* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Presentation
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
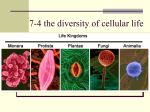
Q4 Benchmark Review hyper • over, above iso • equal or same hypo • below, under hetero • different homo • alike, similar tell the teacher • The most important thing to remember if something happens during a lab and you or someone else has an accident is to ____________________________________. Goggles • ______________________are the most important safety equipment. eat, drink • You should never ________ or __________ things during a lab experiment because you could get sick. quantitative observation • a measurement of what you observe qualitative observation • a description of what you observe inference • A prediction or an educated guess based on what you observe and what you know from past experiences that is used to explain what happened inference or observation? observation, is it quantitative or qualitative? • The flowers on the back porch grew 5 cm taller than the ones on the front porch. inference or observation? inference • There must be someone here because the dog is barking. inference or observation? observation, is it quantitative or qualitative? • The fire alarm is very loud. Biotic Factors The living components of an ecosystem are called biotic factors. Examples of Biotic Factors: • Animals • Plants • Fungi • Bacteria • Protists Abiotic Factors The non-living components of an ecosystem are called abiotic factors. Many abiotic factors are recycled and reused in ecosystems. Examples of Abiotic Factors: • Temperature • Soil and rocks • Water • Carbon • Nitrogen A living thing is called an organism. Example: a deer All of the organisms of the same species that live in an area at the same time is called a population. Example: a herd of deer All the populations of all species that live in an area is called a community. Example: deer + rabbits + bears All the organisms living in an area, as well as the non-living parts of their environment, is called an ecosystem. Example: deer + rabbits + bears + sunlight + soil + air water + carbon + nitrogen What is the order from smallest to largest? • Organism • Population • Community •Ecosystem •Biome Name the biotic factors in this picture. Name the abiotic factors in this picture. energy pyramid • a model that shows the amount of energy at each level of a food chain The triangular face shows that there are more organisms at the bottom (producers) and fewer organisms as you move up to higher trophic levels. There are multiple faces to show the population sizes and the amount of energy available at each level, and that the amount of energy decreases as you move up to the top. • How much energy do organisms use up? • 90% • How much energy do organisms store? • 10% • How much energy is available to the organism that consumes another? • 10% 9 kc 90 kc 10% of the energy is passed on 900 kc 9, 000 kc symbiosis a close relationship between two organisms that benefits at least one of the species In what kind of symbiosis does one organism benefits and one gets neither harmed nor helped? Commensalism In what kind of symbiosis do both organisms benefit? Mutualism In what kind of symbiosis does one organism benefit and the other is harmed? Parasitism Herbivores • animals that only eat plants Producers • living things that can make their own food by using energy in sunlight Carnivores • animals that eat meat Consumers • an organism that gets its energy by eating other organisms Omnivores • organisms that eat both plants and animals Large geographic areas that have similar climates and ecosystems are called biomes. Example: tundra, taiga, desert, etc. Why would an ecosystem have fewer organisms as you move up the food chain? If there is less energy passed on to each level, then there is not enough energy to support a lot of organisms at the higher levels. Water, Carbon, Oxygen and Nitrogen • Living things need water, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen to survive. • These materials flow (cycle) through an ecosystem. • Matter is constantly recycled between Earth’s organisms and the environment. multicellular an organism that is made up of more than one cell eukaryotes cells with a nucleus (You carry oats to the horse.) Cell Theory 1. All known living things are made up of cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living things. 3. All cells come from other living cells. asexual reproduction • when only one parent is required to produce offspring; offspring is identical to its parent (no mixing of genetic material) binary fission • a form of asexual reproduction where a chromosome is copied before the cell divides to form two new cells • used by bacteria (which are unicellular and prokaryotes.) budding • a form of asexual reproduction in which an offspring (called a daughter) forms from an outgrowth of a larger parent organism; • ex. yeast sexual reproduction • when two parents are required to produce offspring (via sperm cells and egg cells); genetic information from each parent is combined fossil record • 48. an ordered arrangement of fossils and the data on where they were found; • used to determine the history of Earth and its organisms and how those organisms are related prokaryotes cells that do not have a nucleus pro rhymes with no unicellular an organism that is made up of only one cell The five characteristics of living things are that they: 1 Use energy 