* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
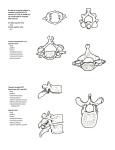
Systemic Anatomy Exam I Prepared especially for the trimester one class, Fall 2001 Please place the single best answer in the space provided (unless designated by the letters MACA, which in this case mark all correct answers that apply) on your scantron sheet. The faculty will not answer any of your questions (unless you find a typo) once the exam begins, as interpretation of the question is a part of the examination. Good luck. FORM B 1) What structure is typically involved in the condition known as “housemaid’s knees”? a) the patellar ligament b) the patellar tendon c) the prepatellar bursa d) the suprapatellar bursa e) the popliteal bursa 2) The iliofemoral ligament, prevents __ of the hip joint. a) hyperextension b) hyperflexion c) medial rotation d) lateral rotation e) adduction 3) Which direction does the head of the humerus typically end up with complete dislocation of the glenohumeral joint? a) superior and lateral b) superior and medial c) inferior and lateral d) inferior and medial 4) What is the function of the transverse humeral retinaculum? a) to attach the coracoid process of the scapula to the greater tubercle of the humerus b) to hold the bicipital tendon in place c) to attach the greater tubercle to the anatomic neck of the scapula d) to hold the subacromial bursa in place e) none of the above 5) The trochlea of the humerus articulates with the ___ . a) head of the radius b) annular ligament of the radius c) semilunar notch of the ulna d) olecranon of the ulna e) styloid process of the ulna 6) The ligamentum teres attaches ___ to ___. a) the fovea capitis, the transverse acetabular ligament b) Gerdy’s tubercle, the tibial tuberosity c) the pubis, the intertrochanteric line d) the anterior superior iliac spine, the intertrochanteric line e) the acetabular notch, the greater trochanter of the femur page 1, SA Exam I, Q.# 1-6 7) When the foot is planted on the ground and the knee is hyperextended, the ____ rotates in a ____ direction. a) femur, lateral b) femur, medial c) tibia, lateral d) tibia, medial 8) The anterior cruciate ligament attaches to the ____ aspect of the ___ condyle of the femur. a) medial, lateral b) lateral, medial c) medial, medial d) lateral, lateral 9) The patellar ligament attaches the ___ to the ___. a) belly of the rectus femoris muscle, base of the patella b) base of the patella, apex of the patella c) belly of the rectus femoris muscle, apex of the patella d) apex of the patella, tibial tuberosity e) base of the patella, tibial tuberosity 10) Most ACL injuries occur when the knee is ______. a) flexed b) extended 11) The sagittal suture is an example of a _________. (MACA) a) serrate suture b) squamous suture c) fibrous joint d) cartilaginous joint e) syndesmosis 12) Which of the following classifications apply to the intervertebral joint? (MACA) a) primary cartilaginous joint b) secondary cartilaginous joint c) diarthrosis d) amphiarthrosis e) multiaxial 13) Which of the following classifications apply to the zypapophyseal joint? (MACA) a) synovial b) symphysis c) diarthrodial d) plane e) gliding 14) Which of the following classifications apply to the temporomandibular joint? (MACA) a) synovial b) hinge c) gliding d) symphysis e) primary cartilaginous page 2, SA Exam I, Q.# 7-14 15) Which one of the following terms best describes primary cartilaginous joints? a) symphysis b) synchondrosis c) uniaxial d) diarthrosis e) amphiarthrosis 16) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) ginglymus – hinge b) saddle – biaxial c) trochoid – uniaxial d) spheroid – biaxial e) knee joint – biaxial 17) Which ligament holds the dens tight against the anterior arch of the atlas? a) posterior longitudinal ligament b) anterior longitudinal ligament c) transverse ligament of the atlas d) ligamentum flavum e) accessory ligaments 18) The radial notch is located on the ____ aspect of the radius. a) proximal medial b) proximal lateral c) distal medial d) distal lateral e) none of the above as it is not located on the radius 19) The ___ epicondyle of the humerus is typically larger that the ___ epicondyle. a) medial; lateral b) lateral; medial 20) Which carpal bones articulate with the radius? a) lunate, capitate b) scaphoid, hamate c) capitate, hamate d) scaphoid, lunate e) none of the above do 21) Which of the following bones contribute to the formation of the acetabulum? a) ileum, ischium, pubis b) pubis, ischium, femur c) ischium, ileum, femur d) pubis, ileum, ischium, femur e) none of the above 22) The popliteal fossa is located on the ___ surface of the femur. a) proximal, posterior b) proximal, anterior c) distal, posterior d) distal, anterior page 3, SA Exam I, Q.