* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 22 RECONSTRUCTION - IB History of the Americas, HL1
Survey
Document related concepts
Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
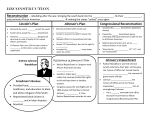
Chapter 22-23 RECONSTRUCTION 1865-1877 3 main issues after the Civil War (1) Getting Southern states back into the Union (2) Who will control it (Congress or the President) (3) Integration of 4 million “freedmen” into American society Lincoln’s 10 % Plan/ “Reconstruction and Amnesty Plan” • The INDIVIDUALS left, not the STATES • Lincoln: *Wanted the return to the South to be “QUICK” and “EASY”! • *Fed. government will PARDON / Forgive everyone (except Conf. generals) of all charges IF they swear allegiance to the Union! Lincoln’s Plan: - 10% of the state will swear allegiance to the Union = readmitted into the Union! Radical Republicans (Congressional Recon.) • Small subculture of Republicans that HATE Lincoln / Johnson’s plans for Reconstruction • Led by “Thaddeus Stevens” • MAIN AGENDA: Fight FOR African American rights! (wants African Americans to have full citizenship (14th) and voting rights(15th) – goes against Johnson’s plans *** THE SOUTH SHOULD BE PUNISHED *** “WADE-DAVIS BILL” (Congressional Response to Lincoln’s 10% Plan) • Passed by the Radical Republicans – Not 10% (as in Lincoln and Johnson)...needs a majority to be readmitted into the Union! *****Lincoln’s reaction to the Wade-Davis Bill “Pocket Veto” killed the bill – Pocket Veto: when the President fails to sign a bill within the 10 days allowed by the Constitution. (ignoring it) – RESULT: Radical Republicans think Lincoln is being too “EASY” on the South *** Both Lincoln AND Johnson – “lenient on the South” Radical Republicans – “Punish the South” ****Freedmen’s Bureau**** 1865-1872 • -Congressional assistance to former slaves (provides housing, food, clothing, education, money….) • POINT: to ease the transition from slavery to freedom (Johnson Vetoes this) but Congress overrides his veto Most significant success: teaching literacy to African Americans **Civil Rights Act 1866** (1) Gave African Americans “Citizenship” Rights – Question: What Supreme Court decision took “citizen rights” AWAY from African American slaves?_________________ (2) Ends the ability for states to pass…. “BLACK CODES” (no more black codes) - severe restrictions on African American lives from 1800 to 1865 (Johnson Vetoes this) but Congress overrides MOST SIGNIFICANT PART: provides strength into Amending the Constitution (14th Amendment) 14th Amendment 1868 • 14th Amendment: (1) all persons born or naturalized in the U.S. are citizens and (2) Equal protection under the law (Agreed upon because the South is not enforcing the Civil Rights Act of 1866) VERY IMPORTANT: • 14th Amendment = Constitutional basis / defense for the Civil Rights Act 1866 = more strength – Proves the federal government is getting stronger! VERY IMPORTANT: If the Southern States practice the 14th Amendment – they will be readmitted and martial law WILL NOT be used! Example: Tennessee agrees to practice the 14th Amendment *Reconstruction Act of 1867* • Abolished governments formed by the Confederacy during the Civil War (Sovereign and independent state governments) • This act created “MARTIAL LAW” (just like borders states during the Civil War) / Military Districts in these southern states (Johnson Vetoed this (unconstitutional?) but Congress overrides his veto – It divided the South into 5 military districts. U.S. soldiers would be stationed in each to make sure things stayed under control. – Congress laid out rules for states to be re-admitted. They said (a) the 14th Amendment must be physically practiced (b) The 15th Amendment (male suffrage) must be guaranteed / opening the door to African America prosperity. African American Gains • 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendment (women suffragist lost an advantage) • Union League: African Americans were informed of their civic duties, built churches, pushed for