* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vocabulary
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
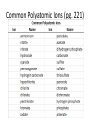
Vocabulary • Ion – An atom or bonded group of atoms with a positive or negative charge • Cation – A positively charged ion • Anion – A negatively charged ion • Ionic bond – The electrostatic force that holds oppositely charged particles together in an ionic compound • Ionic compounds – Compounds that contain ionic bonds Vocabulary • Electron affinity – the energy of a neutral, gaseous atom when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative ion; the neutral atom's likelihood of gaining an electron • Ionization energy – the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom; generally increases in moving from left-toright across a period and decreases in moving down a group. Atomic Size Notice the atomic size increases as period increases and decreases and the group increases. Ionic Sizes Ionic Sizes are different based on whether electrons are added or taken away. Polyatomic Ions • An ion made up of two or more atoms bonded together that acts as a single unit with a net charge • Quiz on polyatomic ions on the next slide on Friday Common Polyatomic Ions (pg. 221) Formation of Ionic Compounds • The charge indicates what ionic compound will form – oxidation number • It will always be with one form of cation and one form of anion. • Criss-cross • Subscripts indicate a ratio • Example: Mg2+ ClMgCl2 Criss-Cross Examples • Ammonium dichromate • Sodium chloride • Calcium oxide Vocabulary • Valence electron – The electrons in an atom’s outermost orbitals; determine the chemical properties of an element. • Molecule – Forms when two or more atoms covalently bond • Covalent bond – A chemical bond that results from the sharing of valence electrons – “co-” means to share – “-valent” refers to valence electrons Naming Ionic Compounds • Cations retain their names • Anions end in “-ide” – e.g. oxygen becomes oxide, chlorine becomes chloride • Metals require a Roman numeral to indicate its charge. – e.g. iron (III) oxide. Cation is Fe3+. Anion is O2-. The compound is Fe2O3 • Polyatomic ions require parentheses if more than one polyatomic ion is indicated. – e.g. ammonium sulfide – NH4+ and S2- becomes (NH4)2S Practice Naming Ionic Compounds • NaBr • Cu(NO3)2 • CaCl2 • Ag2CrO4 • KOH • NH4ClO4 Naming Covalent Compounds • Greek prefixes indicate the number of atoms in each molecule • If the first element noted is one, “mono” is left out, e.g. carbon dioxide = CO2 • Mono – one Hexa – six • Di – two Hepta – seven • Tri – three Octo – eight • Tetra – four Nona – nine • Penta – five Deca – ten Naming Covalent Bonds • H2O • CCl4 • SO2 • diarsenic trioxide • NF3 Lewis Dot Structure • This is a representation of an element or molecule showing the valence electrons. • The element symbol is used, and dots are placed around it to indicate the valence electrons. • Lines are used to show a pair of valence electrons are shared. Lewis Dot Structure • H2 – Hydrogen • CH4 – Methane • H2O – Water • HF – Hydrogen fluoride • NH3 – Ammonia You Try • PH3 • CCl4 • H2S • SiH4 • HCl Double and Triple Bonds • Oxygen shares two pairs • Nitrogen shares three of electrons, so it has a pairs of electrons, so it double bond. has a triple bond. • O2 • N2