# 15-22 23) The apex of the patella is located on the _______ aspect. a) inferior b) superior 24) Gerdy’s tubercle is located on the ___ aspect of the femur. a) distal, anterior and lateral b) distal, anterior and medial c) distal, posterior and lateral d) distal, posterior and medial e) none of the above as it is not located on the femur 25) How many phalanges are there in the adult human body? a) 14 b) 28 c) 30 d) 56 e) 60 26) The superior articular facets of T4 face in a ___ direction. a) anterior b) posterior c) anterolateral d) posterolateral e) none of the above 27) How many ribs articulate with T10 vertebra? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 28) Which one of the following ligaments is found within the confines of the neural ring? a) anterior longitudinal ligament b) posterior longitudinal ligament c) supraspinous ligament d) infraspinous ligament e) interspinous ligament 29) Which of the following ligaments attaches the inion to the spinous process of C7? a) ligamentum flavum b) tectorial membrane c) interspinous ligament d) occipitocervical ligament e) nuchal ligament 30) The angle of Louis is located between the _________. a) humerus and the scapula b) head of the rib and the body of the vertebra c) manubrium and body of the sternum d) sternal end of the clavicle and the manubrium e) tubercle of the rib and the transverse process of the vertebra page 4, SA Exam I, Q.# 23-30 31) T11 and T12 have no transverse costal facets because _________________. a) no ribs articulate with T11 or T12 b) ribs 11 and 12 are floating ribs c) ribs 11 and 12 have no tubercles d) rib 12 is absent in most females e) there are only 7 costal notches on the sternum 32) The subscapular fossa is on the ___ side of the scapula. a) anterior b) posterior 33) Which of the following bones does NOT have a styloid process? a) temporal bone b) scapula c) radius d) ulna 34) Why is there no IV disc between the atlas and the axis? a) the atlas has a dens b) there is no movement between these two vertebra c) the atlas has no body d) the axis has no body e) there is a disc there so this question makes no sense 35) Flexion of the lumbar spine will ___ the diameter of the IVF. a) increase b) decrease 36) Which vertebra is called the epistropheus? a) L5 b) C7 c) the fused sacral vertebrae d) C2 e) C1 37) What structure can you palpate on the posterior side of an adult’s neck, 2 inches inferior to the inion? a) the nuchal crest b) the vertebral prominens c) the spinous process of the axis d) the spinous process of the atlas e) the uncinate process 38) Which of the following vertebrae are considered atypical? a) C1,2,7 b) T1,9,10 c) T11,12 d) L5 e) all of the above page 5, SA Exam I, Q.# 31-38 39) What goes through the transverse foramen of C7? a) the vertebral artery b) spinal nerve C7 c) the spinal accessory nerve d) the jugular vein e) none of the above 40) All mammals have 7 cervical vertebra, except which one of the following? a) whale b) giraffe c) mouse d) duck billed platypus e) Arabian horse 41) How many articular surfaces are present on the first thoracic vertebra? a) 6 b) 8 c) 10 d) 12 e) 14 42) Primary spinal curves are _____ curves. a) lordotic b) kyphotic 43) What are the components of the neural arch of a vertebra? a) transverse process, pedicles, vertebral body b) pedicles, laminae c) vertebral body, pedicles, laminae d) intervertebral foramen, vertebral body, pedicles, laminae e) vertebral foramen, vertebral body, pedicles 44) Which vertebrae have a transverse foramen? a) cervical vertebra b) thoracic vertebra c) lumbar vertebra d) sacral vertebra 45) Which of the following is NOT a boundary of the vertebral foramen? a) posterior portion of the vertebral body b) pedicle of the vertebra c) laminae of the vertebra d) intervertebral disc 46) The neural ring is largest and ___ shaped in the ___ region and smallest and ___ shaped in the ___ region. a) circular, cervical; triangular, thoracic b) triangular, cervical; circular, thoracic c) triangular, sacral; circular, cervical d) circular, cervical; triangular, sacral e) triangular, thoracic; circular, cervical page 6, SA Exam I, Q.