Republican candidates in elections, sought to solve problems, and even recruited a black militia for defense. • Hiram Revels: 1st African American U.S. Senator • Blanche Bruce: Sate for the Senate in Mississippi Politics of Postwar South Scalawags VS. Carpetbaggers Scalawag (R) – White Southerners that supported the Radical Republican’s plan for Recon. (support for African American rights) and joined the Rep. Party *Southern version of a Carpetbagger – Small farmers who wanted to improve the conditions of the South Goals: Mixed - some wanted to truly help A.A / others wanted to get the A.A vote and then use politics to enrich themselves Carpetbaggers (D) – Northerners that move to the South Goals: Mixed: Either make a profit (take advantage of War-torn South) or truly help The South / Freedmen The Ku Klux Klan • “Invisible Empire of the South” started in Tennessee in 1866 • Worked off of a “fear factor” • Main Agenda: Keep African Americans from making political, social and economic advances in America. Ways to hinder advancements Literacy Test: Pass the test = vote Discrimination: African American are asked more difficult questions (Example) Poll Tax: pay the tax = vote Discrimination: Poor whites and African Americans can’t afford to vote Problem: uneducated, poor whites were weeded out too Solution: GRANDFATHER CLAUSE - if your father or grandfather could vote before Jan 1, 1867, then you, as a white man, did not have to pass the literacy test or pay to vote Issue: 15th Amendment was not passed before Jan. 1, 1867 Congressional Response to KKK ENFORCEMENT ACT of 1870 – Gives power to the fed. Government to enforce the 15th amendment & punish those who “try to prevent A.A. from their voting rights”. – PURPOSE: COMBAT KKK VIOLENCE Congress Reacts to Johnson • What has Johnson vetoed? Plot / Plan: put president Johnson in a “lose-lose” situation TENURE OF OFFICE ACT • which said the president needed the Senate's okay to fire anyone who'd been previously appointed by him and approved by the Senate. • Senate Power: they voted him in and now they can vote him out (taking power away from the President) • Purpose: Congressional protection of Edwin Stanton (Radical Republican spy and Secretary of War under president Johnson) • Johnson’s options: (1) Keep Stanton – Congress is happy (2) Fire Stanton – Congress can impeach, bring up formal charges, against Johnson OUTCOME: Johnson fires Stanton JOHNSON’S IMPEACHMENT TRIAL • Senate trial • 2/3 vote to remove him form office • NOT REMOVED: one single vote kept in office Purchase of Alaska • Russia was willing to sell Alaska to America in 1867 for $ 7.2 million. • Led by William Seward (Secretary of State) • 1848 Congressional connection: Seward’s Folly / Icebox (1867):Congress was not convinced to purchase Alaska from Russia. Outcome: large deposits of gold and oil were discovered and Seward is a hero! 1868 Presidential Election • Ulysses S. Grant (Republican) Campaign: “Wave the bloody shirt” – reminding Americans of his war hero persona in the Civil War. Era of Good Stealings Post-Reconstruction America: Political Machines Boss Tweed ran Tammany Hall in New York City Gilded Age of Politics (Corrupt) used bribes, graft, and rigged elections to mooch money and ensure continual power for himself and his buddies. Coined by Mark Twain Thomas Nast v. Corruption – Thomas Nast was a cartoonist who relentlessly attacked Tweed's corruption. Tweed despised Nast because, although many people in Tweed's district couldn't read about the corruption, they could understand those "them damn pictures." • Nast's cartoon's brought down Tweed. Samuel J. Tilden gained fame in prosecuting Tweed. Tweed eventually died in jail. • Tilden would ride the fame to become the nominee for president in 1876 vs. Rutherford B. Hayes. Grant’s Scandals • Credit Mobilier Affair Credit Mobilier: building the trans-continental railroad and effectively sub-hired itself to get paid double. • They also gave stock to Congressmen in order to avoid getting busted. • A newspaper