* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inside Earth: Earth*s Interior - 7-8WMS
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
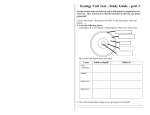
Inside Earth: Earth’s Interior Content Objectives: SWBAT explain how geologists determined Earth’s inner structures. SWBAT explain the characteristics of Earth’s crust, mantle, and core. Language Objectives: SW will discuss the evidence geologists use to determine Earth’s inner structures. SW draw and label a diagram of Earth’s crust, mantle, and core. How do scientists know what the inside of the Earth looks like? Key Concept: Geologists have used two main types of evidence to learn about Earth’s interior: direct evidence from rock samples and indirect evidence from seismic waves. • Seismic waves: waves made by earthquakes. Layers of the Earth Rap Watch the video and write down the layers of the Earth and 5 additional facts. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q9j1xGaxYz Y Layers of the Earth Rap What are the layers of the Earth? What are they made of and how thick are they? How do they behave? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hHteUIS0OF Y Exit Card 8 January 2014 •3 main layers of the Earth •2 types of crust •1 method geologists used to determine the composition of the interior of Earth. A Journey to the Center of Earth • Key Concept: Three main layers of Earth are the crust, the mantle, and the core. These layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature, and pressure. A Journey to the Center of Earth • Temperature increases as you go to the center of the Earth. • Pressure increases as you go to the center of the Earth. • Pressure: a force pressing on an area The Core • Key Concept: The core is made mostly of the metals iron and nickel. It consists of two parts – a liquid outer core and a solid inner core. • • • The Core Core has two layers – outer core and inner core. Outer core– made of liquid metal. It flows in currents. These currents make Earth act like a magnet. Inner core – made of solid metals. The Core •Outer core: a layer of molten metal that surrounds the inner core. •Inner core: a dense ball of solid metal The Mantle • Key Concept: Earth’s mantle is made up of rock that is very hot, but solid. Scientists divide the mantle into layers based on the physical characteristics of those layers. Overall, the mantle is nearly 3000 km thick. MANTLE • Def.: Layer of the Earth between the crust and core • Sent.: Lithosphere is made up of the crust and the top layer of the mantle. • Sp.: manto • Explain to your neighbor where the mantle of the Earth is located. The Mantle • Mantle is the thickest layer, just below the crust. Has 3 layers. • Lithosphere – the crust and the top layer of the mantle. Make of solid rock. Averages 100 km thick. • Asthenosphere – the middle layer of the mantle. Made of pliable rock. • Mesosphere: Lower mantle – solid rock. The Mantle •Mantle: is the layer below the crust •Lithosphere: top layer of the mantle and the crust •Asthenosphere: middle layer of the mantle The Crust •Key Concept: The crust is a layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and the ocean floor. The Crust • Thinnest layer – 5 to 70 km thick • Oceanic crust – makes up ocean floors and made mostly of basalt • Continental crust – makes up the continents and made mostly of granite, thicker than oceanic The Crust • Crust: a layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer skin. • Basalt: a dark rock with a fine texture • Granite: a light color rock with a coarse texture