# 39-46 47) There are _______ intervertebral disc in the adult human. a) 12 b) 18 c) 23 d) 26 e) 31 48) The groove for the vertebral artery is located on the ___ aspect of the ____ of the atlas. a) superior, posterior arch b) superior, anterior arch c) inferior, posterior arch d) inferior, anterior arch e) none of the above as it is not on the atlas 49) What connects the anterior and posterior tubercles located on the transverse process of cervical vertebra? a) the lamina b) the costotransverse bar c) the intertubercular groove d) the posterior arch e) the anterior arch 50) Which one of the following bones does NOT touch the sphenoid bone? a) vomer b) ethmoid c) maxilla d) lacrimal e) occipital 51) If I asked you to trace the mental nerve back to the trigeminal nerve, which of the following represent the correct order of structures it passes through? a) mental foramen, infraorbital foramen, foramen ovale b) mental foramen, mandibular foramen, inferior orbital fissure, foramen rotundum c) mental foramen, mandibular foramen, foramen ovale d) mental foramen, mandibular foramen, inferior orbital fissure, foramen ovale e) mental foramen, mandibular foramen, foramen rotundum 52) Thought + action = _______________. a) innate b) ambition c) Mission, Talent and Destiny d) feelings e) desire 53) Which bone forms the inferior portion of the nasal septum? a) ethmoid bone b) sphenoid bone c) vomer bone d) inferior nasal conchae e) middle nasal conchae page 7, SA Exam I, Q.# 47-53 For the next group of questions, match the structure on the left with the hole in the skull it travels through on the right. Each answer may be used once, more than once or not at all and each question only has one answer. 54) olfactory nerve a) foramen rotundum 55) oculomotor nerve b) foramen ovale 56) mandibular div. of CN V c) superior orbital fissure 57) maxillary div. of CN V d) hypoglossal canal 58) CN II e) jugular foramen 59) CN X ab) cribriform plate 60) CN XII ac) stylomastoid foramen 61) facial nerve ad) optic canal 62) The coronoid process of the mandible is ___ to the condylar process. a) anterior b) posterior 63) The ___ suture connects the asterion to the pterion. a) sagittal b) coronal c) lambdoidal d) squamous 64) The nerve that carries cutaneous sensory information from the skin of the forehead travels through the supraorbital foramen along the roof of the orbit through the _______ to the trigeminal nerve. a) foramen rotundum b) foramen ovale c) superior orbital fissure d) inferior orbital fissure e) optic canal 65) The junction of the sagittal suture with the coronal suture is called the _____. a) asterion b) bregma c) pterion d) lambda e) glabella 66) What structure is on the opposite side of the skull of the external occipital protuberance? a) the foramen magnum b) the glabella c) the occipital crest d) the external acoustic meatus e) the jugular foramen page 8, SA Exam I, Q.# 54-66 67) The supraciliary ridge is ____ to the supraorbital arch. a) superior b) inferior 68) Which cranial nerves enter the internal acoustic meatus? a) VII, VIII b) VI, VII c) IX, X, XI d) III, IV, V1 and VI e) none of the above 69) The hypoglossal canals are ____ to the occipital condyles. a) inferior b) superior 70) The nuchal lines are located on the _____ bone. a) temporal b) occipital c) sphenoid d) parietal e) frontal 71) In the DAMNIT method of determining the diagnosis of a disease process, what does the M stand for? a) metastatic b) monoclonal c) metabolic d) mediated e) mouse trap 72) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) 1 pint = 1 pound b) 5 cc’s = 1 tablespoon c) 1 ounce = 6 teaspoons d) mg% = mg/100 ml e) 5 grain aspirin tablet = 324m’s of aspirin 73) The head of the humerus is on the _______ end of the humerus. a) proximal b) distal 74) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) foramen – hole b) meatus – a fissure c) fossa – depression d) facet – flat articular surface e) alveolus – a socket 75) As arterial levels of carbon dioxide increase the level of OH ion will ______. a) drop b) rise c) stay the same page 9, SA Exam I, Q.# 67-75 76) These are small canals that connect lacunae to the central canal of an osteon. a) perforating canals b) lamellae c) canaliculi d) Sharpey’s fibers e) none of the above 77) The parietal bone of the skull develops by what means of ossification? a) endochondral b) intramembranous c) intraarticular d) intermembranous e) interchondral 78) Which fontanel typically closes first? a) anterior b) posterior c) anterolateral d) posterolateral 79) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) intercellular – inside of a cell b) melanocyte – a cell producing black pigment c) hypovolemia – decreased blood volume d) encephalopathy – disease of the brain e) gastroenteritis – inflammation of the stomach and small intestine 80) A _____ plane divides the body into inferior and superior parts. a) coronal b) sagittal c) frontal d) transverse e) two of the above 81) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) afferent – to conduct away from a central structure b) ipsilateral – on the same side c) plantar – ventral surface of the foot d) supine – to lay horizontal with the face up e) parietal – to line the inside surface of a body cavity 82) The ______ region is lateral and superior to the umbilical region of the abdomen. a) epigastric b) iliac c) hypochondriac d) pubic e) inguinal page 10, SA Exam I, Q.