2 Grow & develop 3 Ability to reproduce 4 Respond to stimuli 5 Can exchange gases with the environment organelles structures inside a cell chloroplast organelles which use the energy from the sun to make food for plants mitochondria the powerhouse of the cell which releases energy from food alleles • the different forms of a gene dominant allele • an allele that can mask another allele and always “shows up” if present heterozygous 2 different alleles for a trait selective breeding • the process through which humans use naturally occurring genetic patterns to pass desired traits on to generations of plants and animals recessive allele • an allele that is hidden when a dominant allele is present; can be masked by another allele • These characteristics only “show up” if both alleles for a trait are this type. homozygous 2 of the same alleles for a trait plants all organisms in this kingdom are • multicellular, eukaryotic, and autotrophic Eubacteria and Archaebacteria all of the organisms in these kingdoms are • unicellular, prokaryotic animals all organisms in this kingdom are • multicellular, eukaryotic, and heterotrophic fungi all organisms in this kingdom are eukaryotic and heterotrophic • most are multicellular, but one kind is unicellular protists all organisms in this kingdom are eukaryotes • divided into 3 groups: plant-like, animal-like, and fungus-like dichotomous key • a tool to classify organisms by choosing their characteristics from a series of paired statements Interactive Dichotomous Key evolution the gradual change in a species over time natural selection the process where individuals which are better suited, or adapted, to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce than other members of the same species It’s sometimes referred to as the “survival of the fittest.” cells • the basic units of structure and function of all living things tissue • a group of similar cells working together to perform a specific function organ • A group of tissues that work together to perform a function or task organ system • a group of organs that work together to perform a complex function organism • a living thing zygote • a new cell formed when an egg cell is fertilized; how all multicellular organisms begin life What are the 3 types of muscle tissue? • Skeletal muscles • Smooth muscles • Cardiac muscles voluntary muscles • muscles that are under your control skeletal muscle • the type of muscle tissue that connects to bone; they pull on bones to make them move (also called striated muscle) involuntary muscles • muscles that are not under your control cardiac muscle • muscle tissue found only in the heart smooth muscle • muscles that are found in many organs such as the stomach or the walls of veins • not usually under conscious control arteries • blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart (with oxygen) • (shown in red) veins • blood vessels that carry blood toward the heart (without oxygen) • (shown in blue) stomach • a muscular organ that carries out both mechanical and chemical digestion small intestine • a long, muscular tube where the body absorbs nutrients from food large intestine • an organ of the digestive and excretory systems that absorbs water from undigested material and helps remove solid wastes from the body reflex • 35. an automatic response that occurs without conscious control Major Organ Systems • There are some parts/organs that are involved in more than one system. • The systems often work with more than one other system. • We are going to list the most important parts/organs for each system. Muscular System Which system includes the following organs? • Muscles • Tendons Skeletal System Which system includes the following organs? • • • • bones ligaments cartilage tendons Reproductive System Which system includes the following organs? • testes (males) • ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus (female) Digestive System Which system includes the following organs? • • • • • • • • • mouth esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum liver gall bladder pancreas Respiratory System Which system includes the following organs? • trachea • bronchi • lungs Circulatory System Which system includes the following organs? • heart • blood • blood vessels Nervous System Which system includes the following organs? • Brain • Spinal cord • Nerves Immune System Which system includes the following organs? • white blood cells Digestive System Name the organ system that: • breaks down food into simpler molecules that can be used by the body Respiratory System Name the organ system that: • provides body with oxygen • removes carbon dioxide from body Nervous System Name the organ system that: • responds to stimuli inside and outside the body • controls the senses • controls and coordinates the body Circulatory System Name the organ system that: • brings oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells • takes wastes away from cells • regulates body temperature Reproductive System Name the organ system that: • produces sperm cells in males and egg cells in females Immune System Name the organ system that: • helps protect the body from disease Skeletal System Name the organ system that: • • • • • Supports the body Protects internal organs Stores minerals Enables the body to move Produces blood cells Muscular System Name the organ system that: • Helps to move the body • Helps blood to circulate • Helps food move through digestive system