finally exposed the scandal, two Congressmen were fired, and the Vice President of the U.S. had even taken payments. Though uninvolved, Grant's name was scarred. Grant’s Scandals • Whiskey Ring Scandal – Internal-revenue collectors accepted bribes from whiskey distillers (so they wouldn’t have to pay taxes) – Federal government lost millions! Collapse of Reconstruction in 1877 • Grant does not run for a third term in 1876 Rutherford B. Hayes (Republican) V. Sam Tilden (Democrats) Tilden famous because he prosecuted Boss Tweed in the Tweed Ring Scandal Problem: Tilden got 184 electoral votes; he needed 185 to win. *20 votes hung in the balance due to questionable returns Issue: Which branch of Congress will count the votes? Democratic House of Republican Senate? The Compromise of 1877 and the End of Reconstruction What will fix the “stalemate” American needs a president Electoral Count Act Purpose: fix the problem 8 Republicans and 7 Democrats - Republican majority - Republicans will get what they want Democratic response: filibuster Compromise of 1877 – The North… – Got Rutherford B. Hayes elected as a Republican president. – The South… • Got a pledge that Hayes would removal of military occupation in the South. • Additionally, money would be spent on the Texas and Pacific railroad. • Also, a Southern sympathizer must be appointed to Hayes's Cabinet Sharecropping v. Tenant Farming *Slavery warmed over LIFE OF AFRICAN AMERICANS IN THE SOUTH AFTER CIVIL WAR (1) Sharecropping: economic necessity forced freed slaves into “contracts” with land owners. – Landowners would divide their land and gave each freed African American…some land, seed, and tools – Harvest / Crops come in: a “SHARE” of the crops go to the landowner! (2) Tenant Farming: another bad system for African Americans (you own your tools and seed, but you RENT the land! – OVERALL: A.A. were “locked in” or “trapped” in a style of slavery / lacked capital = no money to buy their own goods! (Slavery warmed over!) Democrats “REDEEM” the South (NEW SOUTH) / REDEMPTION • Redemption: Democrat’s “return” to power in the South after the Civil War • 1869-1875…the democrats “REDEEM” the South (Democratic “return” to power in the South) • * Redeemers: Want a “return” to the “SOLID SOUTH” – anti-Republican Reconstruction / pro - White supremacy / Return to “black codes / “the way things used to be” • Wants to establish “HOME RULE” – the ability to run a region WITHOUT federal intervention! – VERY HARD TO DO!!!! – Set out to rescue the South from “mismanagement” from Republicans and African Americans Birth of Jim Crow • Illegitimate Southern legislation (state and local) that separated the races / limited the advancement of African Americans • Plessey V. Ferguson (1896) • “separate but equal” separation of races in public accommodations (schools, theaters, transportation, and restrooms) is legal and DID NOT violate the 14th Amendment Class Conflicts and Ethnic Clashes • 4 largest railroad companies got together to slashed worker’s wages by 10% • Strike ensues: Great Railroad Strike of 1877 Rutherford B. Hayes sends in troops to regulate Issue: strikers are threatening interstate commerce Strike outcome: failure and showed the weakness of the early labor movement Class Conflicts and Ethnic Clashes Clash: Irish and Chinese over low-paying jobs Chinese Exclusion Act (1882) - limited immigration to America -first “immigration restriction” legislation in American history Overview Presidential (Lincoln and Johnson) Executive branch leads Recon. Return South “Quickly” South “Swears” allegiance to the Union (10%) South practices the 13th Amendment (Lincoln &Johnson) Extension of 14th amendment is in question (Johnson) Congressional Congress should lead Recon. Southern States readmission ONLY if they ratified the 14th & 15th Amend. & the majority “Swears” allegiance Wade Davis Bill South should be PUNISHED Extends the Freedmen’s Bureau, Civil Right’s Act of 1866 & Reconstruction Act of 1867 5 post-Civil War Problems and “Attempted” Solution