# 76-82 83) Rotation of the forearm so that the palm moves in a medial and posterior direction would be called _____. a) flexion b) extension c) pronation d) supination e) circumduction 84) Turning the foot so that the plantar surface faces medially is called _________. a) dorsiflexion b) plantar flexion c) circumduction d) inversion e) eversion 85) To open the mouth is ____ of the mandible. a) elevation b) flexion c) depression d) protraction e) retraction 86) A patient comes to your office complaining of a low backache. This is a ___ of a disease process. a) sign b) symptom 87) What is the email address to access the Systemic Anatomy web page off campus? a) www.parkercollege.org b) www.parkercc.chiropractic c) access.parkercc.edu d) parkercollege.edu.access e) www.drgswebpage.edu 88) “A change in the state of the soul will produce a _________________________”, Aristotle said. a) state of acedia b) change in the innate of the person c) change in the shape of the body d) change in the curvatures of the spine e) change in the mood of the person 89) Each exam in this class counts ______ of your overall grade. a) 10% b) 15% c) 20& d) 25% e) none of the above 90) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) carcino – cancer b) cephalo – head c) adeno – gland d) glosso – lips e) oto – ear page 11, SA Exam I, Q.# 83-90 91) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) –algia – pain b) –dyne – pain c) –cle – large d) –lith – stone e) –oid – to resemble 92) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) –penia – decreased b) –stasis – a narrowing c) –rrhage – abnormal flow d) –trophy – nourishment e) –phasia – speech 93) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) peri – around b) epi – upon c) contra – against d) syn – to separate e) tachy - fast 94) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) apnea – cessation of breathing b) anosmia – loss of the sense of smell c) ambulate – to walk or move around d) acedia – a sense of impending doom or depression e) afebrile – an elevated body temperature 95) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) anabatic – increase in severity of a disease process b) anisocoria – unequal pupillary diameter c) arboreal – associated with trees, or to branch d) atresia – increased diameter of a body opening e) anaphylaxis – without protection 96) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) bifurcate – to split or divide into two b) brontophobia – the fear of thunder c) cicatrix – a scar d) claudication – to ambulate or move around e) blepharitis – inflammation of the eyelids 97) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) crepitation – popping or crackling sound b) depurant – to cleanse or purify c) diaphoresis – the movement of cells to an area of inflammation d) cynophobia – the fear of dogs e) edentulous – the loss of teeth page 12, SA Exam I, Q.# 91-97 98) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) empirical – trail and error b) glycosuria – the presence of glucose in the urine c) dystocia – abnormal formation of a body part d) heliotherapy – exposure to the sun for the purpose of healing e) gynecomastia – the development of enlarged breasts in the male 99) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) hyperplasia – increase in cell size b) hyperemia – excess blood circulation to a body part imparting a red color c) hypoxemia – decreased oxygen levels in the blood d) iatrogenic – caused by a physician e) in situ – in it’s normal location 100) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) synarthrosis – fibrous joints b) syndesmosis – joined with cartilage c) symphysis – a growing together d) synostosis – joined with bone e) synovial – literally means joined with egg page 13, SA Exam I, Q.# 98-100 The end of the first systemic anatomy exam. Grades will be posted by the end of the day. Please hold your questions concerning the exam until we go over the exam in class. Thanks and have a super great day.