* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Connective Tissue - Model High School
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Nerve guidance conduit wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
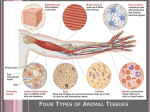
Cells combine to form tissues, and tissues combine to form organs Tissues are groups of cells closely associated that have a similar structure & perform a related function Cells combine to form 4 primary tissues * * * * Epithelial Tissue Locations: ◦ Covers the body ◦ Lines the cavities, tubes, ducts and blood vessels inside the body Covers the organs inside body cavities ◦ Epithelial Tissue Functions: ◦ Protection from physical & chemical injury, ◦ Protection against microbial invasion, ◦ Contains receptors which respond to stimuli, ◦ Filters, secretes & reabsorbs materials and ◦ Secretes serous fluids to lubricate structures. Two types: o membranous epithelia form the coverings or linings of organs o glandular epithelia form exocrine and endocrine glands Sheets of cells with specialized contacts & cell junctions o Basal lamina: protein scaffolding secreted by epithelial cells o Basement membrane: reticular fibers (crossed collagen network) that supports epithelium--really associated connective tissue Connective tissue support Nutrients from capillaries in underlying connective tissue Nerves pass through Easily regenerates Different cell shapes & arrangements Simple: just one layer or cell shape Stratified: multiple layers and cell shapes TYPE Squamous CELL SHAPE Squashed Cuboidal Cubed Columnar Columns Pseudo-stratified Flat cells give rise to columns EXAMPLE Endothelium (lines blood vessels), mesothelium (serous lining of celom) Walls of glands Lining of gut tube; sometimes with cilia like lining of uterine tube With cilia in respiratory tubes to move mucous & particles out of the lungs Simple Squamous o One cell thick o Forms solid layer of cells which line blood vessels, body cavities & cover organs in body cavities o Lubrication Stratified Squamous o Multiple layers o Forms epidermis (Skin) lining of the mouth o Lubrication & protection Simple Cuboidal o One cell thick, roughly cube shaped o Lines ovaries, kidneys, thyroid glands, where secretion & absorption take place Stratified Cuboidal o In multiple layers w/one layer attached to basement membrane & one w/free edge o Mammary & sweat glands o Secretion, absorption & protection Simple Columnar o One cell thick column shaped (long & narrow) o Line digestive tract where re-absorption & secretion occurs. Stratified Columnar o Stacked nucleus on top of nucleus o Lines vas deferans, male urethra o Gives support and some movement. Pseudostratified o gives the appearance of more than one layer of columnar epithelial cells o Every cell is attached to the basement membrane o Lines the trachea, fallopian tubes o movement Transitional o Several layers of epithelial cells o Forms tissue that must stretch like the bladder o Stretches, protects against seepage Glandular Epithelia Glandular o A gland consists of one or more cells that make and secrete a particular product. o Endocrine: secretions diffuse directly into the blood vessels. Ex.– thyroid, adrenals, pituitary o Exocrine: secretions empty through the ducts to the epithelial surface. Ex.- sweat, oil 7 1 4 2 5 3 6 Muscle Tissue: o Associated with the bones of the skeleton, the heart and in the walls of the hollow organs of the body. Muscle Tissue Functions: o Movement & Locomotion o Maintains posture o Produces heat o Facial expressions o Pumps blood o Peristalsis Consists of specialized cells that contract when stimulated The body has three types of muscle tissue: o o o Skeletal Cardiac Smooth muscle Cardiac (involuntary) HEART Smooth (involuntary) ORGANS Skeletal (voluntary) BONES Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Connective tissue location: o Most abundant & widely distributed tissue o Connective tissue has non-living extracellular material (matrix between its cells Connective Tissue Functions: o Connects, binds and supports structures, o Tendons, ligaments, etc. o Protects & cushions organs and tissues, o Insulates (fat) and o Transports substances (blood). Major classes: o Bone o Cartilage o Loose o Dense o Blood All connective tissues consist of two basic components: o Living cells o Extracellular matrix Fibers o Collagen gives structure Reticular fibers (crossed collagen) gives order o Elastin gives elasticity Ground substance o Jelly-like material made of sugar-protein molecules (proteoglycans) o Allows connective tissue to retain water and serve as support and protection of organs o Type: Loose, adipose Type: Loose, areolar Contains elastin Nourishes & stretches o Provides blood vessels to skin o Fills muscle gaps Adipose o Stores energy (fat) & insulates o Mostly under the skin Areolar o Wraps the organs o Cushions & protects Dense Fibrous o Collagen is the main matrix element o Thick fibers running in many planes • o Dermis, fibrous capsules around organs Aligned parallel fibers that resists tension • Tendon, ligaments Perform specific functions essential to homeostasis The body contains three types of specialized connective tissue: o o o Bone Cartilage Blood Bone o o Consists of bone cells (osteocytes) and a calcified cartilage matrix Two types of bone tissue exist: spongy and compact Tree ring-like appearance Supports & protects Mineral storage Fat storage Blood cell production Supports while providing flexibility Hyaline cartilage absorbs compression between bones in joints (bone ends) o Most abundant type of cartilage found in the body Fibrocartilage forms cushion like disks between the vertebra The ears and nose are more flexible and are elastic cartilage Blood o Red & white blood cells o Platelets o Plasma o Regulates temperature o Transportation system Nervous Tissue: ◦ Main component of the nervous system ie., brain, spinal cord & nerves. Nervous Tissue Functions: ◦ Regulates & controls body functions ◦ Generates & transmits nerve impulses ◦ Supports, insulates and protects impulse generating neurons. Contains specialized cells that conduct impulses Conducting cells, called neurons, transmit impulses from one region of the body to another. Nonconducting cells, neuroglia, are a type of nervous system connective tissue.