* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Energy - mrsfairweather
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
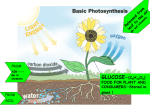
Cellular Energy Photosynthesis & Respiration Energy Flow • Sun Glucose (photosynthesis) ATP (Respiration) Cell Energy • Energy ~ The ability to do work. • Main source of energy in living things: Glucose! C6H12O6 – – – – Glucose is a monosaccharide. Glucose is made by photosynthesis for autotrophs. Glucose is part of food eaten by heterotrophs. Glucose is powerful – it must be turned into a gentler form of energy called ATP to be used by a cell. Glucose C6H12O6 How do you get glucose? • Autotroph ~ Organism that makes its own food (glucose) by photosynthesis. – Ex: plant • Heterotroph ~ Organism that must eat food (glucose) from an outside source. – Ex: human Energy Storing Compounds • NADPH • ATP ATP • Adenosine Triphosphate • ATP is an energy storing compound made in the mitochondria. It is made when glucose is broken down. ADENOSINE ATP • http://www.biologyinmotion.com/atp/index.h tml • Be sure to watch! Cellular Organelles • Chloroplasts: plant cells; energy from the sun is converted into glucose • Mitochondria: glucose is converted into ATP Chloroplast Structure • Outer and Inner membranes contain and protect the inner parts • Stroma: area where reactions occur and sugars are created • Thylakoids: have chlorophyll molecules on their surface • Chlorophyll – pigment that uses sun’s energy to create glucose • Stroma lamella: act like the skeleton of the chloroplast, keeping all of the sacs a safe distance from each other and maximizing the efficiency of the organelle. Mitochondria • Outer membrane • Cristae: the folds • Matrix: contains high number of enzymes; several steps of cellular respiration are performed here • DNA • Ribosomes Photosynthesis • A chemical reaction in which light energy is converted into bond energy stored in a glucose molecule. Photosynthesis Reaction 6CO2 6 H 2O Light C 6 H12O6 6O2 Chlorophyll • • • • Requirements for photosynthesis: Carbon dioxide (CO2) Water (H2O) Light Chlorophyll Products of photosynthesis: • Glucose (C6H12O6) • Oxygen (O2) Plant Pigments • • • • Chlorophyll - green Xanthophyll - yellow Carotene - orange Anthocyanins *Plant Pigments absorb energy and pass on to chlorophyll Chlorophyll • Chlorophyll is green in color, meaning that green light is reflected, not absorbed. • Chlorophyll absorbs primarily red and blue light for photosynthesis. What is happening? Red Light: Green Light: Light Reactions • • Starting molecules: CO2, H2O Ending molecules: O2, NADPH, ATP e- Dark Reactions (Calvin Cycle) • • Starting molecules: Ending molecules: CO2 C6H12O6 C5 Cellular Respiration • Chemical reactions that convert glucose into ATP. • May or may not use oxygen. • Occurs in mitochondria. Aerobic Respiration Materials Needed: – Oxygen – Glucose Materials Made: – 36 ATP – Water – Carbon dioxide C6 H12O6 6O2 6CO2 6H 2O 36 ATP Anaerobic Respiration •Breaks down glucose without using oxygen. •Produces a poisonous waste product. •Only produces 2 ATP molecules from one glucose molecule. •Two types of anaerobic respiration: •Alcoholic fermentation •Lactic acid fermentation Lactic Acid Fermentation • C6H12O6 CO2 + lactic acid + 2ATP Produces lactic acid as a waste product. Carried out by bacteria. Causes milk to go sour. Carried out by human muscle cells (reason you are sore after a workout) Used in industry to make cheese and yogurt. Alcoholic Fermentation • C6H12O6 CO2 + alcohol + 2ATP • Yeasts and other microorganisms carry out alcoholic fermentation • Formation of ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide as wastes • Causes bread dough to rise Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic • Uses O2. • Breaks down glucose. • Produces 36 ATP. • Carried out by plants and animals. Anaerobic • Does not use O2. • Breaks down glucose. • Produces 2 ATP. • Alcoholic fermentation is carried out by yeast. • Lactic acid fermentation is carried out by bacteria. Aerobic organisms • An organism that requires oxygen Anaerobic organisms • An organism that does not require oxygen Photosynthesis vs. Respiration Photosynthesis • Produces C6H12O6 (glucose). • Occurs in the chloroplasts. • Produces O2 (oxygen gas). • Carried out by autotrophs. Respiration • Produces ATP. • Occurs in the mitochondria. • Produces CO2 (carbon dioxide). • Carried out by heterotrophs and autotrophs. • Aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP, anaerobic 2 ATP.