hacking 5 pro-slavery men to death with their sabers. •Senator Brooks attacked Senator Sumner with his cane on the floor of Congress! •Southerners sent Brooks replacement canes as gifts. •Northerners viewed this as yet another example of Southern brutality. . 5. TheDred Scott Decision (1857): A slave named Dred Scott sued for his freedom after his owner died. He claimed that because his owner had once taken him to free states, he was entitled to his freedom. The Supreme Court ruled that African Americans were not citizens and therefore could not sue. The court also ruled that the restriction of slavery is unconstitutional because the 5th amendment states that no one may be “deprived of life, liberty or property without due process of law.” Because slaves were property this meant that Congress had no power to ban slavery anywhere. This reversed earlier decisions and was an enormous step back for abolitionists (state legislatures could still ban but anything Congress had decided was null and void.) 6. Harper’s Ferry, VA (1859): John Brown, abolitionist, attempted to start a slave revolt with 22 others at Harper’s Ferry, VA by raiding a federal arsenal and taking hostages. The plan failed and Brown was hanged, but Southerners began to fear abolitionists and slave rebellions (remember Nat Turner’s Rebellion 28 years earlier??). The election of Lincoln 7. Lincoln was elected President in 1861 with just 40% of the vote (all from the Northern states; Southern votes were divided between two candidates). The Southern states felt they had lost their voice in government. Lincoln was elected President in 1861 with just 40% of the vote (all from the Northern states; Southern votes were divided between two candidates). Since Lincoln won with a minority vote, the South was outraged. The Southern states felt they had lost their voice in government and no longer wanted to be part of this country. Secession 8.The Confederate States of America (CSA) formed in 1861-- even before Lincoln’s inauguration, seven states seceded from the Union. Secession means The act of formally withdrawing from the Union. a. South Carolina b. Mississippi 1858 Lincoln responded by saying… c. Florida “A house divided against itself can not stand. d. Alabama I believe this government cannot endure, Permanently half slave and half free.” e. Georgia f. Louisiana g. Texas There will be a total of 11 states leaving the Union. The CSA chose Jefferson Davis as their President, wrote their own Constitution which guaranteed citizens could hold slaves, printed their own money….. This Means WAR!! Civil War on our own turf! In what ways does secession benefit the South????? Yes, go ahead and answer this question my intelligent students! Think $$$$ economy, free labor (unrestricted trade with Europe, revive African slave-trade, necessity would compel South to manufacture/develop, southern way of life) BORDER STATES • Border States were on the Border of the USA and CSA. • Missouri, Kentucky, Delaware, Maryland, and Virginia • The border states did have slavery but chose not to secede because they couldn’t agree on which side to fight. • Virginia ended up splitting into two because Lincoln sent troops into Western VA due to their Union Loyalty and they set up their new gov’t and joined the Union as W. VA (1863). So now there are two states, VA and West VA. EXTRA INFO… • MO and KY controlled key stretches of the Ohio and Mississippi rivers. • Washington DC was bordered on three sides by MD. DC is the capital for the Union, yet it’s surrounded by a lot of people that are pro-South. • DEL- slave holders supported secession but they were outnumbered. • KY, MO, MD people were deeply divided on the issue of secession and some fought for Union and Some Confederate. • Important to note that slavery WAS NOT the only issue states were fighting about. Start of War